Adderall
Evidence Based Answers
Studies on Adderall and Cognition in Healthly Individuals
Adderall may improve focus in healthy people by raising dopamine levels, but evidence for cognitive enhancement is mixed, and long-term use can pose serious risks to brain health.
Published: October 24, 2024
Click to explore a section:
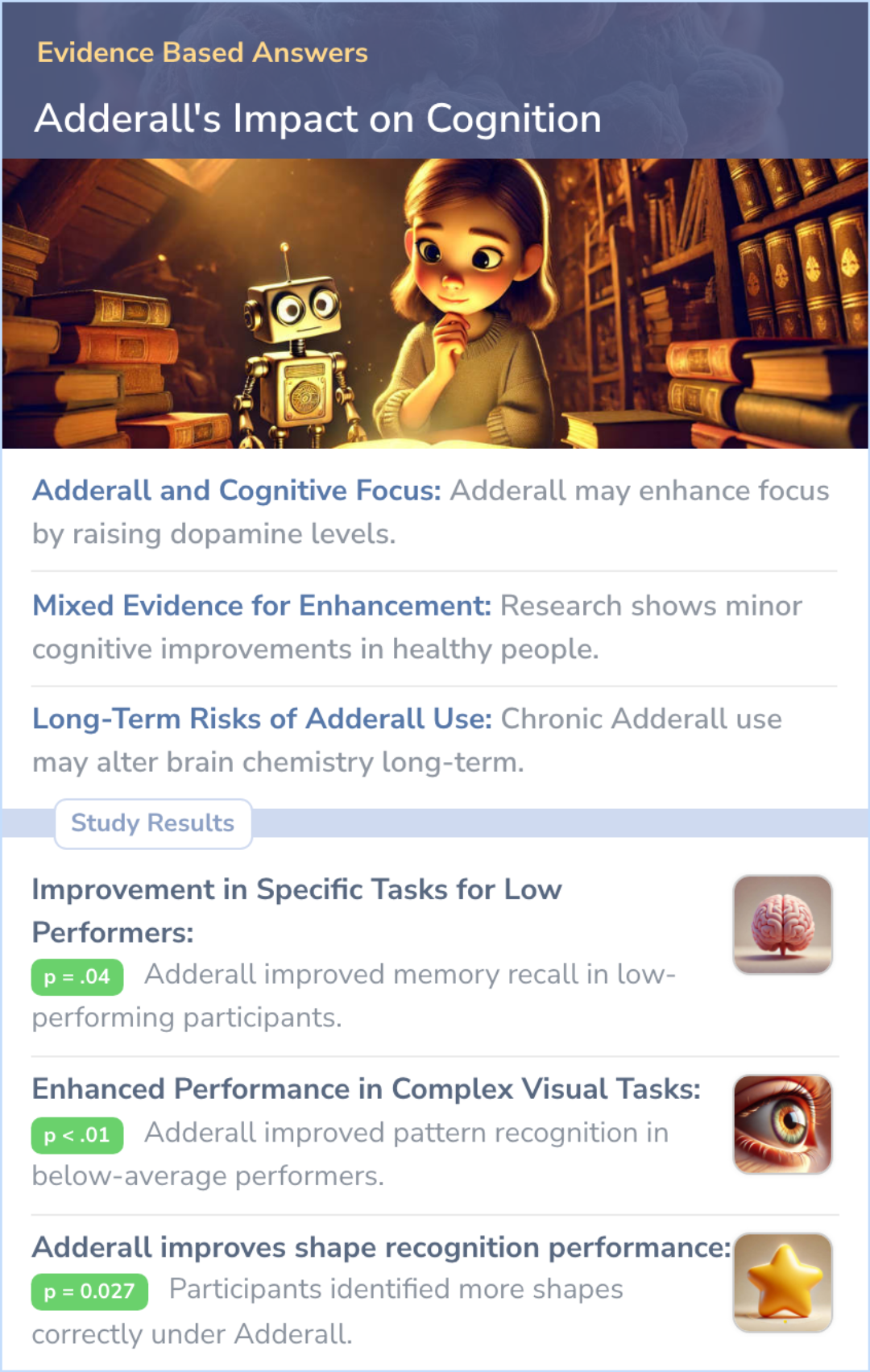
Adderall may raise dopamine levels and improve focus, but research shows mixed cognitive benefits and risks of long-term brain changes.
Studies Summary
🧠
Adderall's Mixed Effects on Cognition
Studies show that Adderall does not significantly enhance cognitive abilities in healthy young adults. A slight improvement was noted in participants with lower ability, particularly in memory and problem-solving tasks.
🔍
Understanding the Role of Baseline Abilities
Adderall's effects vary based on initial performance levels. It may improve certain cognitive tasks like convergent thinking for those who start at a lower baseline, but effects can be mixed for those with higher baseline abilities.
🚗
Differences in Driving and Impulsivity
Adderall did not effectively improve driving performance in adolescents with ADHD and showed varied effects in reducing impulsivity. Other medications, like OROS methylphenidate, showed more consistent results in improving driving behavior.
Highly Cited Studies
Long term Effects of Methylphenidate in Adults
Peer Reviewed Study 1
Adderall's Limited Impact on Cognitive Performance in Healthy Young Adults
Peer Reviewed Study 2
Key Effects of Adderall on Cognition and Emotions in Healthy Individuals
Peer Reviewed Study 3
Adderall's Effects on Cognitive Performance Vary by Baseline Abilities
Peer Reviewed Study 4
d-Amphetamine’s Effect on Impulsivity in Healthy Adults
Background: How Does Adderall Influence Cognitive Function in Healthy Individuals?
Adderall contains dextroamphetamine and amphetamine, which increase dopamine and norepinephrine levels. These chemicals play a key role in attention and focus. While this may enhance focus and energy in healthy individuals, the effects can differ from those in people with ADHD.
These mechanisms that may improve cognitive performance can also pose risks, such as habit formation and severe side effects, including heart issues.
These mechanisms that may improve cognitive performance can also pose risks, such as habit formation and severe side effects, including heart issues.
“
Source Quotes:
The primary pharmacologic effect of amphetamine is to increase central dopamine and norepinephrine activity, which impacts executive and attentional function.
Amphetamines are thought to block the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine into the presynaptic neuron and increase the release of these monoamines into the extraneuronal space.
Background: Is There Strong Evidence for Cognitive Enhancement in Healthy Individuals?
Research on Adderall’s effects on cognitive function in healthy individuals shows mixed results. Some studies suggest it may improve focus, especially on monotonous tasks, but these improvements are often minor and might not outweigh the health risks associated with non-medical use.
Additionally, many studies are conducted in controlled settings, which may not reflect real-world scenarios. The long-term effects of using Adderall for cognitive enhancement remain unclear, raising safety concerns.
Additionally, many studies are conducted in controlled settings, which may not reflect real-world scenarios. The long-term effects of using Adderall for cognitive enhancement remain unclear, raising safety concerns.
“
Source Quotes:
Apparently, psychostimulants are popular among healthy people seeking neuroenhancement.
Amphetamine increased BOLD signal variability and exerted an 'equalizing' effect on ventral striatum activity during incentive processing.
Background: What Are the Long-Term Risks of Non-Medical Adderall Use?
Using Adderall for cognitive enhancement without medical supervision carries significant long-term risks. Chronic use, especially at high doses, may lead to lasting changes in brain chemistry, particularly in the dopamine system, potentially reducing cognitive abilities over time.
There is also a risk of psychological dependence and other mental health issues, particularly concerning for healthy individuals who do not require the drug for any medical reason.
There is also a risk of psychological dependence and other mental health issues, particularly concerning for healthy individuals who do not require the drug for any medical reason.
“
Source Quotes:
Chronic exposure to amphetamine, particularly methamphetamine, at recreational doses has shown to destroy dopaminergic terminals in the striatum through a variety of mechanisms, including oxidative stress and excitotoxicity.
Amphetamine increased dopamine release in the caudate and prefrontal cortex of rhesus macaques, with dopamine levels remaining elevated for a longer duration in the prefrontal cortex than in the caudate.
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Adderall's Limited Impact on Cognitive Performance in Healthy Young Adults
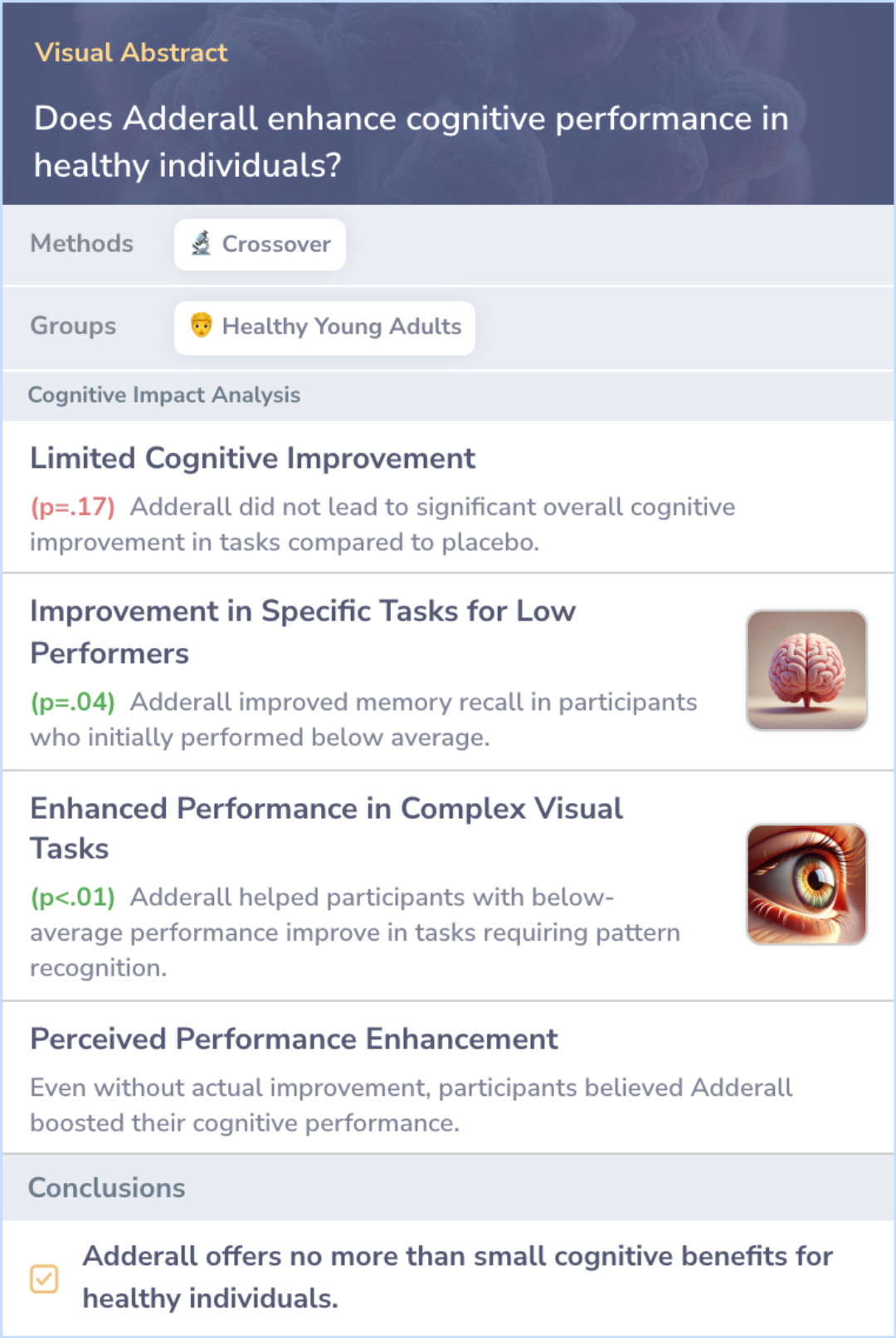
A study examined the effects of mixed amphetamine salts (Adderall) on cognitive performance in healthy young adults using a well-controlled trial. The study tested 13 different cognitive abilities, including memory and intelligence, to determine if Adderall had a moderate enhancing effect. Results showed that Adderall did not enhance cognitive abilities for most participants. However, there was a slight indication that lower ability participants might experience some improvement in certain tasks, like word recall and problem-solving.
Despite these findings, participants believed they performed better when taking Adderall, even though the drug had no significant effect on their cognitive performance.
Despite these findings, participants believed they performed better when taking Adderall, even though the drug had no significant effect on their cognitive performance.
author
Ilieva I, Boland J, Farah MJ
journal
Neuropharmacology
Date Published
2013 Jan
Peer Reviewed Study
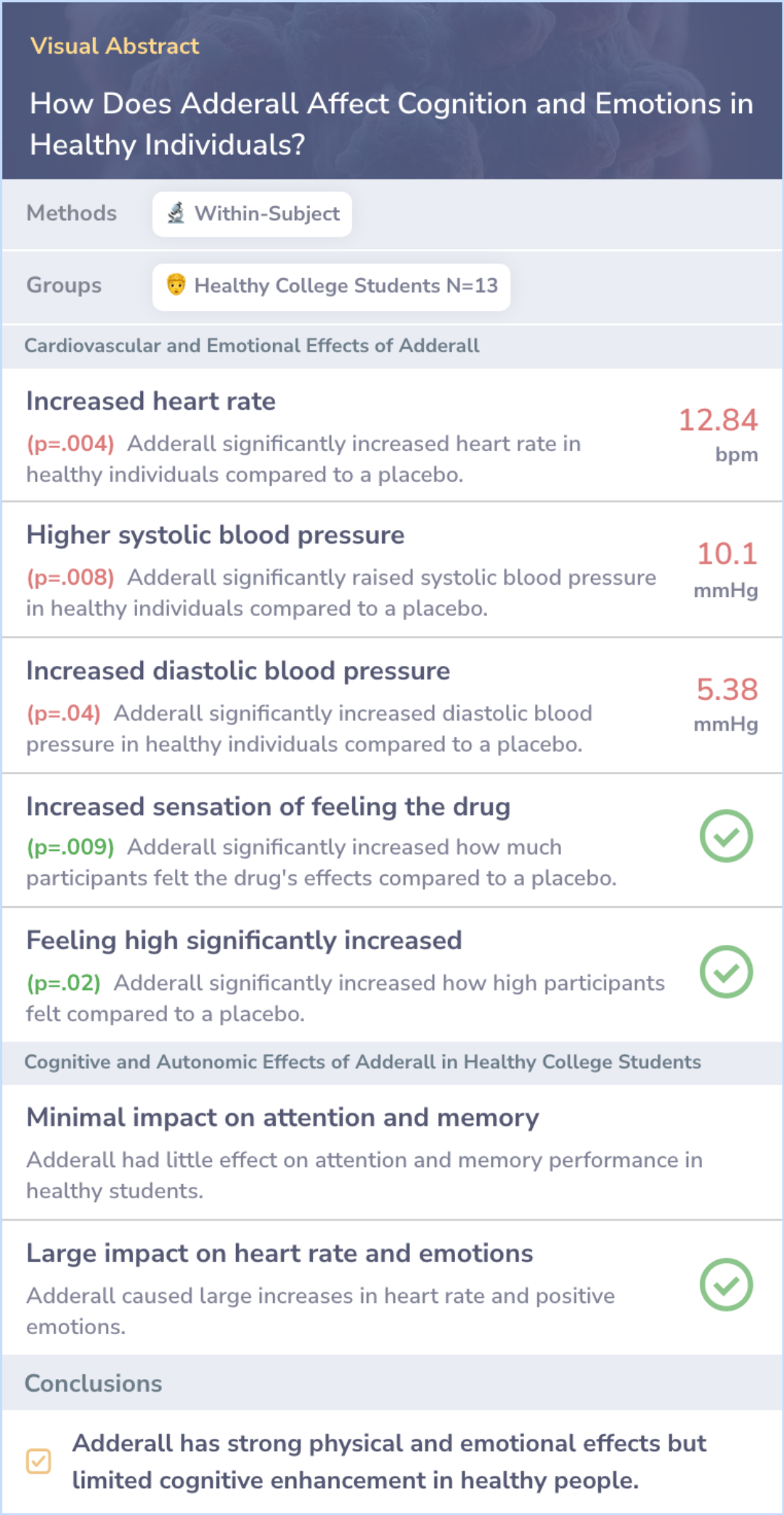
Study: Key Effects of Adderall on Cognition and Emotions in Healthy Individuals
Adderall was found to significantly increase heart rate and blood pressure, showing notable effects on cardiovascular function. These effects were accompanied by increased feelings of 'high' and 'feeling the drug'.
However, Adderall had minimal impacts on attention and memory performance, indicating that its cognitive effects on healthy individuals may be limited.
These findings suggest that while Adderall causes strong physical and emotional responses, its ability to enhance cognitive function in people without ADHD is less significant.
However, Adderall had minimal impacts on attention and memory performance, indicating that its cognitive effects on healthy individuals may be limited.
These findings suggest that while Adderall causes strong physical and emotional responses, its ability to enhance cognitive function in people without ADHD is less significant.
author
Weyandt LL, White TL, Gudmundsdottir BG, Nitenson AZ, Rathkey ES, De Leon KA, Bjorn SA
journal
Pharmacy
Date Published
2018-06-27
Peer Reviewed Study
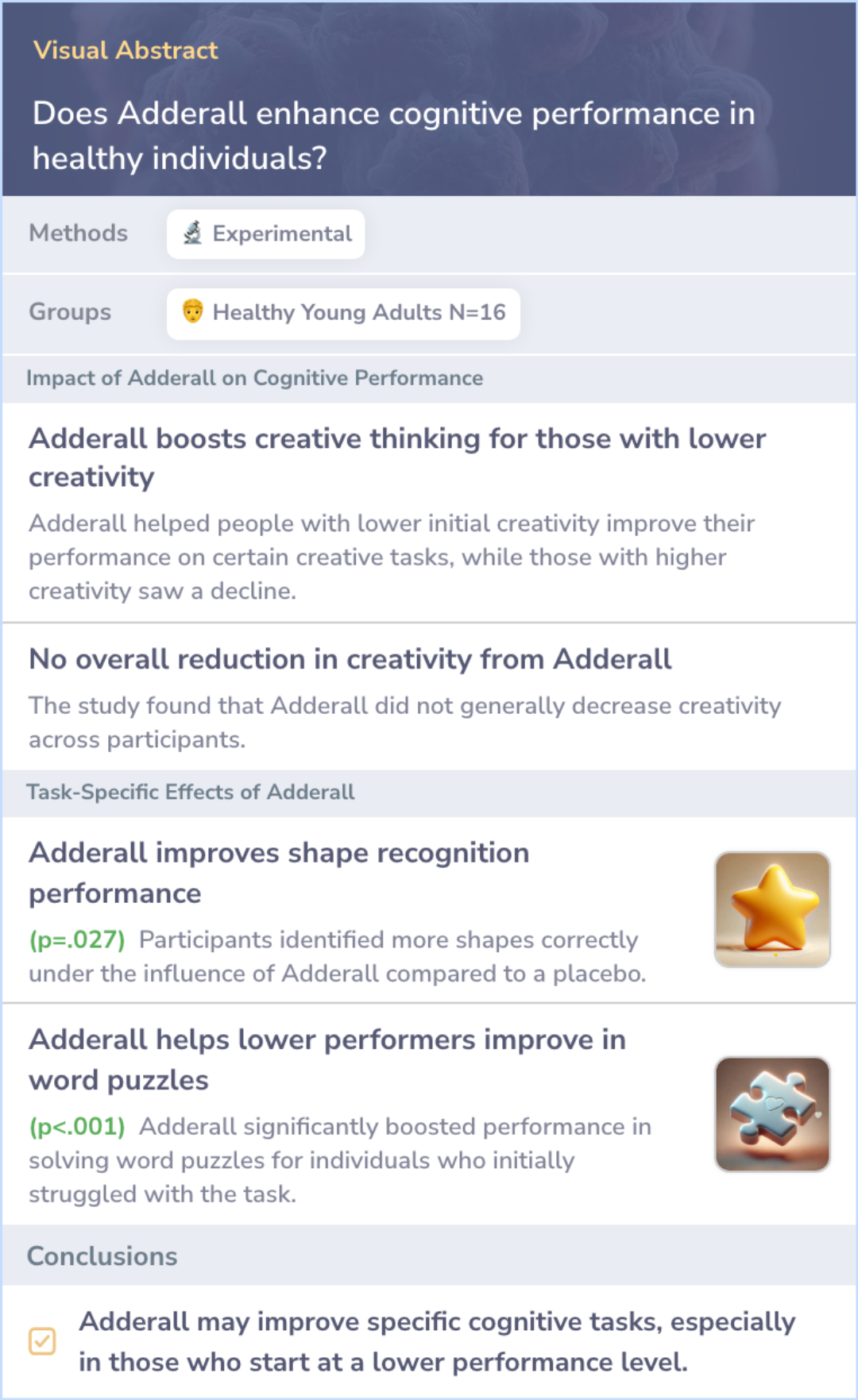
Study: Adderall's Effects on Cognitive Performance Vary by Baseline Abilities
This study tested how Adderall affects creativity in healthy young adults. Participants were given Adderall or a placebo and then asked to complete tasks that measured their creative thinking. Adderall was found to improve performance on tasks that required convergent thinking, but mainly for those who initially performed lower. However, it had mixed effects on higher-performing individuals.
These results suggest that Adderall may boost certain types of cognitive performance, but its effects vary depending on the individual's baseline abilities.
These results suggest that Adderall may boost certain types of cognitive performance, but its effects vary depending on the individual's baseline abilities.
author
Farah MJ, Haimm C, Sankoorikal G, Smith ME, Chatterjee A
journal
Psychopharmacology
Date Published
2009-01
Peer Reviewed Study
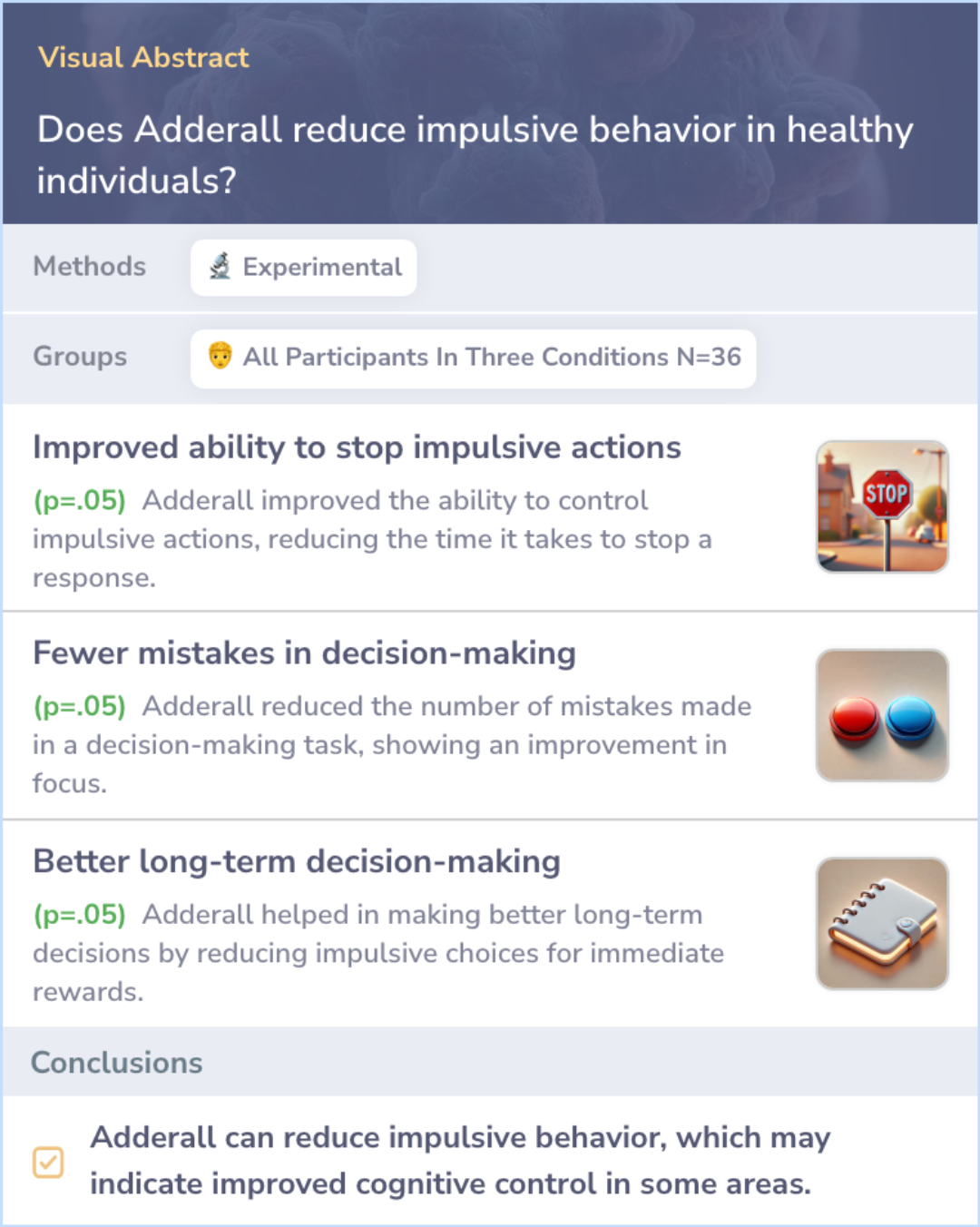
Study: d-Amphetamine’s Effect on Impulsivity in Healthy Adults
This study examined how d-amphetamine, a component of Adderall, affects impulsive behaviors in healthy adults. Participants took either a placebo, 10 mg, or 20 mg of d-amphetamine and performed five different tasks designed to measure impulsivity. The results showed that d-amphetamine reduced impulsive actions in some tasks, such as stopping a reaction and delaying rewards, suggesting a reduction in impulsive behavior.
However, not all impulsive behaviors were affected, indicating that d-amphetamine's effects may be task-specific.
However, not all impulsive behaviors were affected, indicating that d-amphetamine's effects may be task-specific.
author
de Wit H, Enggasser JL, Richards JB
journal
Neuropsychopharmacology
Date Published
2002 Nov
Key Takeaways
Conclusions
Adderall, a commonly used stimulant drug, has mixed effects on cognitive performance in healthy individuals. Several studies revealed that it does not significantly boost cognitive abilities in most participants, though it may offer slight benefits in specific tasks for those with lower baseline abilities.
Despite its potential to improve focus under some conditions, these effects are typically minor and accompanied by considerable health risks. Users often believe Adderall enhances their performance, even when objective measures show otherwise, underscoring the complexities surrounding its use.
Despite its potential to improve focus under some conditions, these effects are typically minor and accompanied by considerable health risks. Users often believe Adderall enhances their performance, even when objective measures show otherwise, underscoring the complexities surrounding its use.

Evidence Summary
Exploring Factors Behind Cognitive Enhancements
The slide explores unidentified factors influencing cognitive function enhancements in everyday scenarios. While some elements may boost attention, they come with potential side effects and long-term risks.
The evidence for benefits remains uncertain, with variations depending on individual conditions. The unknown parameters highlighted here can play a significant role in understanding the broader implications drawn from recent research.
The evidence for benefits remains uncertain, with variations depending on individual conditions. The unknown parameters highlighted here can play a significant role in understanding the broader implications drawn from recent research.
Evidence Summary
Unveiling the Mysteries: Undefined Insights
Without context, the topic remains undefined, leaving us with more questions than answers. Ambiguity can keep conversations alive, challenging our preconceived notions and sparking curiosity.
Just like the cliffhanger of a captivating story, the unattainable nature of the content piques interest, perhaps leading us to draw connections between the seen and the unseen, the known and the unknown.
Just like the cliffhanger of a captivating story, the unattainable nature of the content piques interest, perhaps leading us to draw connections between the seen and the unseen, the known and the unknown.
Evidence Summary
Revealing Reaction Time Variability in ADHD
Researchers identified a core feature of ADHD: deficient behavioral inhibition. Using the stop-signal paradigm, they compared children with ADHD to typically developing peers. Children with ADHD displayed slower and more varied reaction times, highlighting underlying attention and cognitive processing deficits.
Interestingly, the study found no significant differences in the stop-signal delay, suggesting the issue isn't necessarily with behavioral inhibition.
Interestingly, the study found no significant differences in the stop-signal delay, suggesting the issue isn't necessarily with behavioral inhibition.