Background
The Basics
Key Facts
Key Facts
- TypeFat Soluble
- Other Namesα-tocopherol
- SourcesDiet, Liver
Appearance

Uses:

Antioxidant

Inflammation

Immunity
Amount per day
15mg
Source: Institute of Medicine

Types of Foods
Nuts & Seeds
Sunflower seeds, wheat germ, and almonds

Deficiency
Rare in healthy individuals

Vitamin E Benefit #1

Vitamin E & Parkinson's Disease
Several studies have demonstrated that high Vitamin E correlates with a lower risk of Parkinson's Disease. As the meta-analysis below shows, those who eat just a moderate amount of Vitamin E have a significantly lower risk of developing Parkinson's Disease.
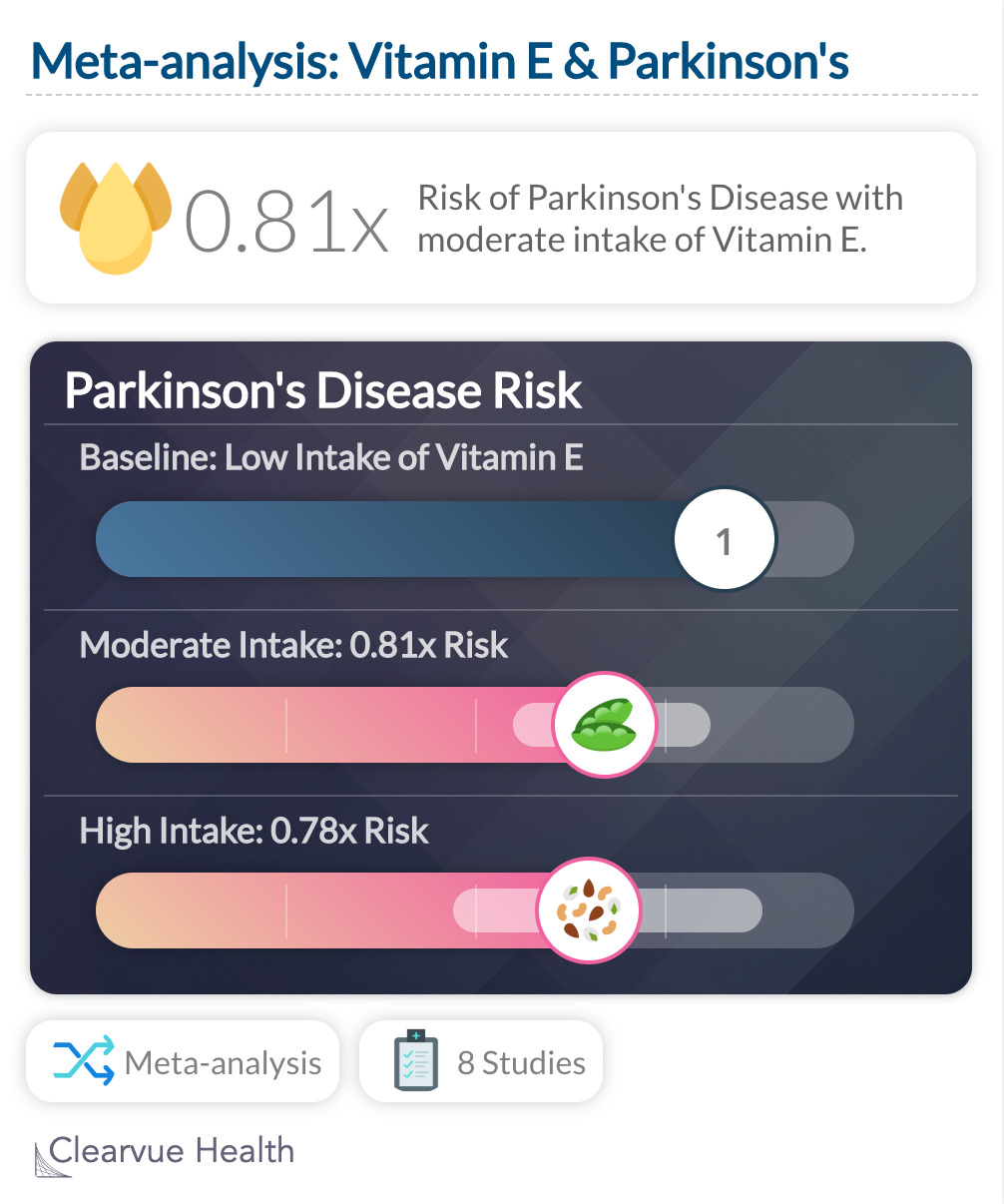
A meta-analysis found that those who ate lots of Vitamin E also had a lower risk of Parkinson's Disease. This was found for both moderate intake, "relative risk 0·81, 95% CI 0·67–0·98", and high intake: 0·78, 0·57–1·06
Data Source
"We found that dietary intake of vitamin E protects against PD. This protective influence was seen with both moderate intake (relative risk 0·81, 95% CI 0·67–0·98) and high intake (0·78, 0·57–1·06) of vitamin E"
What is it?
Key facts
Type

Neurodegenerative Disease
Affects

Dopaminergic neurons in the brain
Key symptoms:

Shaking

Stiffness

Balance issues

# of Americans
900,000+
900,000+ Americans have Parkinson's Disease.

Before Age 50
4%
Only 4% of cases are diagnosed before age 50.
Gender ratio


Vitamin E Benefit #2

Vitamin E Diets & Brain health
A diet rich in Vitamin E, which includes lots of nuts and seeds, has been linked to a lower risk of cognitive decline. Our brains can get less sharp with age for a multitude of reasons. Studies have shown diet can play a role in preventing this. The study below suggests that a diet rich in nuts and seeds may be particularly beneficial.
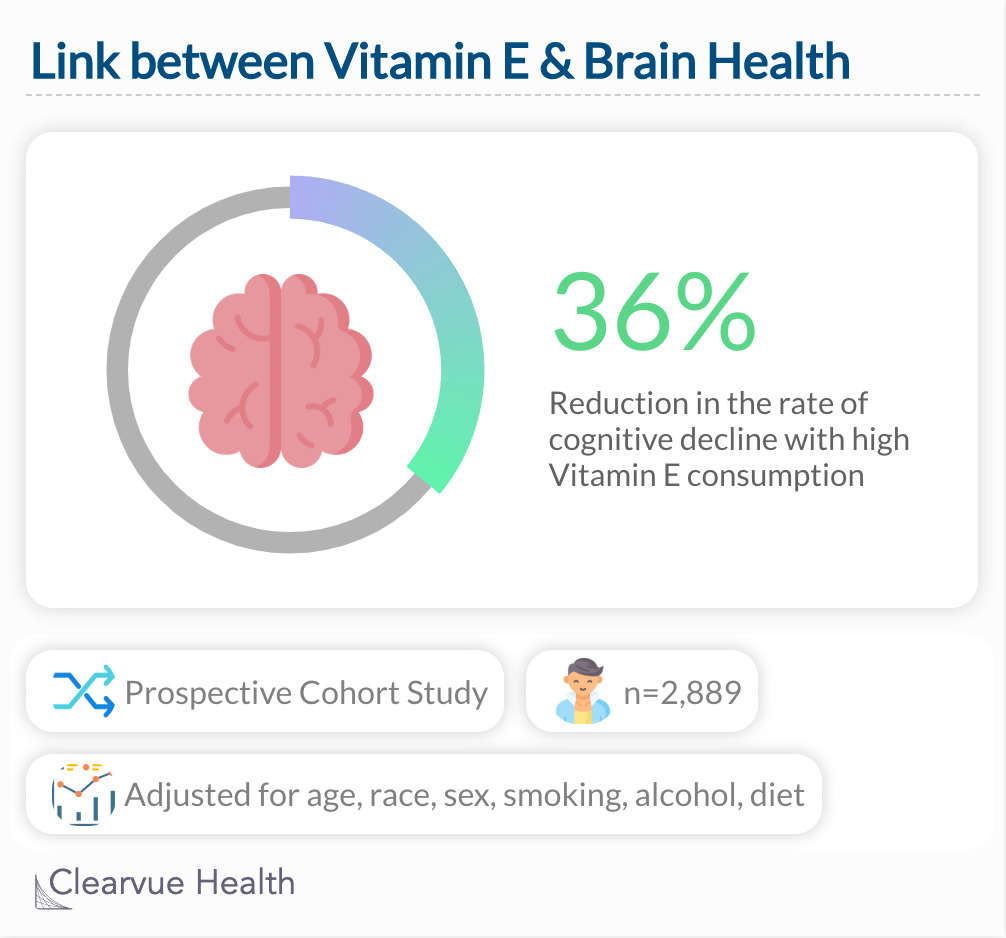
A study looking at the dietary habits of 2,889 individuals found that those who had a lot of Vitamin E in their diet had a lower rate of cognitive decline compared to those who did not.
Data Source
"Vitamin E intake, from foods or supplements, is associated with less cognitive decline with age."
Vitamin E Benefit #3

Vitamin E & Heart Disease
The relationship between Vitamin E & Heart Disease is quite controversial. An early study below showed that consuming a lot of Vitamin E correlated with a significantly lower risk of heart disease among nurses.
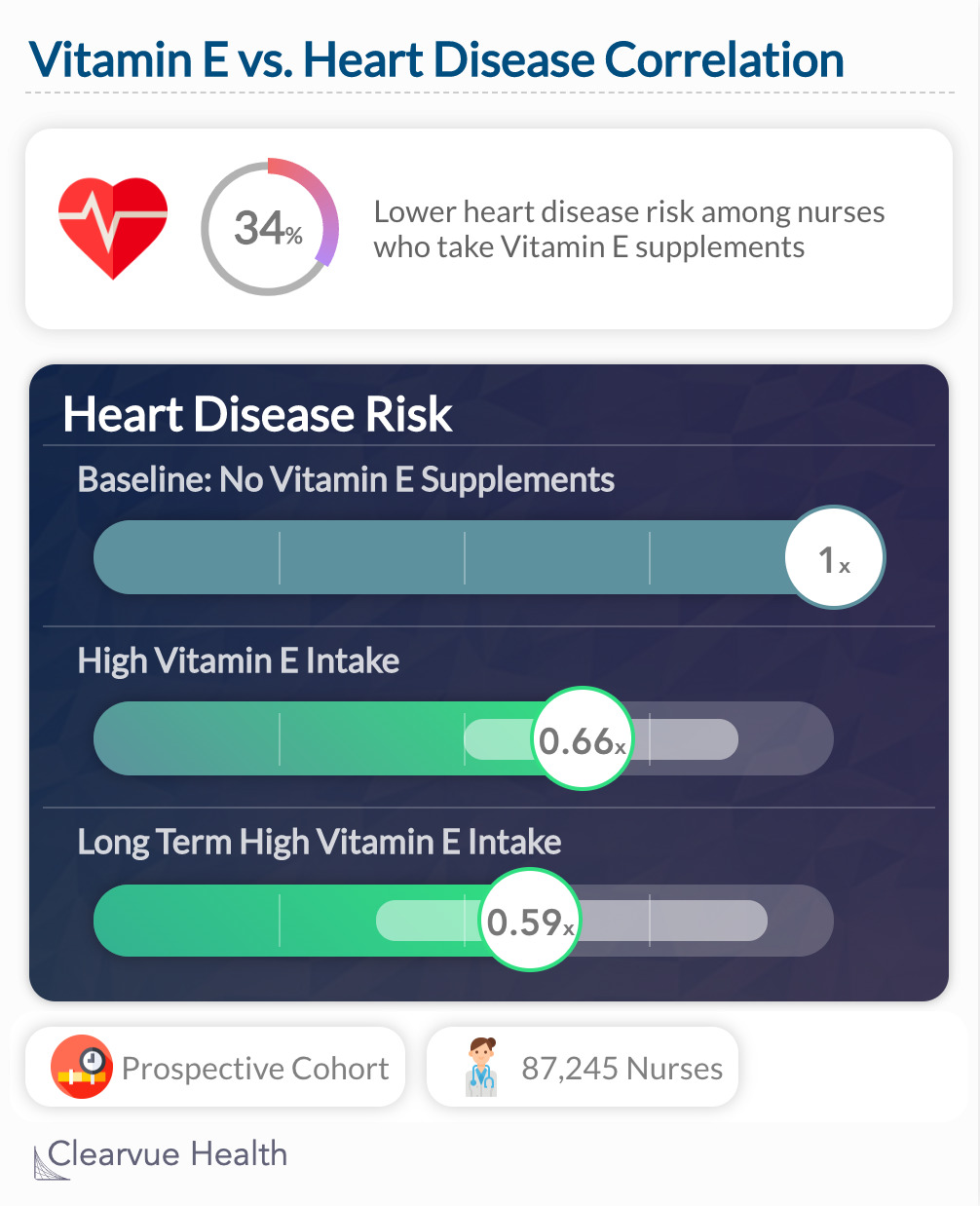
Nurses who chose to take Vitamin E also tended to have a lower risk of heart disease. (0.66 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.50 to 0.87) after adjustment for age and smoking). In the long run, their risk was even lower: RR= "0.59 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.38 to 0.91) after adjustment for age, smoking status, risk factors for coronary disease, and use of other antioxidant nutrients"
Data Source
"As compared with women in the lowest fifth of the cohort with respect to vitamin E intake, those in the top fifth had a relative risk of major coronary disease of 0.66 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.50 to 0.87) after adjustment for age and smoking. "

Clinical Trial Failures
However, a clinical trial that tried to give people vitamin E in a pill failed to show any benefits. One possible reason may be that diets rich in Vitamin E can prevent heart disease, but vitamin E by itself might not.
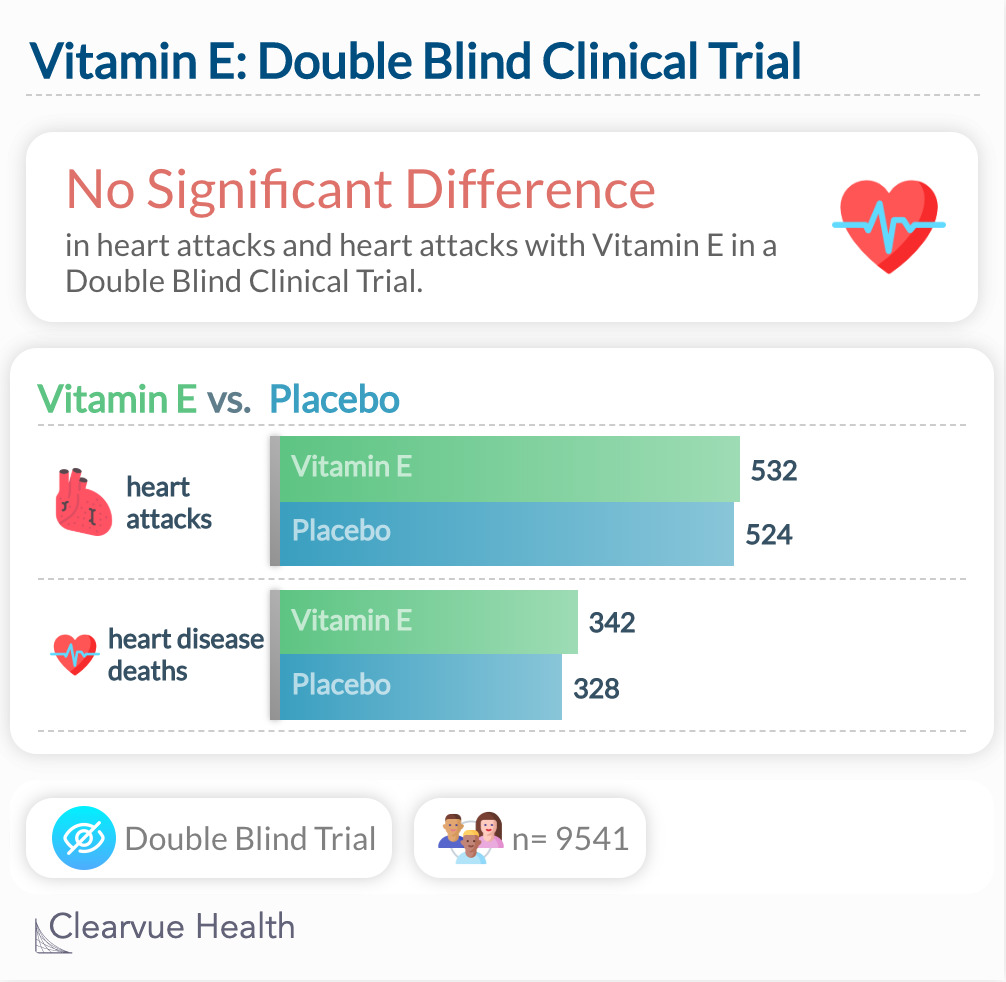
The study above shows that in a randomized double-blind clinical trial, the gold standard of medical research, Vitamin E may not have a benefit for heart disease. Those who were assigned to take Vitamin E had the same number of heart attacks and deaths from heart disease as those who were assigned to take placebo, a control.
Data Source
"In conclusion, the WHS does not support recommending vitamin E supplementation for CVD or cancer prevention among healthy women. This large trial supports current guidelines stating that use of antioxidant vitamins is not justified for CVD risk reduction."
Vitamin E
Key Facts
Examples

How they work
Antioxidants prevent cell damage by counteracting free radicals.

Effect on Disease
Research on Antioxidants and disease prevention has shown mixed results.
Common Sources

Chocolate

Berries & Fruit

Coffee

beta-carotene
Your body makes vitamin A with beta-carotene, commonly found in carrots.

Vitamin C
Found in all sorts of fruits, Vitamin C is a very commonly consumed antioxidant.

Vitamin E
Vitamin E can be found in nuts and seeds.

Unproven Benefit

Vitamin E & Cancer Risk
Like with heart disease, scientists believed that Vitamin E may have an effect on reducing cancer risk due to its antioxidant effects. However, a clinical trial shown below found that taking Vitamin E supplements by themselves doesn't show any cancer prevention benefits.
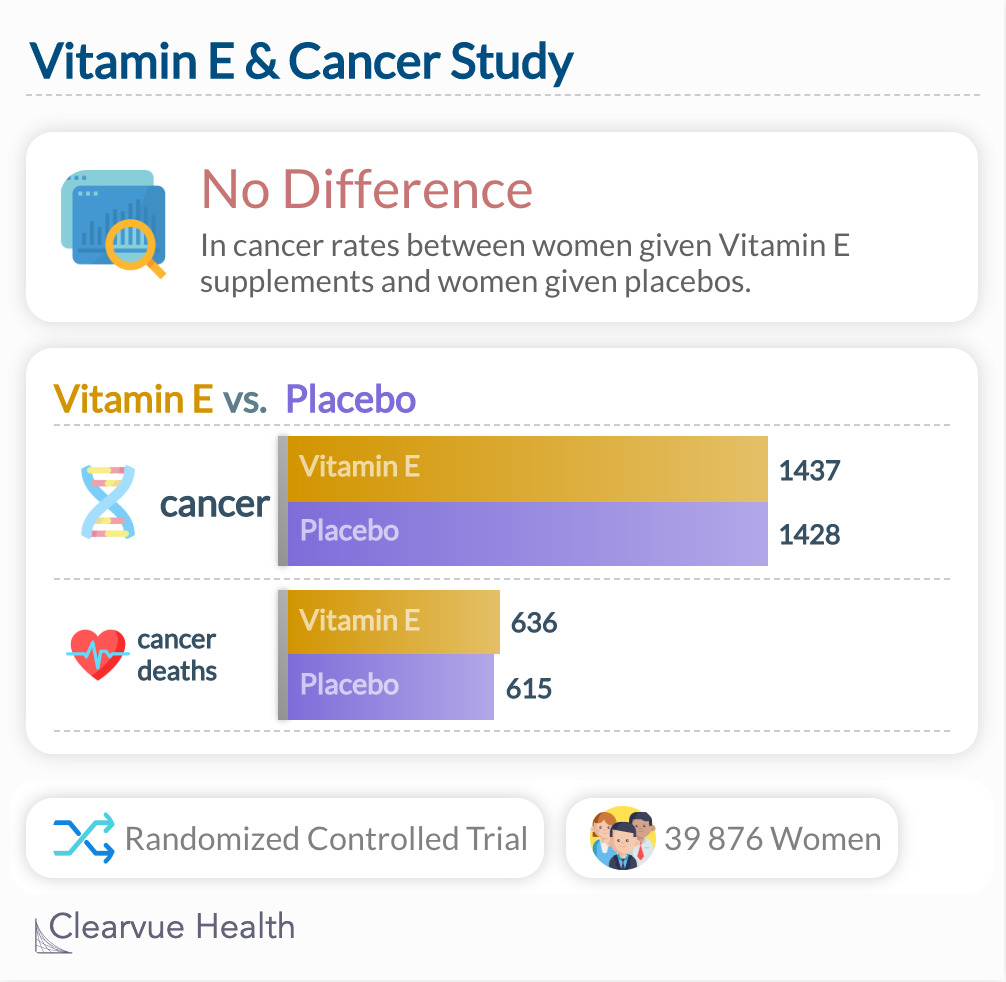
Vitamin E & Cancer Risk. A study of nearly 40,000 women found that VItamin E had no effect in preventing cancer and no effect in preventing cancer deaths. The rate of cancer was nearly equivalent between women given Vitamin E and women given a placebo: 1437 cases in the vitamin E group and 1428 in the placebo group; RR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.94-1.08; P = .87. The results were similar for cancer deaths: 636 in the vitamin E group and 615 in the placebo group; RR, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.93-1.16; P = .53
Data Source
"There was no significant effect on the incidences of total cancer...Cancer deaths also did not differ significantly between groups. There was no significant effect of vitamin E on total mortality."

Risk of Too Much Vitamin E
In fact, one study actually showed that vitamin E can increase cancer risk if you take too much.
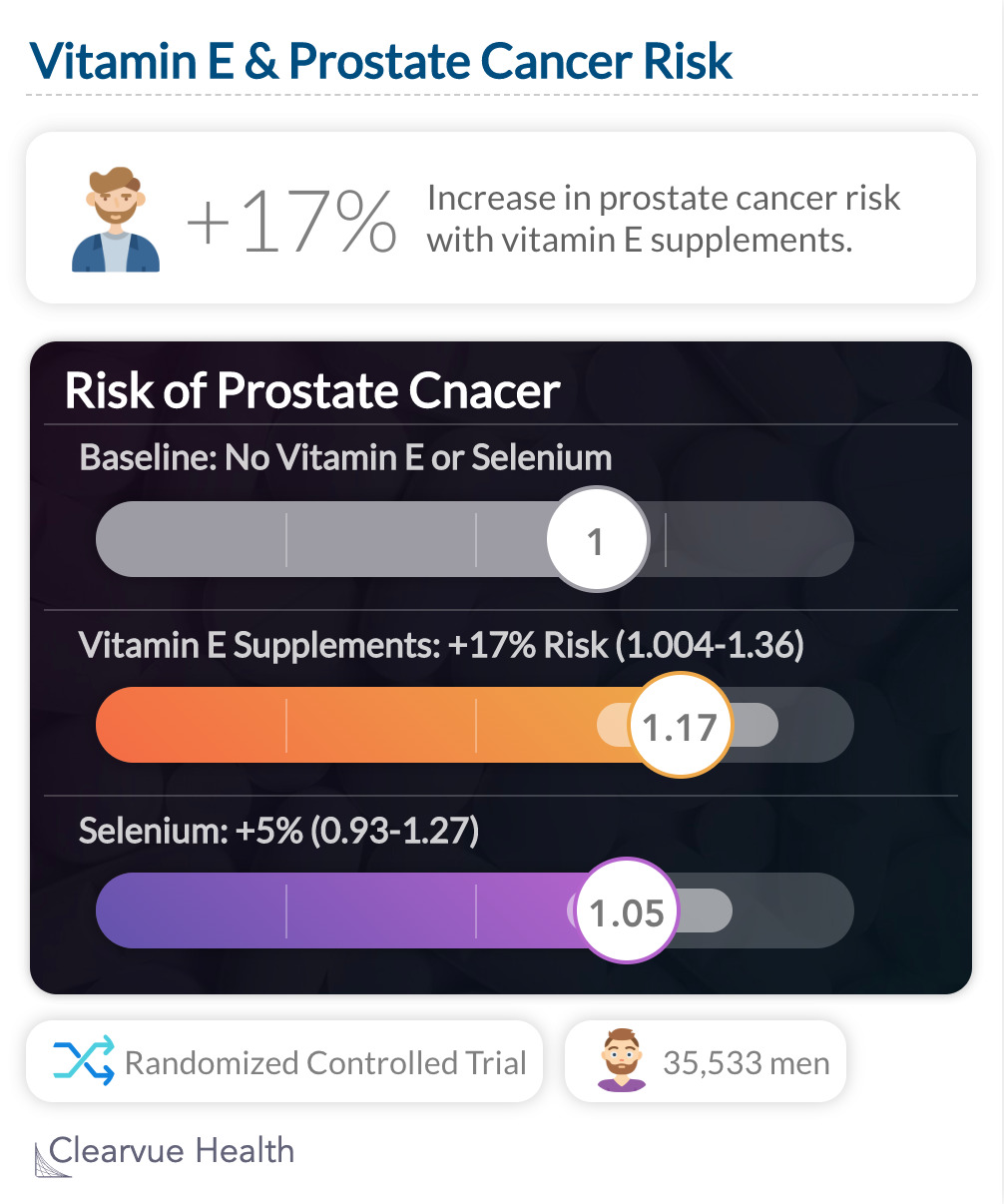
A study of 35,533 men found that Vitamin E may increase the risk of prostate cancer. Participants were given selenium, 400 IU/d of vitamin E, both, or a placebo, for 7-12 years. Researchers found that those who were given Vitamin E had a significantly higher risk of developing prostate cancer.
Data Source
"Dietary supplementation with vitamin E significantly increased the risk of prostate cancer among healthy men."

#nutrition
Scroll for more ->





#vitamine
Scroll for more ->




#new
Scroll for more ->