Psoriasis
Evidence Based Answers
Psoriasis Treatment Options
Psoriasis treatments include topical lotions for mild conditions, specially-targeted light therapy, and systemic approaches for severe cases. Combining different therapies often improves results by targeting symptoms more efficiently.

Different therapies, from topical to systemic, offer tailored strategies for psoriasis.
Starting with Topical Treatments for Psoriasis
Topical treatments are often the initial choice for managing psoriasis, especially when the condition affects a small portion of the skin. These treatments include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and other agents.
Topical therapies are generally easy to use at home and have fewer side effects compared to systemic treatments. The effectiveness of these therapies depends significantly on patient adherence and the form of the medication, which should align with the patient's habits and preferences.
Topical therapies are generally easy to use at home and have fewer side effects compared to systemic treatments. The effectiveness of these therapies depends significantly on patient adherence and the form of the medication, which should align with the patient's habits and preferences.
“
Source Quotes:
For most patients with a limited degree of skin involvement, topical therapy is our preferred initial mode of therapy.
The efficacy of topical therapy depends on adherence to the treatment regimen. Patient involvement and clinician understanding of patient preferences and habits are essential for appropriate vehicle selection.
Exploring Systemic and Phototherapy Options
When topical therapies are not enough, phototherapy and systemic treatments are considered. Phototherapy, like narrowband ultraviolet B (NBUVB) therapy, uses UV light to treat larger skin areas.
Systemic treatments, such as biologics or oral medications like methotrexate, are used for more severe cases. These options are chosen based on the extent of psoriasis and the patient’s condition, but they may involve more significant side effects.
Systemic treatments, such as biologics or oral medications like methotrexate, are used for more severe cases. These options are chosen based on the extent of psoriasis and the patient’s condition, but they may involve more significant side effects.
“
Source Quotes:
Phototherapy and systemic therapy are generally considered when the response to topical therapy is inadequate.
Biologic agents include the most effective therapies for chronic plaque psoriasis that cannot be managed with topical therapy.
Benefits of Combination Therapy for Psoriasis
Combination therapy, which involves using more than one treatment approach, can sometimes be more effective than using a single therapy. For instance, combining topical corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs may provide better results.
In more severe cases, combining topical therapies with systemic or phototherapy can manage larger areas or more persistent symptoms. This approach requires careful planning to reduce side effects and ensure patients stick to their treatment.
In more severe cases, combining topical therapies with systemic or phototherapy can manage larger areas or more persistent symptoms. This approach requires careful planning to reduce side effects and ensure patients stick to their treatment.
“
Source Quotes:
Use of more than one mode of therapy to achieve optimal results may be necessary. Often, patients treated with systemic therapy or phototherapy use topical therapy as adjunctive therapy.
Combination therapy with a topical corticosteroid and topical vitamin D analog can be more effective than topical corticosteroid monotherapy.
The Role of Patient Education in Psoriasis Treatment
Patient education plays a significant role in psoriasis treatment. It helps patients understand their condition, the treatment options available, and how to properly use their prescribed therapies.
Educating patients about treatment application, expected outcomes, and potential side effects supports better adherence to the regimen and allows them to communicate effectively with their healthcare providers.
Educating patients about treatment application, expected outcomes, and potential side effects supports better adherence to the regimen and allows them to communicate effectively with their healthcare providers.
“
Source Quotes:
Patient education and counseling are important components of management. The clinician should aim to understand patient concerns; adequately answer questions; and optimize the patient's understanding of the disease and treatment options, expectations, and risks.
Patient education — Careful review of the application regimen, expected outcomes, potential adverse effects, and patient concerns may support successful use of topical therapy.
Key Takeaways
Conclusions
Psoriasis treatment strategies extend beyond just applying ointments, requiring a careful balance of ease and efficacy.
Starting with manageable at-home topical treatments, options expand to phototherapy and systemic treatments for widespread or severe cases.
Patient education is key to effective management, helping ensure patients adhere to the regimen while combinations of therapies offer enhanced benefits.
Starting with manageable at-home topical treatments, options expand to phototherapy and systemic treatments for widespread or severe cases.
Patient education is key to effective management, helping ensure patients adhere to the regimen while combinations of therapies offer enhanced benefits.

Literature Review
Schwarz, 2021
Study Insights:
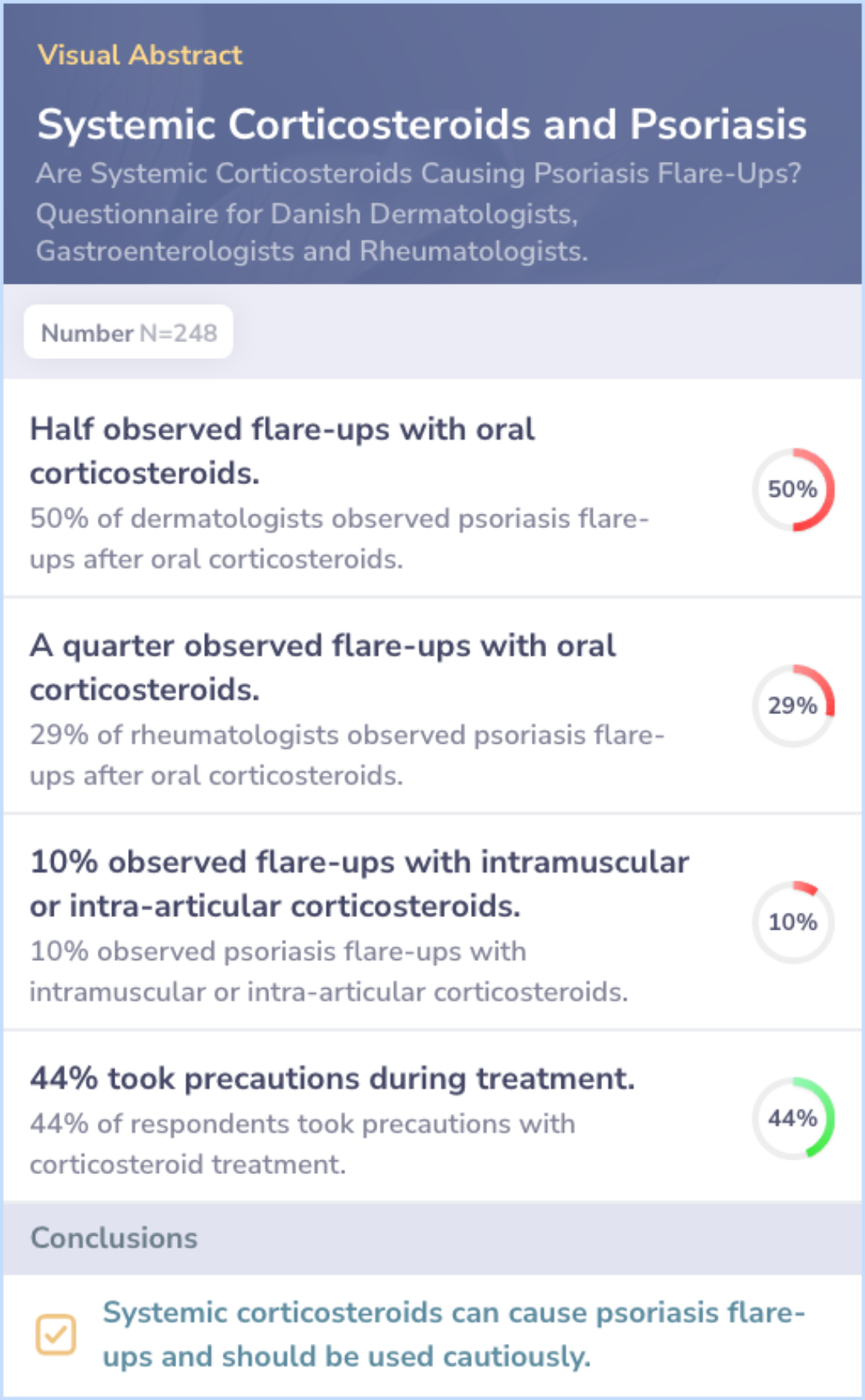
Use of corticosteroids in psoriasis: Systemic corticosteroids often prescribed despite risks.
Observations of flare-ups: 50% of dermatologists and 29% of rheumatologists noted flare-ups after oral use.
Precautions taken: 44% of physicians took precautions during treatment.
Most common use:Intra-articular corticosteroids most used but only by rheumatologists.
Literature Review
Lv, 2018
Treatment options:
Five classes of therapies: Includes anti-metabolites, anti-IL12/23, anti-IL17, anti-T-cell, and anti-TNF-α.
Efficacy findings: Anti-IL12/23 and anti-IL17 show excellent efficacy.
Safety concerns: Anti-IL12/23, anti-IL17, and anti-TNF-α may cause infections.

Literature Review
Festugato, 2011
Dietary Factors:
Common Foods Impacting Psoriasis: Beef, monosodium glutamate, yerba mate, black coffee, and others are frequently consumed.
Effects of Dietary Changes: 88.37% reported reduced symptoms and improved quality of life after adjusting diet.
Lack of Dietary Influence: 11.63% of patients did not observe any skin changes after dietary modifications.
Diet and Psoriasis Management:Patients with psoriasis should be informed about diet's role alongside medical treatment for improved outcomes.
