Cognitive correlates of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents with high intellectual ability
ADHD and IQ in Cognitive Testing
María Cadenas , Catharina Hartman , Stephen Faraone , Kevin Antshel , África Borges , Lianne Hoogeveen , Nanda Rommelse
Objectives
ADHD is commonly associated with academics and classroom performance, which is often where the condition first gets noticed.
Because of this association, there is debate over whether highly intelligent, gifted children can have ADHD. If a brilliant child with ADHD is performing just fine at school, despite their symptoms, do they truly have ADHD?
There is an ongoing debate as to whether attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in highly intelligent individuals has a similar presentation as in average intelligent individuals. The aim of this study was to examine the cognitive correlates of ADHD in highly intelligent childr...
Methods
Researchers conducted a study on children with high IQs and ADHD. They compared them to a closely matched group of children with ADHD and more average IQs,as well as a group of children without ADHD.
They then performed cognitive tests to analyze the relationship between IQ, ADHD, and cognitive test performance.
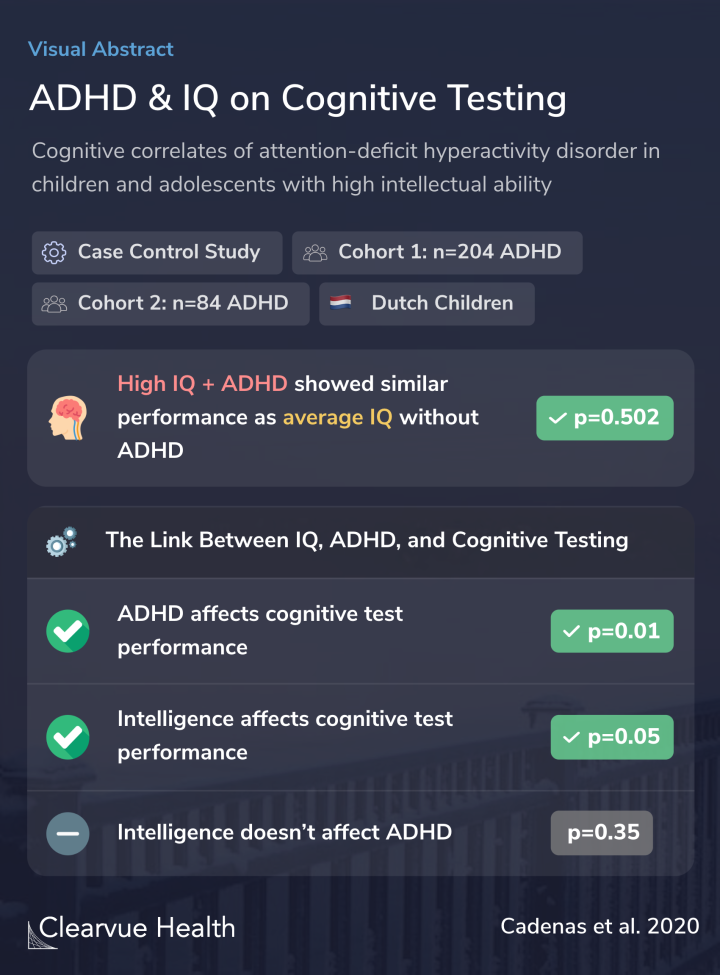
Two independent samples (N = 204 and N = 84) of (1) high intelligence quotient (IQ) (IQ ≥ 120) children and adolescents with ADHD were used, carefully matched on age, gender, ADHD severity, and IQ with (2) control participants with high intelligence, (3) participants with ADHD with an av...
Results
Researchers found that children with high IQs and ADHD performed at the same level as children with average IQs without ADHD. Despite their higher IQs, gifted children performed around average on the cognitive tests because of their ADHD symptoms.
Intelligence was shown to affect cognitive test performance, confirming the validity of the measurements.
Similarly, ADHD was also found to affect cognitive test performance. This is consistent with previous studies showing the effects that ADHD can have on test-taking.
However, intelligence was not shown to affect ADHD. This means that children at all intelligence levels could get ADHD. Having ADHD doesn’t mean someone is less intelligent, though it may impact performance on intelligence tests due to their symptoms.
ADHD-control group differences were not moderated by IQ; mostly equally large ADHD-control differences in cognitive performance were found for high versus average intelligent groups. The small moderating effects found mostly indicated somewhat milder cognitive problems in highly intellig...
Conclusions
This study showed that ADHD affects both intelligent children and average children. ADHD is not a mark of intelligence or a lack of intelligence.
But, it can get in the way of test-taking. As this study shows, even with high intelligence, ADHD symptoms can reduce test performance. Likewise, high intelligence can potentially mask ADHD symptoms, allowing gifted children with ADHD to function normally. However, as the data shows, even gifted children with ADHD are likely not meeting their full potential.
Our findings indicate the cognitive profile of ADHD is similar in highly versus average intelligent individuals with ADHD, although ADHD-related cognitive deficits may be easily overlooked in the high intelligence population when compared to the typical (i.e., average intelligent) contr...