Ritalin
Evidence Based Answers
3 Studies: The Long-Term Effects of Methylphenidate on Children with ADHD?
Published: August 17, 2024
Studies Summary
👥
Social Functioning Over Time
A study on the effects of methylphenidate, with or without additional social skills training, showed that the drug improved social functioning in children with ADHD over 2 years, but no extra benefits came from the added training.
📏
Concerns About Growth Rates
Methylphenidate may slow children's growth in height and weight. While some children catch up during adolescence, others might not fully recover. Regular growth monitoring and possible 'drug holidays' are recommended.
🧩
Behavioral and Cognitive Effects
Methylphenidate improves attention and memory but may cause mild side effects like nervous habits and blunted emotions. These side effects require close monitoring during long-term treatment.
Highly Cited Studies
Long term Effects of Methylphenidate in Adults

Peer Reviewed Study 1
Long-Term Effects of Methylphenidate on ADHD and Tics in Children
Peer Reviewed Study 2
No Added Long-Term Benefits of Combining Methylphenidate with Extra Treatments in ADHD
Peer Reviewed Study 3
Methylphenidate's Effects on Social Functioning in Children with ADHD Over 2 Years
Background: Methylphenidate and Growth Concerns in Children
One of the main concerns with long-term methylphenidate use in children is its possible impact on growth. Studies indicate that regular use of the drug may slow the growth rates of both height and weight. This effect might be temporary, with some children catching up during adolescence, especially if the treatment is paused. However, other children might not fully recover in growth. This potential impact underscores the importance of regular growth monitoring. Some healthcare providers consider 'drug holidays,' or short breaks from the medication, to help alleviate these effects.
It is important for parents and healthcare providers to track growth changes regularly to make informed treatment decisions.
It is important for parents and healthcare providers to track growth changes regularly to make informed treatment decisions.

“
Growth retardation (decreased height, weight, and bone marrow density) is observed when taken long-term in children.
“
Drug holidays may be beneficial for children in whom stimulant therapy is associated with a growth trajectory that crosses two major percentiles.
Background: Behavioral and Cognitive Effects of Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate has notable effects on both behavior and cognitive functions in children with ADHD. It enhances performance on tasks that require attention and working memory, which are commonly challenging for children with ADHD. However, it also carries the risk of side effects, including the development of nervous habits, blunted emotions, and obsessive thinking. These side effects are generally mild but require close monitoring during long-term treatment.
Understanding the balance between cognitive benefits and potential behavioral side effects helps ensure that the treatment remains beneficial without significant drawbacks.
Understanding the balance between cognitive benefits and potential behavioral side effects helps ensure that the treatment remains beneficial without significant drawbacks.

“
Methylphenidate enhances cognitive performance in adults and children diagnosed with ADHD, and also in human volunteers, on tasks that are sensitive to frontal lobe damage.
“
In addition to improvement in core symptoms of ADHD, treatment with stimulants also improves caregiver-child interactions, aggressive behavior, and academic productivity and accuracy.
Background: Cardiovascular Health and Methylphenidate Use
Although methylphenidate is generally well-tolerated, it is essential to be aware of its potential impact on cardiovascular health, particularly in children with pre-existing heart conditions. Reports have highlighted the risk of serious cardiovascular events, including sudden death and stroke, in children with underlying heart problems. Therefore, it is recommended that blood pressure and heart rate be monitored regularly in children undergoing long-term methylphenidate treatment.
This regular monitoring can help detect early signs of cardiovascular complications, ensuring timely intervention and safe ongoing treatment.
This regular monitoring can help detect early signs of cardiovascular complications, ensuring timely intervention and safe ongoing treatment.

“
There have been reported cases of sudden death in both children and adults with a pre-existing structural cardiac abnormality.
“
Sudden death has been reported in association with CNS stimulant treatment at usual doses in children and adolescents with structural cardiac abnormalities.
Background: Psychiatric Side Effects of Long-Term Methylphenidate Use
Long-term use of methylphenidate may lead to psychiatric risks such as mood swings, irritability, and in some cases, the appearance of psychotic symptoms like hallucinations or delusional thinking. These effects are rare but highlight the importance of closely monitoring children during treatment, especially those without a prior history of psychiatric conditions. If any psychiatric symptoms appear, adjusting the treatment or stopping the medication may be necessary.
Early detection of these psychiatric risks can help prevent more severe outcomes, ensuring safer treatment for children with ADHD.
Early detection of these psychiatric risks can help prevent more severe outcomes, ensuring safer treatment for children with ADHD.

“
Patients are more prone to become easily agitated, irritable, or depressed and go through mood swings/lability.
“
Treatment emergent psychotic or manic symptoms, e.g., hallucinations, delusional thinking, or mania in children and adolescents without a prior history of psychotic illness or mania can be caused by stimulants.
Background: Seizure Risks Linked to Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate might affect neurological health in children, especially by lowering the seizure threshold. This is particularly concerning for children with a history of seizures or other neurological conditions. While the evidence isn't entirely conclusive, it is advisable to monitor children for signs of seizures, especially if they have previously abnormal EEGs. If seizures do occur, the medication should be stopped immediately.
Understanding these risks allows for more informed decisions about continuing or adjusting treatment.
Understanding these risks allows for more informed decisions about continuing or adjusting treatment.

“
Controversial evidence exists regarding the potential for methylphenidate to affect seizure threshold. If seizures develop while being treated with methylphenidate, the prescribing clinician should immediately stop the drug.
“
There is some clinical evidence that stimulants may lower the convulsive threshold in patients with prior history of seizures, in patients with prior EEG abnormalities in absence of seizures.
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Long-Term Effects of Methylphenidate on ADHD and Tics in Children
This study followed 34 children with ADHD and chronic tic disorder for 2 years during methylphenidate treatment. Researchers observed no changes in motor or vocal tics over time, and the behavioral improvements seen during initial treatment were maintained.
There were also no significant adverse effects on heart function or growth at the 2-year mark, suggesting that the drug is generally safe and effective over the long term for managing ADHD in children with tics.
There were also no significant adverse effects on heart function or growth at the 2-year mark, suggesting that the drug is generally safe and effective over the long term for managing ADHD in children with tics.
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: No Added Long-Term Benefits of Combining Methylphenidate with Extra Treatments in ADHD
A study tested whether adding academic help and therapy to methylphenidate improves academic and emotional outcomes in children with ADHD. Over 103 children, aged 7-9, were followed for two years. The treatments compared were methylphenidate alone, methylphenidate with specific psychosocial treatment, and methylphenidate with attention control. The study found no added benefits in academic performance or emotional well-being for children who received additional treatments.
All groups showed improvement, and these improvements were maintained over the two-year period.
All groups showed improvement, and these improvements were maintained over the two-year period.

Peer Reviewed Study
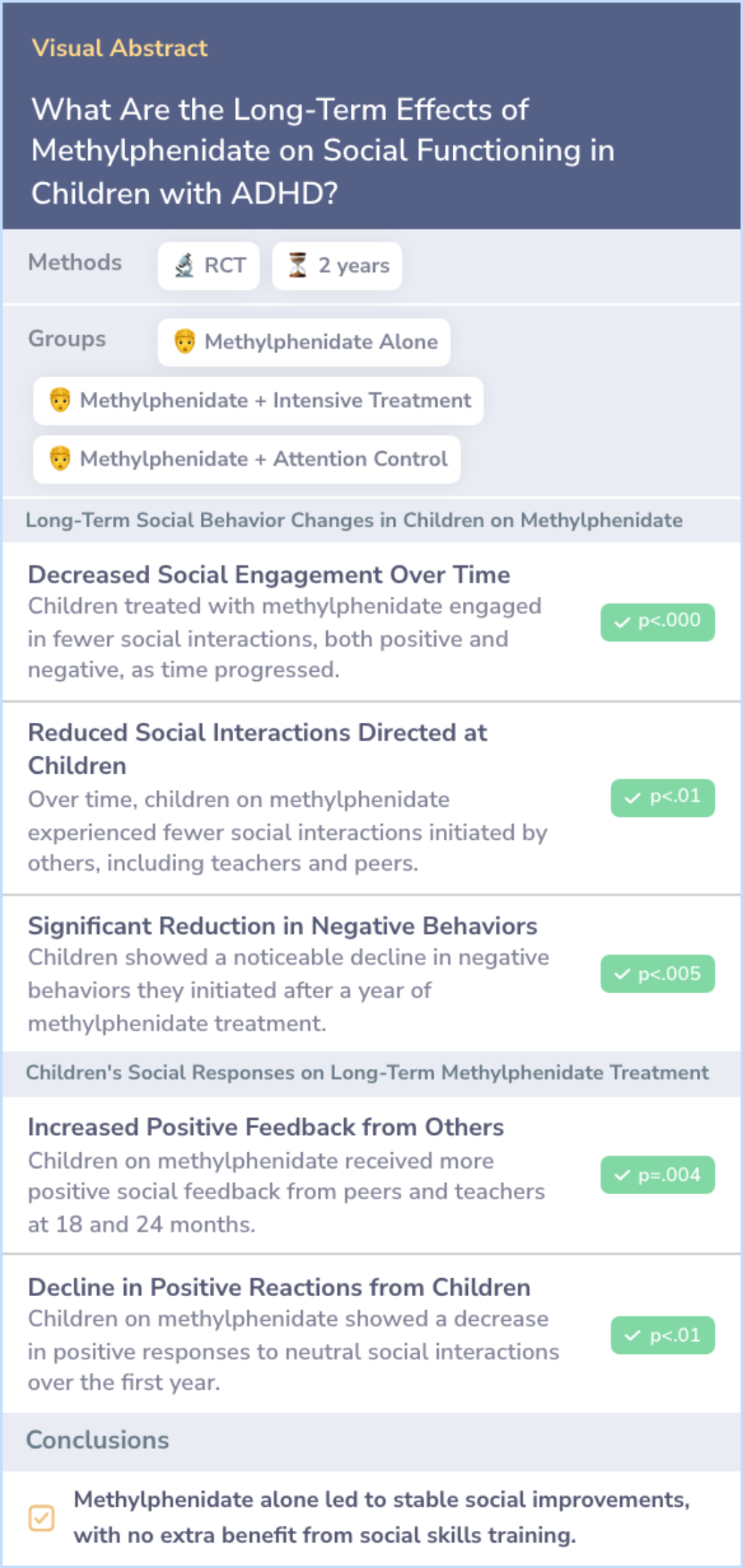
Study: Methylphenidate's Effects on Social Functioning in Children with ADHD Over 2 Years
This study examined whether adding intensive social skills training to methylphenidate treatment would improve social functioning in children with ADHD. The study found that over 2 years, methylphenidate alone, combined with social skills training, or combined with nonspecific psychosocial treatment all led to significant improvements in social functioning. However, there was no additional benefit from including social skills training.
These findings suggest that the long-term use of methylphenidate, with or without additional social skills training, results in stable social improvements.
These findings suggest that the long-term use of methylphenidate, with or without additional social skills training, results in stable social improvements.

Key Takeaways
Conclusions
Methylphenidate has been shown to effectively manage ADHD symptoms in children over the long term, with studies indicating stable improvements in behavior, cognitive function, and social interactions. While the treatment appears to be safe for most children, it requires careful monitoring to manage potential side effects, such as growth suppression, cardiovascular risks, psychiatric symptoms, and seizure concerns.
Research suggests that while methylphenidate alone provides substantial benefits, adding other treatments like social skills training or academic support doesn't significantly enhance long-term outcomes. Therefore, the focus should remain on regular monitoring and personalized treatment adjustments to ensure safety and effectiveness over time.
Research suggests that while methylphenidate alone provides substantial benefits, adding other treatments like social skills training or academic support doesn't significantly enhance long-term outcomes. Therefore, the focus should remain on regular monitoring and personalized treatment adjustments to ensure safety and effectiveness over time.
Evidence Summary
Time Perception Challenges in ADHD: Medication's Limited Role
Research shows that children with ADHD struggle with accurately reproducing time intervals, especially when distracted. This difficulty increases as the intervals lengthen, and unlike their peers without ADHD, they don't improve with stimulant medication.
Even under different doses of methylphenidate, these children showed no improvement in their time reproduction accuracy, suggesting that the medication doesn't aid in this particular cognitive task.
Even under different doses of methylphenidate, these children showed no improvement in their time reproduction accuracy, suggesting that the medication doesn't aid in this particular cognitive task.
Evidence Summary
How Methylphenidate Affects Focus and Memory
Methylphenidate, commonly known as Ritalin or Concerta, treats ADHD by influencing attention and memory. The article examines how this medication benefits these cognitive functions while also exploring its potential side effects.
Specifically, it looks into both the enhancements it brings to focus and memory tasks and the possible downsides, providing insights into the overall cognitive impact of methylphenidate.
Specifically, it looks into both the enhancements it brings to focus and memory tasks and the possible downsides, providing insights into the overall cognitive impact of methylphenidate.
Evidence Summary
Comparing ADHD Medications: Atomoxetine vs. Methylphenidate
The slide compares Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate, two common ADHD medications. It lays out differences in their effectiveness, side effects, and how patients respond to each drug. This comparison helps people see which medication might suit them or their children better based on the unique pros and cons of each option.
Both medications are designed to address ADHD symptoms, but the slide clearly presents the distinctiveness in how each works and their varied impacts on patients.
Both medications are designed to address ADHD symptoms, but the slide clearly presents the distinctiveness in how each works and their varied impacts on patients.
Evidence Summary
How Methylphenidate Enhances Cognitive Function in ADHD
Methylphenidate, a medication prescribed for ADHD, has been found to enhance cognitive functions like attention, focus, and overall mental performance. The research highlighted in the article supports these claims, showing measurable improvements in children with ADHD who are treated with the drug.
This enhancement in cognitive ability aligns with findings across various studies, illustrating how the medication helps in managing ADHD symptoms more effectively.
This enhancement in cognitive ability aligns with findings across various studies, illustrating how the medication helps in managing ADHD symptoms more effectively.