Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Efficacy of sertraline in a 12-week trial for generalized anxiety disorder
Sertraline for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
November 25, 2024
author
Allgulander C, Dahl AA, Austin C, Morris PL, Sogaard JA, Fayyad R, Kutcher SP, Clary CM
journal
Am J Psychiatry
Date Published
2004 Sep
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
Sertraline's efficacy and tolerability in treating generalized anxiety disorder.
💡
What They Found
Sertraline resulted in significantly greater improvement in anxiety symptoms than a placebo, with more patients responding positively to sertraline and few adverse events reported.
📚
What This Means
This study reinforces current guidelines, which suggest using medications like SSRIs, including sertraline (Zoloft), as part of treatment for generalized anxiety disorder.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study focused on evaluating how well sertraline, a common antidepressant, could treat both mental and physical symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder. Researchers wanted to see if it could improve not just emotional well-being but also physical discomfort related to anxiety. The findings show that sertraline has potential benefits for both aspects of this condition.
Notably, sertraline's ability to improve life quality alongside anxiety suggests it could be a valuable option for those dealing with this disorder.
Notably, sertraline's ability to improve life quality alongside anxiety suggests it could be a valuable option for those dealing with this disorder.
Abstract: background
Sertraline's efficacy and tolerability in treating generalized anxiety disorder were evaluated.

Study Focus
"The study aimed to test sertraline for efficacy in both psychic and somatic symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder."
Insights from the Study
"The current study provides significant insights into how sertraline may address both the psychic and somatic symptoms of anxiety, adding to the growing body of evidence supporting its use in a broad range of anxiety disorders."
Quality of Life Improvement
"Improvement in symptom measures was associated with significantly greater improvement in quality of life and functional outcomes for sertraline than for placebo."
Study Summary
Methods
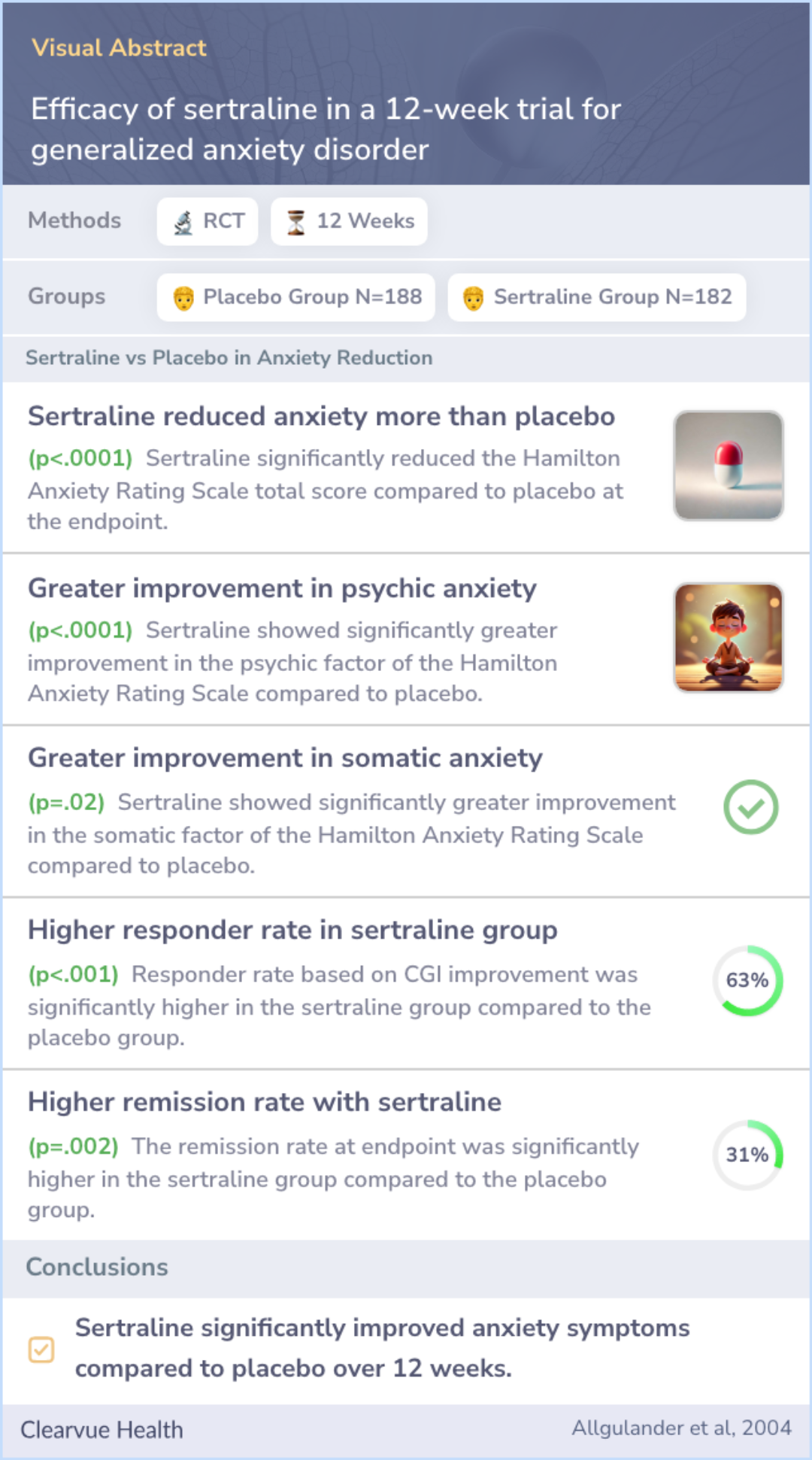
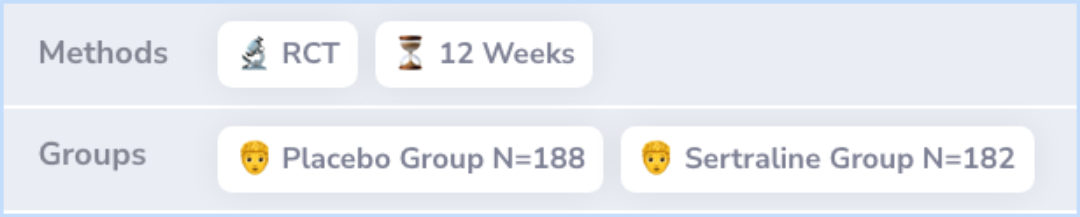
The research included adult patients diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder using DSM-IV criteria. Participants started with a placebo for one week and then were randomly given either sertraline (Zoloft) or a placebo for 12 weeks.
The doses of sertraline varied from 50-150 mg a day. Patients' anxiety levels were measured using a tool called the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale, with improvement being gauged by changes in these scores over the study period.
The doses of sertraline varied from 50-150 mg a day. Patients' anxiety levels were measured using a tool called the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale, with improvement being gauged by changes in these scores over the study period.
Abstract: methods
Adult outpatients with DSM-IV generalized anxiety disorder and a total score of 18 or higher on the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale were eligible. After a 1-week single-blind placebo lead-in, patients were randomly assigned to 12 weeks of double-blind ...more
Study Summary
Results
Patients taking sertraline showed more improvement in their anxiety symptoms by week 4 compared to those on placebo. The analysis indicated a substantial reduction in anxiety based on the total score on the Hamilton Anxiety scale.
By the study’s end, 63% of the sertraline group responded positively to treatment, edging out the 37% response rate in the placebo group. Sertraline's tolerability was similar to the placebo, with few people discontinuing due to side effects.
By the study’s end, 63% of the sertraline group responded positively to treatment, edging out the 37% response rate in the placebo group. Sertraline's tolerability was similar to the placebo, with few people discontinuing due to side effects.
Abstract: results
Sertraline patients had significantly greater improvement than placebo patients on all efficacy measures at week 4. Analysis of covariance of the intent-to-treat group at endpoint (with the last observation carried forward) showed a significant diffe...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
Sertraline, or Zoloft, appears effective in reducing symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder, with a notable improvement over placebo.
The medication is also well tolerated, making it a viable option for individuals suffering from this condition, potentially enhancing their quality of life.
The medication is also well tolerated, making it a viable option for individuals suffering from this condition, potentially enhancing their quality of life.
Abstract: conclusions
Sertraline appears to be efficacious and well tolerated in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder.
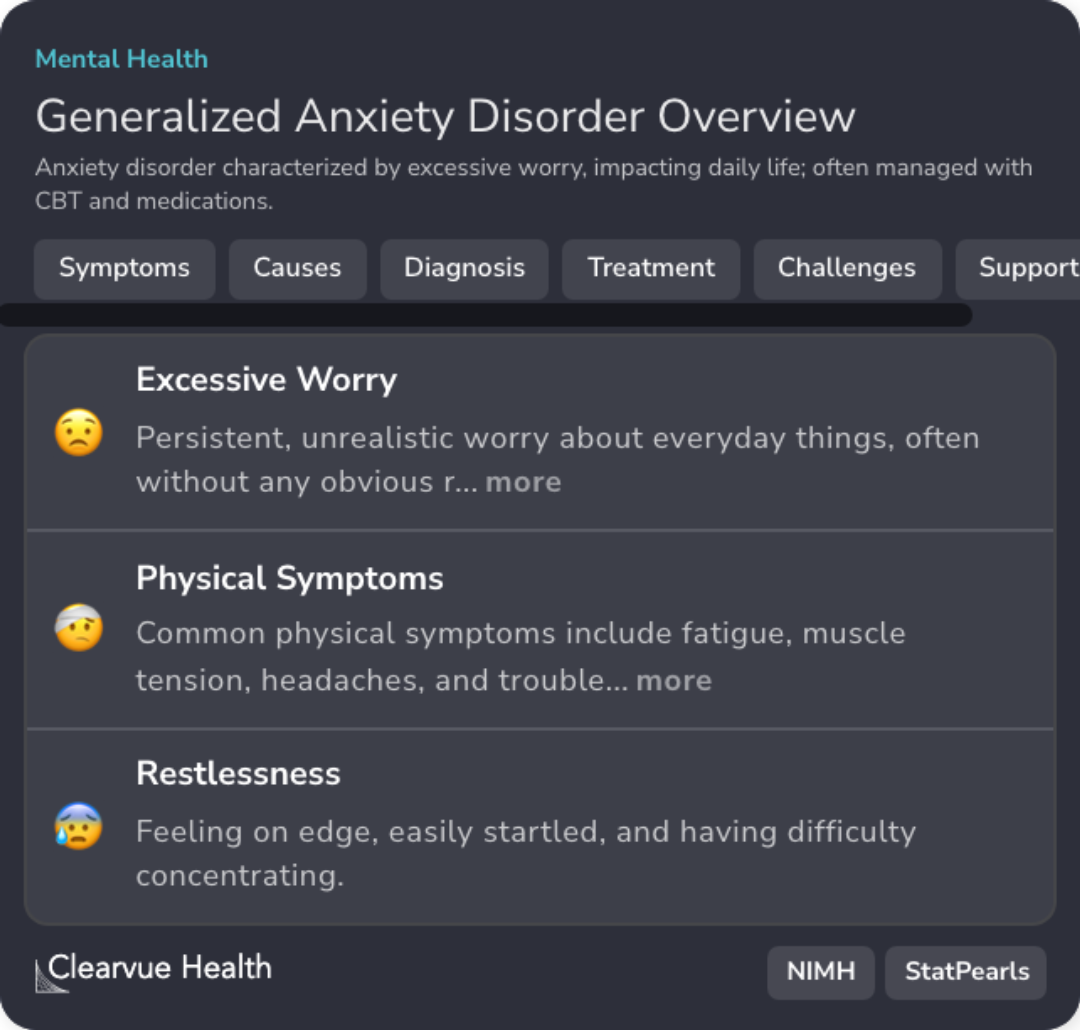
Background Information
Patient Guide
😟
Prevalence and Management of GAD
GAD involves excessive worry affecting daily life, typically managed with therapy and medications.
🧠
Biological Underpinnings
Genetic predisposition and neurotransmitter imbalances, such as serotonin, play a role in GAD.
💊
Treatment Approaches
SSRIs like sertraline are commonly used, often in combination with therapy, for effective management.
📅
Diagnosis Criteria
DSM-5 outlines anxiety and worry occurring more days than not for 6 months as GAD.
🔗
Challenges in GAD Treatment
Patients face medication compliance issues and comorbid conditions complicating treatment.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Sertraline for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
The study highlights the efficacy of sertraline, aligning with guidelines that emphasize SSRIs and SNRIs as preferred treatments for generalized anxiety disorder.
Clinical evidence indicates SSRIs maintain effectiveness and demonstrate superior anxiety reduction compared to placebo over time.
Initiating treatment at a low dose is advised to minimize initial side effects, ensuring continued patient adherence and quality of life.
Clinical evidence indicates SSRIs maintain effectiveness and demonstrate superior anxiety reduction compared to placebo over time.
Initiating treatment at a low dose is advised to minimize initial side effects, ensuring continued patient adherence and quality of life.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Treatments for Reducing Anxiety
This page reviews studies comparing different treatments for generalized anxiety disorder. It analyzes data to see which methods are most effective at reducing anxiety symptoms.
The focus is on identifying which treatments consistently show better outcomes in reducing anxiety across various studies, helping to clarify their effectiveness in real-world applications.
The focus is on identifying which treatments consistently show better outcomes in reducing anxiety across various studies, helping to clarify their effectiveness in real-world applications.
Evidence Summary
Effectiveness and Safety of Medications for GAD
This overview highlights the effectiveness and safety of medications used to manage Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). It compares different drug treatments based on clinical evidence and expert guidelines. The insights focus on how these medications perform in reducing symptoms of GAD and their associated safety profiles.
The review emphasizes the importance of clinical trials in guiding treatment decisions, reflecting current expert consensus on medication use for GAD.
The review emphasizes the importance of clinical trials in guiding treatment decisions, reflecting current expert consensus on medication use for GAD.
Evidence Summary
CBT vs. Applied Relaxation: Different Approaches to Anxiety Treatment
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Applied Relaxation both target anxiety symptoms, but they approach treatment differently. CBT works by changing the negative thoughts and behaviors that fuel anxiety, aiming to modify how individuals respond to stress.
Applied Relaxation focuses on teaching techniques for muscle relaxation, helping individuals reduce physical tension, which can alleviate anxiety symptoms over time.
Applied Relaxation focuses on teaching techniques for muscle relaxation, helping individuals reduce physical tension, which can alleviate anxiety symptoms over time.