Hyperactive Child Syndrome and Estimated Life Expectancy at Young Adult Follow-Up: The Role of ADHD Persistence and Other Potential Predictors
ADHD and Estimated Life Expectancy
Russell A. Barkley and Mariellen Fischer

Objective
ADHD affects our everyday lives and our well-being. Can it also affect our life expectancy?
Researchers wanted to see whether those with ADHD as children live shorter lives.
Some children with ADHD continue to have ADHD as adults. This is termed persistent ADHD and has been linked to worse outcomes.
Researchers also wanted to see whether having persistent ADHD affects life expectancy.
We examined if ADHD Combined Type or Presentation (ADHD-C) reduced estimated life expectancy (ELE) at young adulthood and if the persistence of ADHD to adulthood further adversely affected ELE.
Method
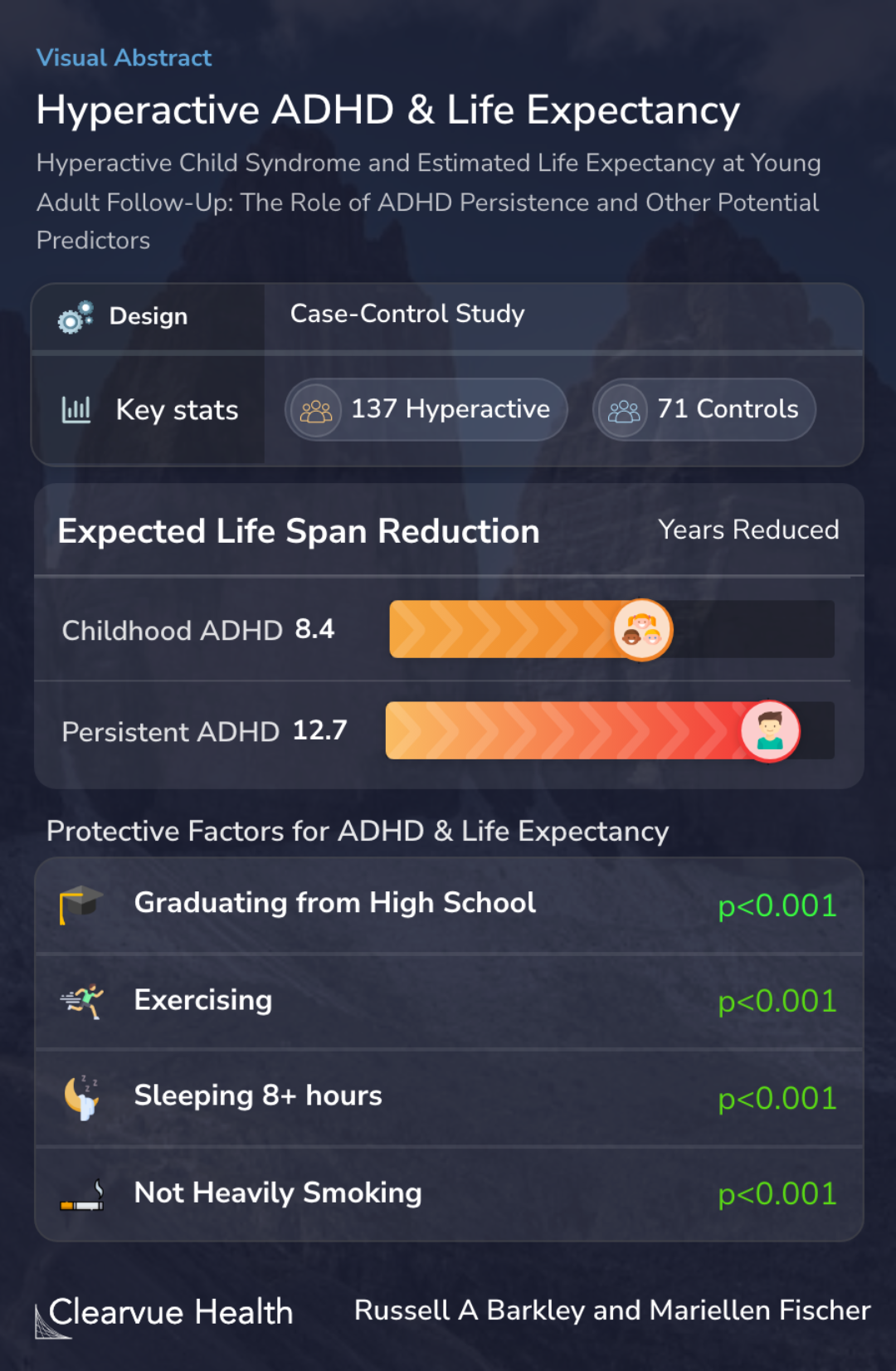
Researchers performed a case-control study comparing 137 individuals with ADHD to 71 closely matched individuals without ADHD.
They measured 14 metrics associated with life expectancy and used these to estimate life expectancy statistically.
These metrics include factors like heavy smoking, which have been linked to specific changes in life expectancy.
A young adult follow-up of 131 hyperactive and 71 control cases was used to derive 14 variables that were entered into a life expectancy calculator to generate ELE scores. Both ratings of executive function (EF) in everyday life and tests of EF and IQ were measured along with comorbid ps...
Results
Researchers found that having ADHD as a child was correlated with an 8-year reduction in lifespan.
This was calculated based on lifestyle factors in the participants they surveyed while they were young adults.
It’s important to note that the study didn’t follow the participants through their lives, so these figures are only estimates. However, they are a good reflection of the general health of those with ADHD.
Individuals who continue to have ADHD as adults had an even greater reduction in life expectancy. They were expected to live nearly 13 years less than those without ADHD.
Many of the factors that were linked to a shorter lifespan were factors within our control. Some people in the study were expected to live longer than others, even with ADHD, because of their healthy lifestyles.
For example, those who exercised, graduated from high school, didn’t smoke, and got enough sleep were expected to live longer.
Childhood ADHD-C was associated with a 9.5-year reduction in healthy ELE, and a 8.4-year reduction in total ELE relative to control children by adulthood. The persistence of ADHD to adulthood was linked to a 12.7-year reduction in ELE. Several background traits accounted for more than 39...
Conclusion
In general, those with ADHD are not expected to live as long as those without ADHD—those who continue to have ADHD as adults live even shorter lives.
Much of this may arise from the symptoms of ADHD. Factors like smoking can be related to ADHD impulsivity. Education and exercise can be affected by attention deficit symptoms.
Fortunately, by pursuing a healthy lifestyle, much of this life expectancy reduction can be modulated.
Childhood ADHD-C predicts a significantly reduced ELE by adulthood, which is further reduced by the persistence of ADHD to adult follow-up.