Hyperactive children as young adults: driving abilities, safe driving behavior, and adverse driving outcomes
ADHD and Driving Stats
Mariellen Fischer , Russell A Barkley, Lori Smallish, Kenneth Fletcher
Objectives
Previous studies have found that adults with ADHD tend to drive more dangerously than adults without ADHD.
ADHD encompasses difficulties with attention and impulsivity, essential for safe driving.
The study wanted to see how those with childhood ADHD drive as adults.
ADHD has been linked to poorer driving abilities and greater adverse outcomes (crashes, citations) in clinic-referred cases of teens and adults with ADHD. No study, however, has focused systematically on ADHD children followed into adulthood. The present paper does so while measuring dri...
Methods
Researchers conducted a case-control study that tested a group with ADHD and a closely matched group without ADHD.
Researchers tested participants on a series of measurements related to safe driving and followed the participants for 13 years.
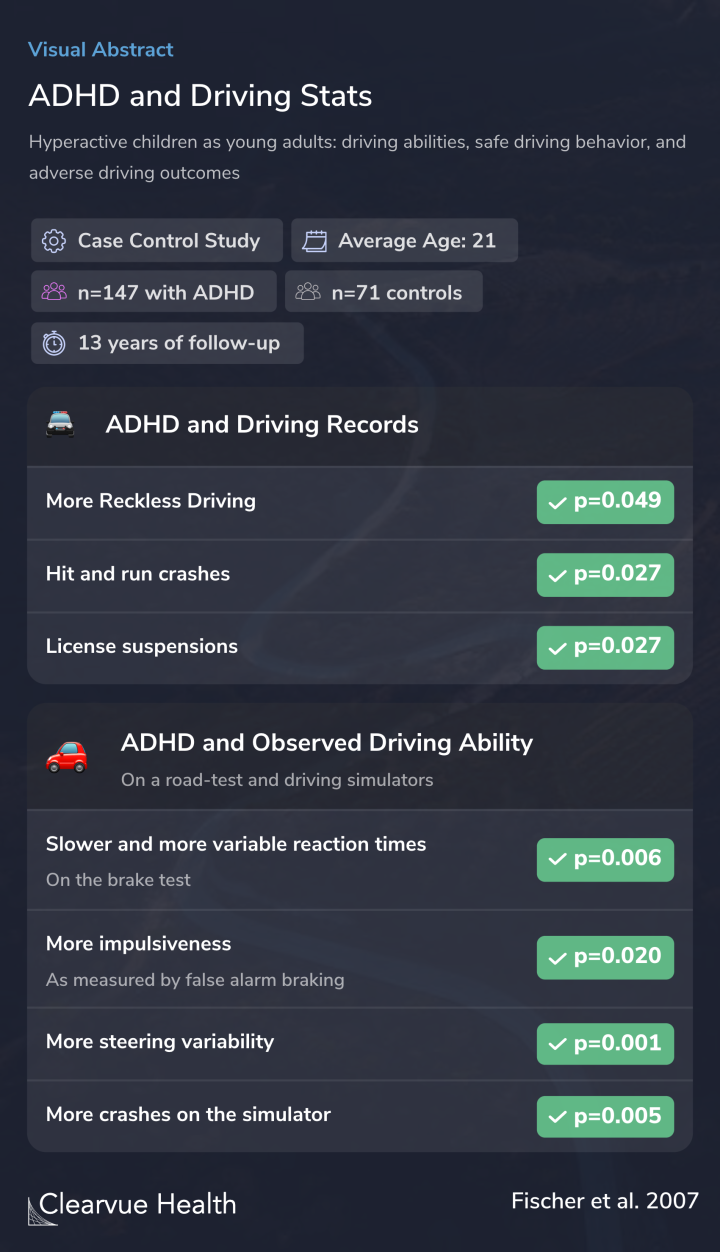
A multi-method, multi-source battery of driving measures was collected at the young adult follow-up on hyperactive (H; N=147; mean age=21.1) and community control children (CC; N=71; mean age=20.5) followed for more than 13 years.
Results
The results showed that those with ADHD engaged in more reckless driving. They had more hit-and-run accidents and were likelier to get their license suspended.
On driving simulators and road tests, researchers found that those with ADHD showed clear evidence of worse driving ability. They were slower to react, were more impulsive, had more steering variability, and were more likely to crash on simulators.
More of the H than CC groups had been ticketed for reckless driving, driving without a license, hit-and-run crashes, and had their licenses suspended or revoked. Official driving records found more of the H group having received traffic citations and a greater frequency of license suspen...
Conclusions
Driving is one of the most dangerous things we do, particularly for young adults.
These results show that ADHD can significantly affect safety and potentially mortality when it comes to driving.
Like many aspects of ADHD, this is likely treatable. ADHD symptoms can be managed with medication and therapy.
These findings suggest that children growing up with ADHD may either have fewer driving risks or possibly under-report those risks relative to clinic-referred adults with this disorder. Deficits in simulator performance and safe driving behavior, however, are consistent with clinic-refer...