Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Problem solving and problem orientation in generalized anxiety disorder
Problem solving and orientation in GAD
November 25, 2024
author
Ladouceur R, Blais F, Freeston MH, Dugas MJ
journal
J Anxiety Disord
Date Published
1998 Mar-Apr
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original

Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study focused on whether problem orientation and problem-solving skills differ based on GAD symptom level or clinical status.
💡
What They Found
Researchers found that problem orientation, intolerance of uncertainty, and beliefs about worry showed differences between moderate worriers and individuals meeting GAD criteria, while problem-solving skills were unaffected by GAD symptom level or clinical status.
📚
What This Means
The findings suggest that problem orientation and certain cognitive variables are more influenced by GAD symptom level than clinical status, aligning with the understanding that anxiety management involves cognitive aspects.
Study Summary
Study Overview
Researchers want to understand how excessive worry affects problem-solving skills, especially with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). They found that people with GAD struggle with problem orientation, which affects their ability to apply what they know about problem-solving. Interestingly, the study shows that even though knowledge of problem-solving skills remains constant, how we feel about our ability to solve problems can differ greatly based on worry levels.
This highlights how feelings of control and confidence in problem-solving can vary among individuals dealing with anxiety, shedding light on the complexities of dealing with worry.
This highlights how feelings of control and confidence in problem-solving can vary among individuals dealing with anxiety, shedding light on the complexities of dealing with worry.
Abstract: background
The present study's main objective is to examine whether problem orientation and problem-solving skills differ according to generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) symptom level or clinical status (seeking help for GAD). Its secondary goal is to examine w...more

Cognitive Challenges of GAD
"According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is characterized by excessive and uncontrollable worry."
Problem Orientation and GAD
"For both nonclinical individuals meeting GAD criteria and GAD patients, poor problem orientation may hinder the proper application of problem-solving skills, thereby interfering with the problem-solving process and prolonging worry."
Intolerance of Uncertainty
"Our clinical experience also supports the relevance of intolerance of uncertainty in poor problem orientation, as GAD patients often struggle with the ambiguous or uncertain elements of the problem situation as well as the problem-solving process and its outcome."
Study Summary
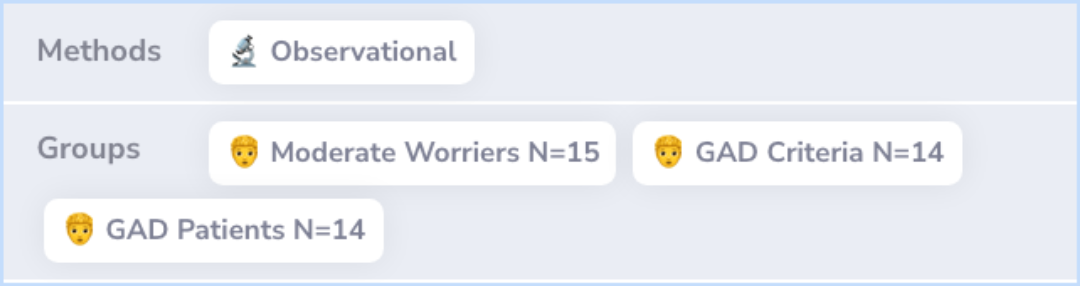
Methods
Researchers formed three groups: moderate worriers who haven't sought treatment, those meeting anxiety disorder criteria through surveys, and diagnosed patients.
They used questionnaires to measure problem-solving and psychological elements like dealing with uncertainty. This approach provides a clear view of how anxiety impacts problem-solving from different angles.
They used questionnaires to measure problem-solving and psychological elements like dealing with uncertainty. This approach provides a clear view of how anxiety impacts problem-solving from different angles.
Abstract: methods
Three groups of subjects participated in the study: (a) nonclinical moderate worriers (N = 15), (b) nonclinical subjects meeting GAD criteria by questionnaire (N = 14), and (c) GAD patients (N = 14). Problem orientation and problem-solving skills wer...more
Study Summary
Results
Findings reveal that surveyed individuals and diagnosed anxiety patients share similar traits regarding worry and uncertainty, unlike moderate worriers who differ. This suggests that anxiety symptoms impact these aspects more than seeking treatment does.
Contrarily, people’s knowledge of problem-solving didn't tie to their anxiety levels or treatment need, hinting that anxiety doesn't necessarily impair their problem-solving understanding.
Contrarily, people’s knowledge of problem-solving didn't tie to their anxiety levels or treatment need, hinting that anxiety doesn't necessarily impair their problem-solving understanding.
Abstract: results
The results show that problem orientation, intolerance of uncertainty, and beliefs about worry were similar in subjects meeting GAD criteria by questionnaire and GAD patients, whereas moderate worriers had different scores on these variables. Thus, t...more


Study Summary
Conclusions
The study's outcomes have significant implications both theoretically and clinically. They propose that therapeutic strategies could target specific aspects of anxiety, like worry and uncertainty, rather than focusing solely on enhancing problem-solving skills.
Understanding these differences can help therapists tailor treatments for individuals with varying anxiety symptoms.
Understanding these differences can help therapists tailor treatments for individuals with varying anxiety symptoms.
Abstract: conclusions
The findings are discussed in terms of their theoretical and clinical implications.

Background Information
Patient Guide
😟
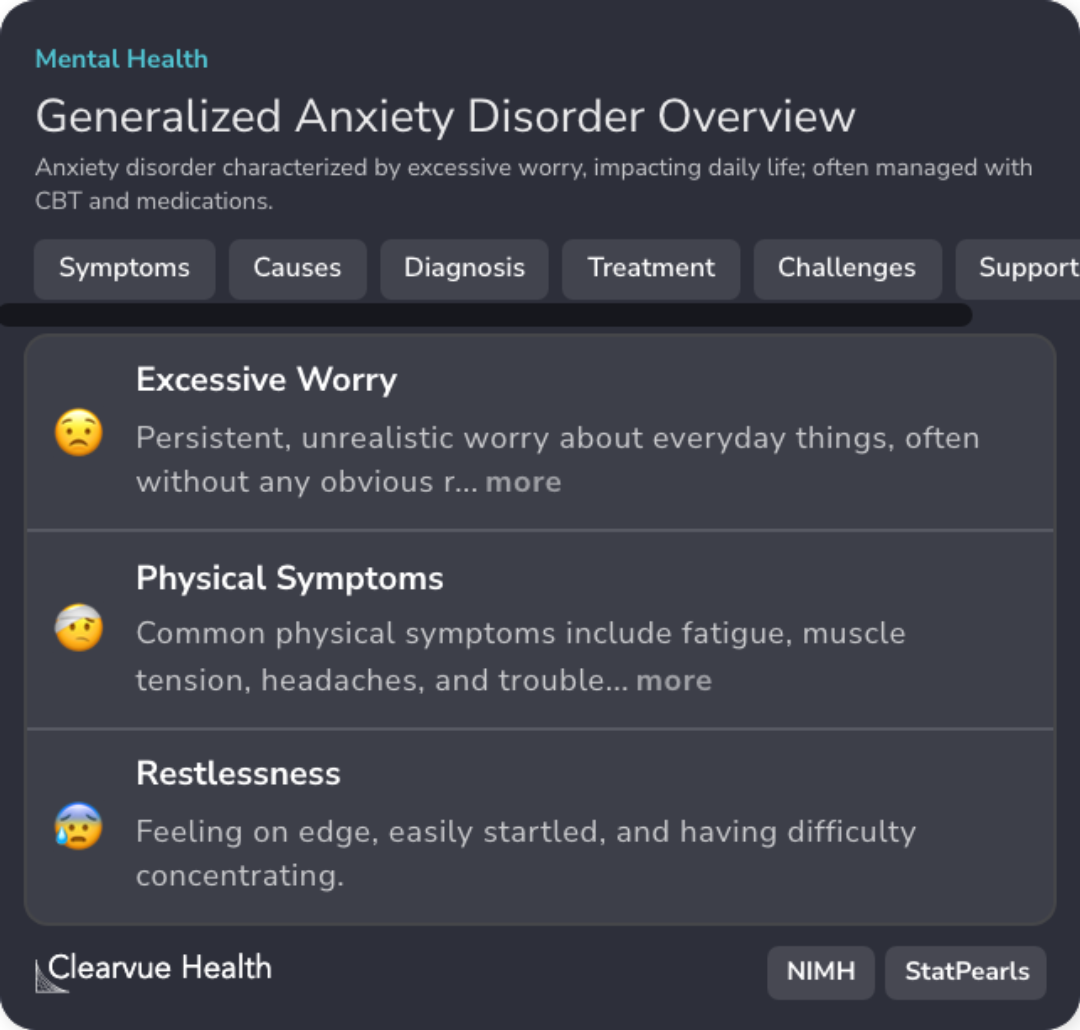
Excessive Worry in GAD
Persistent, unrealistic worry impacts daily life in those with GAD, integral to problem orientation.
💭
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for GAD
CBT focuses on changing thought patterns and reducing anxiety, relevant for addressing problem-solving skills.
🤔
Intolerance of Uncertainty
Cognitive variable often present in GAD, affecting problem-solving and decision-making processes.
📅
Diagnosis of GAD
GAD-7 tool and DSM-5 criteria evaluate excessive anxiety, foundational for understanding clinical status.
🔗
Common GAD Comorbidities
Frequently coexists with depression, complicating problem orientation and cognitive evaluations.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Problem solving and orientation in GAD
The findings suggest that GAD symptom levels significantly influence problem orientation and cognitive variables.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy for GAD addresses key symptoms like excessive worry and avoidance behaviors.
While SSRIs and SNRIs serve as first-line treatments, some patients prefer CBT due to concerns over medication side effects.
Booster CBT sessions can enhance long-term outcomes, accommodating varying symptom severities.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy for GAD addresses key symptoms like excessive worry and avoidance behaviors.
While SSRIs and SNRIs serve as first-line treatments, some patients prefer CBT due to concerns over medication side effects.
Booster CBT sessions can enhance long-term outcomes, accommodating varying symptom severities.
Evidence Summary
Understanding Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Its Management
The article focuses on Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), outlining its symptoms and effects on daily life. It reviews how worry plays a central role in the disorder, detailing both the psychological and physical aspects of living with GAD.
Additionally, it explores various treatment approaches, from therapeutic methods to practical coping strategies, providing an overview of what can help manage the disorder more effectively.
Additionally, it explores various treatment approaches, from therapeutic methods to practical coping strategies, providing an overview of what can help manage the disorder more effectively.
Evidence Summary
CBT and Mindfulness for Managing Anxiety
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps people manage generalized anxiety by targeting negative thought patterns. Integrating mindfulness techniques into therapy adds another layer of effectiveness, offering better symptom control through consistent use.
Mindfulness enhances CBT's impact by helping individuals stay grounded, which leads to improved anxiety management over time with regular practice.
Mindfulness enhances CBT's impact by helping individuals stay grounded, which leads to improved anxiety management over time with regular practice.
Evidence Summary
How CBT Techniques Reduce Anxiety Symptoms in GAD
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has various components that play a role in treating Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). This breakdown looks at specific techniques used in CBT to address anxiety and which are the most effective in reducing symptoms.
Each CBT element contributes differently, and the article highlights how some methods stand out in helping those with GAD feel relief from their symptoms.
Each CBT element contributes differently, and the article highlights how some methods stand out in helping those with GAD feel relief from their symptoms.