Ritalin
Evidence Based Answers
What are the neurological effects of Ritalin?
Ritalin enhances dopamine levels by blocking its reuptake, leading to improved focus and motivation, but can occasionally cause mood swings and insomnia. Individual responses vary due to brain chemistry and may affect cognitive and behavioral outcomes.
Click to explore a section:
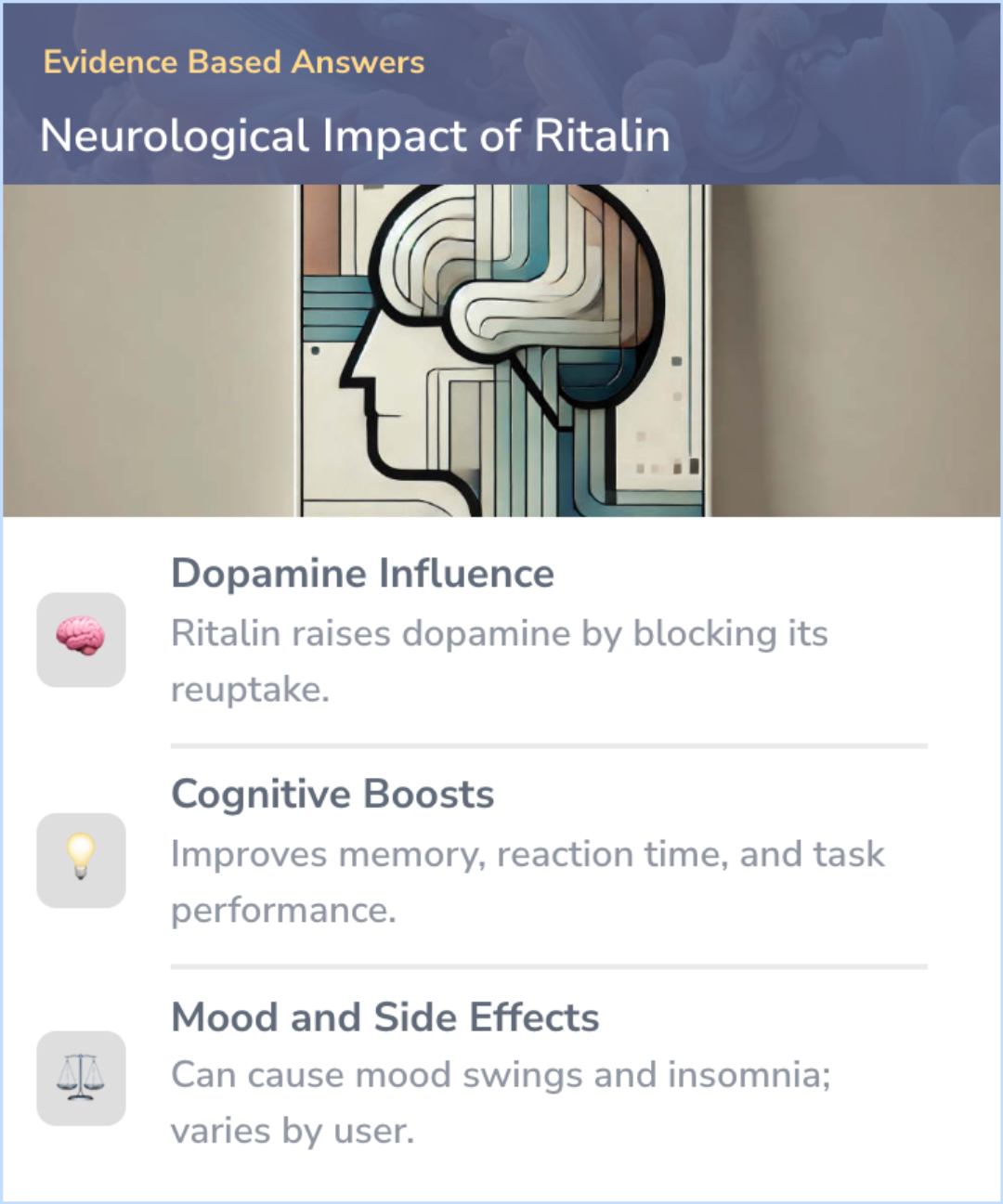
Ritalin raises dopamine uptake and improves cognition but may cause mood swings.
Ritalin's Effects on Dopamine and Neurotransmitters
Ritalin (methylphenidate) primarily affects dopamine levels by blocking its reuptake, leading to higher dopamine concentrations in the brain. This action is believed to improve focus, attention, and motivation.
It can also weakly influence other neurotransmitters like norepinephrine and serotonin, contributing to varied effects on cognition and mood.
It can also weakly influence other neurotransmitters like norepinephrine and serotonin, contributing to varied effects on cognition and mood.
“
Source Quotes:
Methylphenidate binds to the dopamine transporter in the presynaptic cell membrane, blocking reuptake of dopamine and causing a resultant increase in extracellular dopamine levels.
Methylphenidate (like cocaine) increases dopamine by blocking dopamine transporters, and amphetamine (like methamphetamine) increases dopamine by releasing dopamine from the terminal.
Cognitive and Behavioral Effects of Ritalin
Ritalin has demonstrated improvements in reaction time, memory, and task performance. These benefits are linked to its role in increasing dopamine, which boosts motivation and engagement.
Responses can vary widely. While many see enhanced focus, some may not benefit or might experience side effects.
Responses can vary widely. While many see enhanced focus, some may not benefit or might experience side effects.
“
Source Quotes:
Several studies have shown that methylphenidate improves cognition, vigilance, reaction time, short term memory and the learning of verbal and non-verbal material.
Stimulant-induced dopamine increases in the striatum are believed to decrease background firing rates and increase signal-to-noise ratio of striatal cells, which we postulate as a mechanism for improving attention by enhancement of task-related neuronal cell firing.
Possible Neurological Side Effects of Ritalin
Ritalin can cause side effects like mood swings, irritability, and insomnia in some users due to its effects on brain pathways that regulate mood and alertness.
In rare cases, it may worsen symptoms for individuals with certain mental health conditions or elevate the risk of psychosis.
In rare cases, it may worsen symptoms for individuals with certain mental health conditions or elevate the risk of psychosis.
“
Source Quotes:
Patients are more prone to become easily agitated, irritable, or depressed and go through mood swings/lability.
Treatment emergent psychotic or manic symptoms, e. g., hallucinations, delusional thinking, or mania in children and adolescents without a prior history of psychotic illness or mania can be caused by stimulants at usual doses.
Variability in Individual Response to Ritalin
Ritalin's impact varies based on individual brain chemistry and dopamine receptor availability. Imaging studies suggest these differences influence both its therapeutic effects and potential side effects.
This variability means some users see major benefits, while others might experience minimal changes or negative effects.
This variability means some users see major benefits, while others might experience minimal changes or negative effects.
“
Source Quotes:
Imaging studies have also shown that the availability of dopamine D2 receptors in the brain may modulate the reinforcing responses to methylphenidate in humans.
It is, however, subject to marked individual differences in the response so that some subjects experience anxiety, dysphoria and tiredness.
Key Takeaways
Conclusions
Ritalin, a medication often used to enhance focus and attention, primarily functions by increasing dopamine levels in the brain, which is key to its effects on improving cognitive abilities such as reaction time and memory.
It's important to note that responses to Ritalin can vary significantly among individuals due to differences in brain chemistry, sometimes leading to side effects like mood swings and irritability.
It's important to note that responses to Ritalin can vary significantly among individuals due to differences in brain chemistry, sometimes leading to side effects like mood swings and irritability.

Evidence Summary
How Ritalin Impacts Focus and Impulse Control
Ritalin changes how the brain handles focus and impulse control by increasing activity in areas responsible for attention and behavior. It mainly targets brain regions that manage these functions, enhancing the ability to focus and manage impulses.
Frequently used to treat ADHD, Ritalin alters brain function to reduce symptoms tied to attention difficulties and behavioral issues. Its effects are most pronounced in areas controlling focus and impulsivity.
Frequently used to treat ADHD, Ritalin alters brain function to reduce symptoms tied to attention difficulties and behavioral issues. Its effects are most pronounced in areas controlling focus and impulsivity.
Evidence Summary
Harnessing Brain Energy for Better Focus
Methylphenidate, widely known for treating ADHD, plays a vital role in how our brains use energy. It directly influences the brain's metabolism, which is essential for maintaining focus and attention. By optimizing how this medication works, healthcare providers can enhance its effectiveness in patients.
This information sheds light on how the medication can help manage ADHD symptoms by providing a clearer picture of its impact on brain energy usage, making treatment more tailored and effective.
This information sheds light on how the medication can help manage ADHD symptoms by providing a clearer picture of its impact on brain energy usage, making treatment more tailored and effective.
Evidence Summary
Comparing ADHD Treatments: Methylphenidate vs. Atomoxetine
Methylphenidate and atomoxetine, both used to treat ADHD, are compared for their effectiveness in managing symptoms. While both medications target ADHD-related challenges, they work differently in the body, impacting symptom relief in unique ways.
This comparison highlights which drug may be more beneficial for specific needs in ADHD treatment, giving a clearer picture of their roles and effectiveness in improving daily functioning for individuals with ADHD.
This comparison highlights which drug may be more beneficial for specific needs in ADHD treatment, giving a clearer picture of their roles and effectiveness in improving daily functioning for individuals with ADHD.