Adderall
Evidence Based Answers
3 Studies on Adderall and Behavior
Adderall helps control impulsivity, improves daily functioning, but can cause side effects like irritability. Monitoring is important to manage its effectiveness and side effects.
Published: October 24, 2024
Click to explore a section:
Adderall reduces impulsivity, improves functioning but may cause irritability or aggression.
Studies Summary
🧠
Adderall's Role in Impulsivity Control
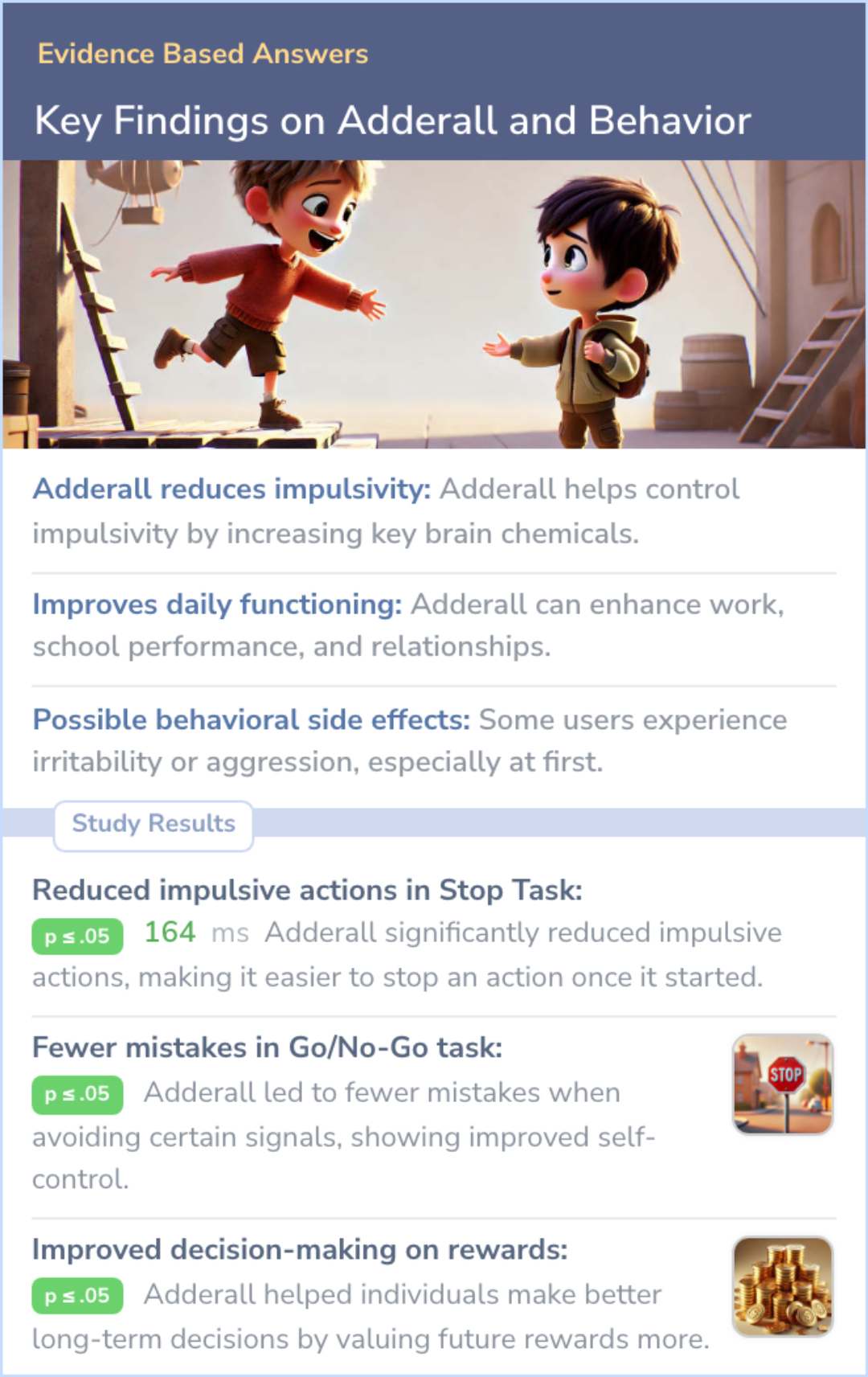
Adderall increases levels of neurotransmitters that help control attention and impulsivity, potentially reducing impulsive behaviors in those with ADHD.
⚠️
Potential Behavioral Side Effects
While Adderall reduces impulsivity, it can cause side effects like restlessness and irritability, especially early on in treatment.
🔄
Impact on Daily Life
Adderall can improve daily functioning such as work performance and relationships, but results may differ among individuals.
Highly Cited Studies
Long term Effects of Methylphenidate in Adults
Peer Reviewed Study 1
Adderall's Impact on Impulsivity and Behavioral Control in ADHD
Peer Reviewed Study 2
Impact of Adderall on Driving Performance in Adolescents with ADHD
Peer Reviewed Study 3
Adderall Significantly Reduces ADHD Symptoms in Adults, Lasting Up to 12 Hours
Background: How Adderall Affects Impulsivity and Behavioral Control
Adderall is often prescribed to help control impulsivity and other behavioral issues in individuals with ADHD. It works by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters, like dopamine and norepinephrine, in the brain, which play a crucial role in regulating attention and impulsive behaviors.
While Adderall can effectively reduce impulsivity and improve focus, it may also have varying effects depending on the individual, and regular monitoring is essential to ensure its effectiveness and manage any potential side effects.
While Adderall can effectively reduce impulsivity and improve focus, it may also have varying effects depending on the individual, and regular monitoring is essential to ensure its effectiveness and manage any potential side effects.
“
Source Quotes:
Adderall® may help increase attention and decrease impulsiveness and hyperactivity in patients with ADHD.
Amphetamines showed greater effect on clinician rating scales of overall ADHD symptoms, including impulsivity, than methylphenidate.
Background: Impact on Daily Functioning Beyond Impulsivity
In addition to reducing impulsivity, Adderall can also lead to improvements in daily functioning for individuals with ADHD. This might include enhanced performance at work or school and better interpersonal relationships.
However, the extent of these improvements varies from person to person, and not all aspects of ADHD-related behavior may be addressed by the medication. Continuous evaluation is important to ensure that the benefits of Adderall are maximized.
However, the extent of these improvements varies from person to person, and not all aspects of ADHD-related behavior may be addressed by the medication. Continuous evaluation is important to ensure that the benefits of Adderall are maximized.
“
Source Quotes:
Stimulant medications have been shown to offer symptomatic improvement in attention and on-task behaviors, as well as improvement in daily functioning in adults.
Treatment with stimulants also improves caregiver-child interactions, aggressive behavior, and academic productivity and accuracy.
Background: Behavioral Side Effects of Adderall
While Adderall is effective in controlling impulsivity, it can also cause behavioral side effects such as restlessness, irritability, and aggression. These side effects are more likely to occur when starting treatment or when the dosage is increased.
Patients and caregivers should monitor for these changes, especially during the early stages of treatment, and report any significant behavioral shifts to their healthcare provider. Proper management and adjustment of the dosage can help mitigate these side effects.
Patients and caregivers should monitor for these changes, especially during the early stages of treatment, and report any significant behavioral shifts to their healthcare provider. Proper management and adjustment of the dosage can help mitigate these side effects.
“
Source Quotes:
If you take too much dextroamphetamine and amphetamine, you may experience unusual changes in your behavior, such as restlessness, irritability, hostility, and aggression.
Amphetamines produce a wide range of dose-dependent behavioral changes, including increased arousal, hyperactivity, and, in particular, a state of pleasurable affect, elation, and euphoria.
Background: Long-Term Behavioral Monitoring
Adderall's effects on behavior, including impulsivity and aggression, should be regularly monitored, especially during long-term use. While the medication can be highly effective, there is limited data on its effects over extended periods.
Healthcare providers should periodically reevaluate the treatment to ensure it remains beneficial and to manage any emerging behavioral side effects. This is crucial for maintaining both the efficacy and safety of the treatment.
Healthcare providers should periodically reevaluate the treatment to ensure it remains beneficial and to manage any emerging behavioral side effects. This is crucial for maintaining both the efficacy and safety of the treatment.
“
Source Quotes:
The effectiveness of Adderall® for long-term use has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials. Therefore, the physician who elects to use Adderall® for extended periods should periodically reevaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
Although most adult patients also use amphetamines effectively and safely, occasional case reports indicate that prescription use can produce marked psychological adverse events, including stimulant-induced psychosis.
Background: Adderall and Aggressive Behaviors
Some individuals taking Adderall may experience an increase in aggressive behaviors or hostility, though this is not common. Such side effects can be distressing and should be closely monitored.
Healthcare providers often recommend regular check-ins to observe any signs of increased aggression, especially during the early stages of treatment or after dose adjustments. Addressing these side effects promptly can help in managing the treatment effectively.
Healthcare providers often recommend regular check-ins to observe any signs of increased aggression, especially during the early stages of treatment or after dose adjustments. Addressing these side effects promptly can help in managing the treatment effectively.
“
Source Quotes:
Aggressive behavior or hostility has been reported in clinical trials and postmarketing experience with some ADHD medications.
Occasional case reports indicate that prescription use of amphetamines can produce marked psychological adverse events, including stimulant-induced psychosis.
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Adderall's Impact on Impulsivity and Behavioral Control in ADHD
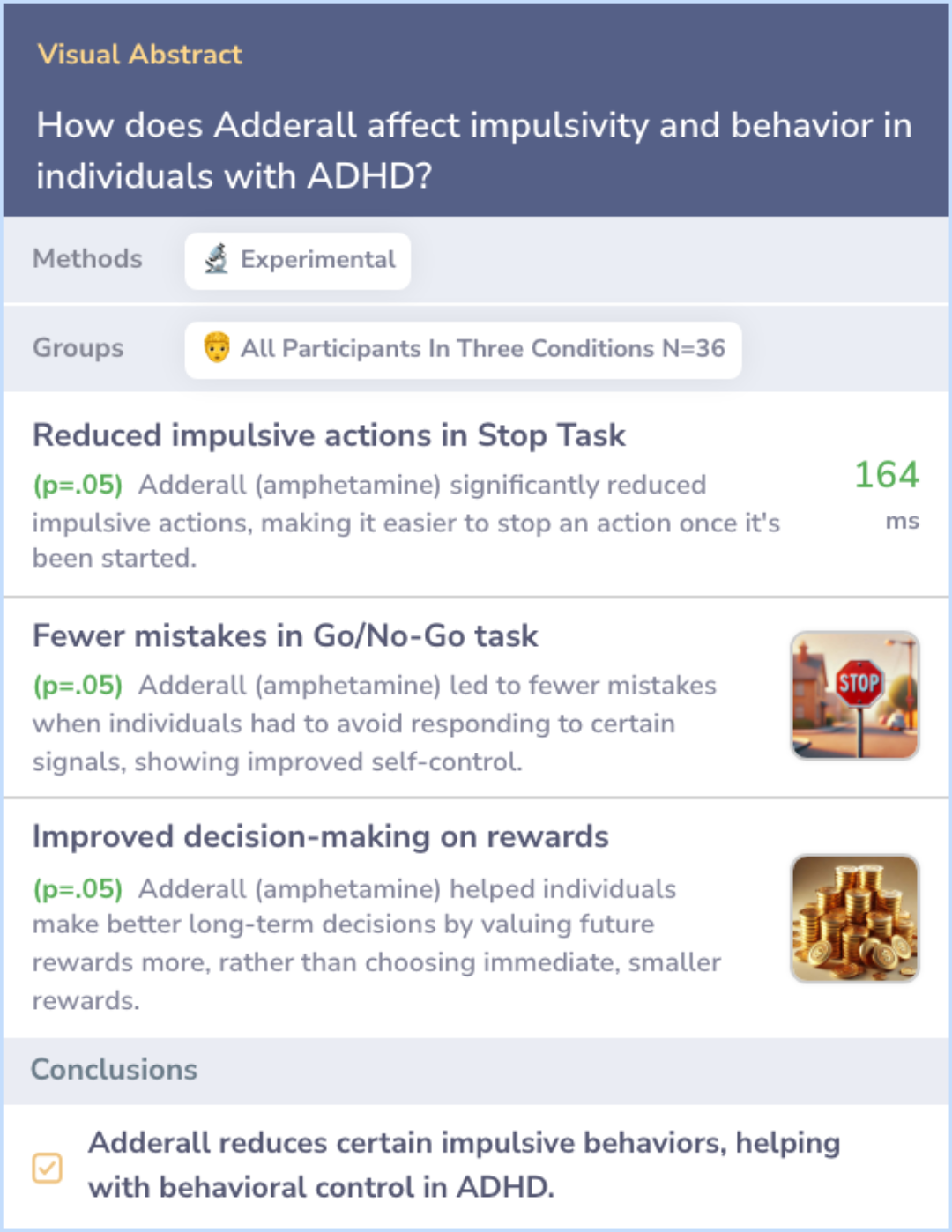
This study examined the immediate effects of Adderall (d-amphetamine) on different aspects of impulsivity. Impulsivity refers to difficulties in controlling inappropriate actions, waiting for rewards, or being less sensitive to delayed consequences. The research tested 36 participants using five tasks designed to measure these behaviors after taking different doses of Adderall or a placebo.
The results showed that Adderall decreased impulsive behavior on several tasks. It improved the ability to stop actions in the Stop Task, reduced errors in the Go/No-Go task, and lowered the tendency to favor immediate rewards in the delay discounting task. However, other measures of impulsivity were not affected.
The results showed that Adderall decreased impulsive behavior on several tasks. It improved the ability to stop actions in the Stop Task, reduced errors in the Go/No-Go task, and lowered the tendency to favor immediate rewards in the delay discounting task. However, other measures of impulsivity were not affected.
author
de Wit H, Enggasser JL, Richards JB
journal
Neuropsychopharmacology
Date Published
2002 Nov
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Impact of Adderall on Driving Performance in Adolescents with ADHD
This study examined the effects of Adderall (mixed amphetamine salts extended release) on driving performance in adolescents with ADHD. The study found that Adderall did not statistically improve driving performance compared to a placebo, particularly in areas like erratic speed control and inappropriate use of brakes. In contrast, another stimulant, OROS methylphenidate, showed significant improvements in driving behaviors.
The study suggests that while both medications are used to manage ADHD symptoms, Adderall may not be as effective in reducing impulsive driving behaviors.
The study suggests that while both medications are used to manage ADHD symptoms, Adderall may not be as effective in reducing impulsive driving behaviors.
author
Cox DJ, Merkel RL, Moore M, Thorndike F, Muller C, Kovatchev B
journal
Pediatrics
Date Published
2006 Sep
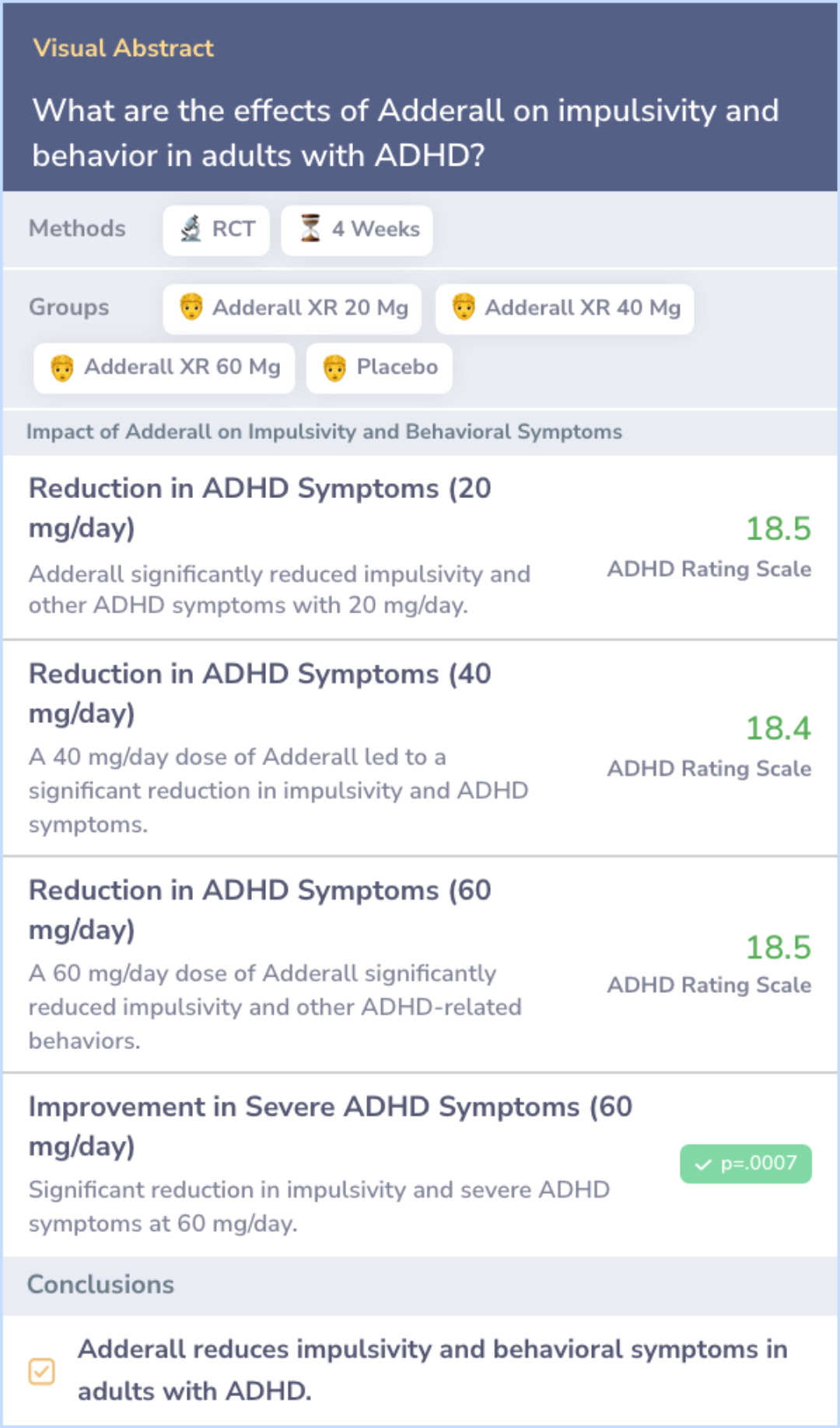
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Adderall Significantly Reduces ADHD Symptoms in Adults, Lasting Up to 12 Hours
This study assessed the effects of Adderall (MAS XR) on adults with ADHD over 4 weeks. Participants received varying doses of Adderall or a placebo. The main measures were the ADHD Rating Scale and CAARS-S-S.
Adderall led to significant reductions in ADHD symptoms, with improvements noticeable within the first week. The effects lasted up to 12 hours after dosing, with the highest dose showing the greatest improvement in those with severe symptoms.
Adderall led to significant reductions in ADHD symptoms, with improvements noticeable within the first week. The effects lasted up to 12 hours after dosing, with the highest dose showing the greatest improvement in those with severe symptoms.
author
Weisler RH, Biederman J, Spencer TJ, Wilens TE, Faraone SV, Chrisman AK, Read SC, Tulloch SJ
journal
CNS Spectr.
Date Published
2006 Aug
Key Takeaways
Conclusions
Research highlights that Adderall targets neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which are fundamental in managing impulsivity in those with ADHD.
While studies underline its role in alleviating impulsive actions, they also note possible behavioral side effects, such as increased irritability and aggression during treatment initiation.
While studies underline its role in alleviating impulsive actions, they also note possible behavioral side effects, such as increased irritability and aggression during treatment initiation.

Evidence Summary
Adderall's Varied Impact on ADHD Behavior
Adderall plays a notable role in reducing impulsivity, enhancing focus, and improving daily functioning in those with ADHD. While helping at work or school and fostering better relationships, the effects vary from person to person. Some may experience behavioral side effects such as restlessness or irritability, especially at the start or with dosage increases. Monitoring and management help mitigate these effects.
Evidence Summary
Exploring Impulsivity Dimensions in Adults with ADHD
ADHD isn't just about hyperactivity—impulsivity remains a challenge for many adults. This study explores three types of impulsivity: attentional, non-planning, and motor, all of which affect daily life. Adults with ADHD show heightened impulsivity across these areas, using both self-reports and neuropsychological assessments. Together, these tools provide a comprehensive look at how impulsivity manifests and differs in those with ADHD compared to healthy peers.
Evidence Summary
Exploring Impulsivity Variants in ADHD
The analysis delves into how impulsivity, a core feature of ADHD, varies between those with the disorder and their peers. Impulsivity isn't one-dimensional; it's split into rapid-response impulsivity and reward-delay impulsivity.
The study found that children with ADHD show a moderate increase in impulsive decisions, underscoring notable differences in decision-making. Patterns for tasks requiring delay of gratification and discounting were consistent within ADHD groups compared to others.
The study found that children with ADHD show a moderate increase in impulsive decisions, underscoring notable differences in decision-making. Patterns for tasks requiring delay of gratification and discounting were consistent within ADHD groups compared to others.