Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Pharmacotherapy for generalized anxiety disorder in adult and pediatric patients: an evidence-based treatment review
Pharmacotherapy for GAD: an evidence-based review
November 25, 2024
author
Strawn JR, Geracioti L, Rajdev N, Clemenza K, Levine A
journal
Expert Opin Pharmacother
Date Published
2018 Jul
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers studied which medications are effective and tolerable for treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in adults and children.
💡
What They Found
They found that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are effective first-line treatments, while other medications like benzodiazepines, buspirone, and pregabalin may be used as second-line treatments.
📚
What This Means
These findings support current guidelines that SSRIs and SNRIs are generally the best first-line treatments for GAD in adults, and emphasize the importance of psychotherapy in combination with SSRIs for children.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study focused on understanding the treatment options for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), especially in youth. It found that while SSRIs are commonly prescribed, SNRIs also show efficacy. The research emphasizes the importance of early treatment response as a predictor of long-term improvement. It suggests a need for more studies exploring various treatments, including psychotherapy, to better guide individual patient care.
Mental health professionals should be aware of the different medication options and their implications for effective GAD treatment.
Mental health professionals should be aware of the different medication options and their implications for effective GAD treatment.
Abstract: background
The authors review the literature concerning pharmacotherapy for pediatric and adult patients with GAD with specific commentary on the efficacy and tolerability of selected agents in these age groups.

Understanding Treatment Options
"This review of pharmacotherapy for GAD underscores the complexities involved in selecting the right treatment, highlighting how psychopharmacologic treatments, especially SSRIs and SNRIs, are the cornerstones, while benzodiazepines and other adjunctive medications play secondary roles depending on patient-specific considerations."
Importance of Early Response
"The literature consistently shows that early treatment response is a strong predictor of long-term remission, underscoring the importance of prompt intervention in patients with GAD."
Future Research Directions
"The study highlights that future research should prioritize head-to-head trials between different classes of medications, and studies should aim to identify predictors of treatment response to help guide patient-specific therapy selection."
Study Summary
Methods
The researchers describe a step-by-step approach to treating GAD in both children and adults. They highlight important factors to consider when prescribing medications.
Additionally, the study outlines various medications and their use for these patients, helping clinicians choose the most appropriate treatment plan.
Additionally, the study outlines various medications and their use for these patients, helping clinicians choose the most appropriate treatment plan.
Abstract: methods
The authors describe an algorithmic approach to the pediatric and adult patient with GAD and highlight considerations for the use of selected medications in these patients.

Study Summary
Results
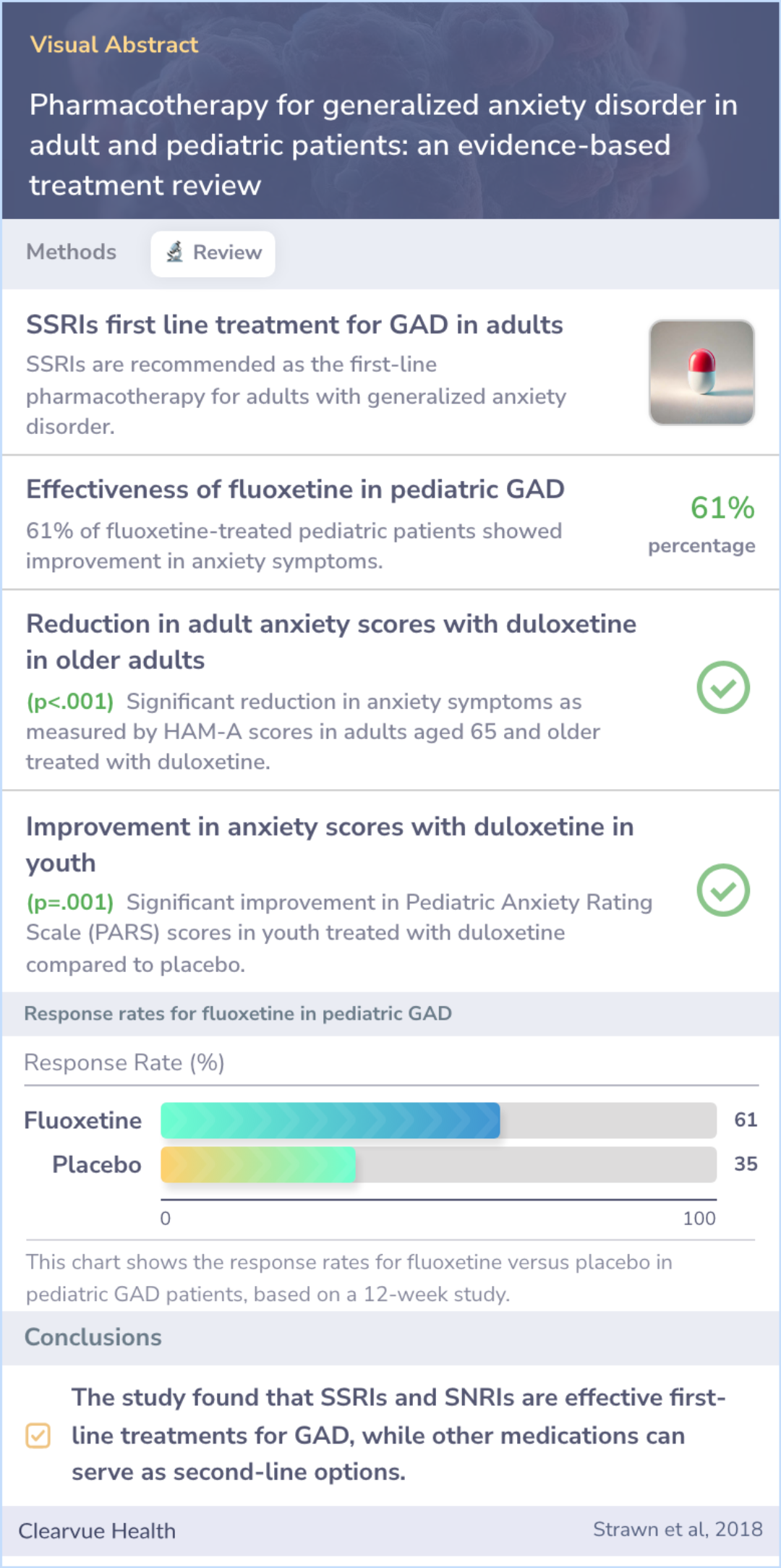
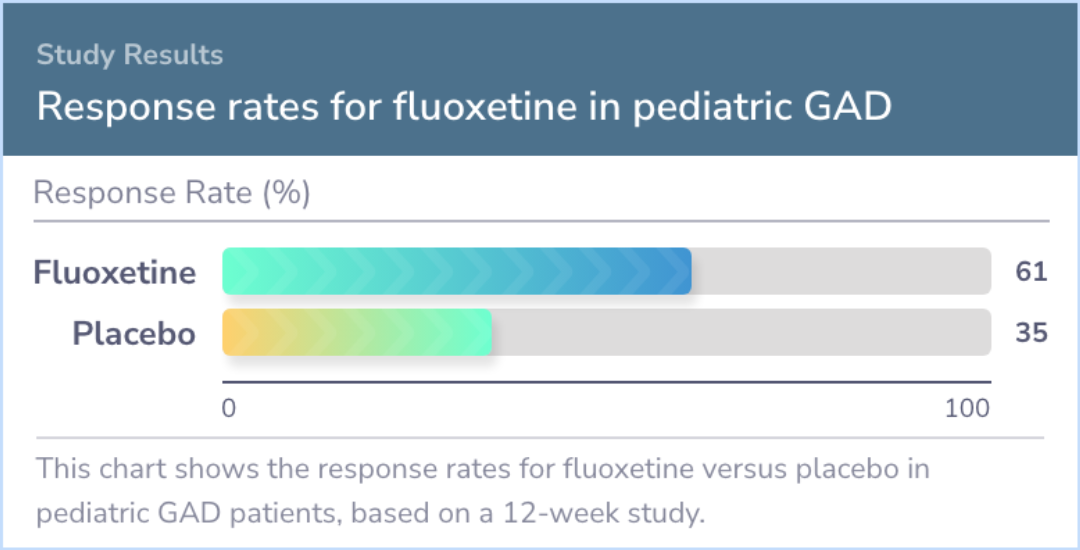
In adults with Generalized Anxiety Disorder, medications such as SSRIs (like Prozac and Zoloft) and SNRIs (like Cymbalta and Effexor) are usually the first choice. Second-line medications might include buspirone (Buspar), benzodiazepines (like Valium and Xanax), second-generation antipsychotics, and pregabalin (Lyrica).
For children with GAD, SSRIs are also recommended as the first-line treatment. Adding psychotherapy can significantly improve the response to these antidepressants.
For children with GAD, SSRIs are also recommended as the first-line treatment. Adding psychotherapy can significantly improve the response to these antidepressants.
Abstract: results
In adults with GAD, SSRIs and SNRIs represent the first-line psychopharmacologic treatment while second-line pharmacotherapies may include buspirone, benzodiazepins, SGAs and pregabalin. In pediatric patients with GAD, SSRIs should be considered the ...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
Selecting the right medication for treating GAD involves considering many factors, such as the patient's age, any other medical conditions they have, and previous treatments they’ve tried.
Clinicians need to personalize treatment plans to address these varying factors, ensuring that each patient receives the most effective and suitable care.
Clinicians need to personalize treatment plans to address these varying factors, ensuring that each patient receives the most effective and suitable care.
Abstract: conclusions
Psychopharmacologic treatment selection requires clinicians to consider multiple factors, including age, co-morbidity and prior treatment.

Background Information
Patient Guide
📅
Generalized Anxiety Disorder often begins early
GAD typically starts during adolescence or early adulthood and affects individuals throughout their life.
💊
First-line pharmacotherapy options
SSRIs and SNRIs are considered first-line treatments for adults with GAD, with SSRIs recommended for pediatric patients.
⚖️
Factors affecting treatment choice
Pharmacologic treatment selection for GAD must consider age, co-morbidities, and prior treatments.
🔗
Combined approach for optimal results
Combining psychotherapy with pharmacotherapy enhances treatment efficacy, especially in pediatric patients with GAD.
🧠
Variety of medication options
A range of medications including SSRIs, SNRIs, benzodiazepines, and melatonin analogues are used to treat GAD.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Pharmacotherapy for GAD: an evidence-based review
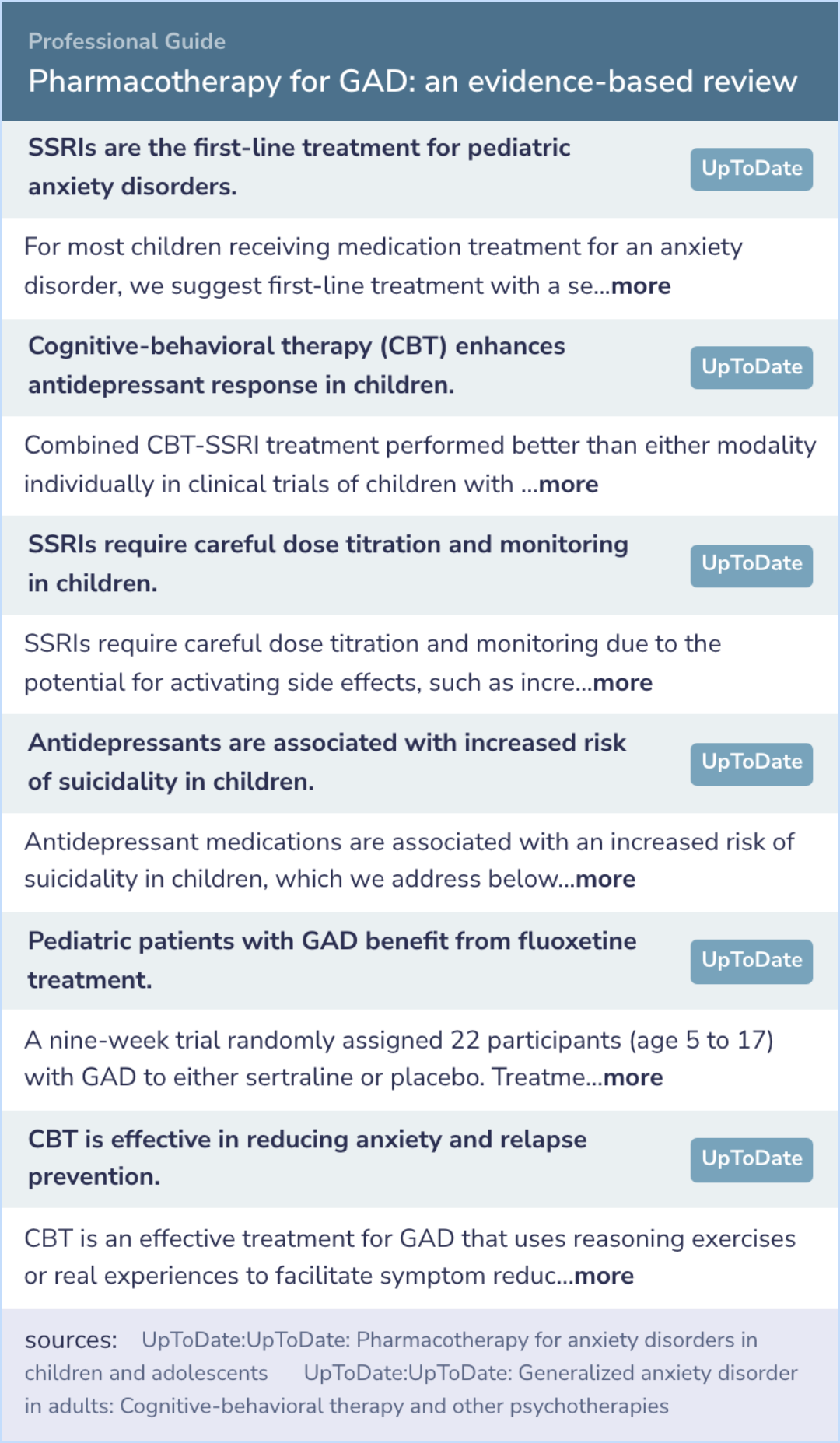
In line with the review of pharmacotherapy for pediatric and adult patients with GAD, current professional recommendations state that SSRIs are the first-line treatment for children due to their tolerability.
SNRIs, due to their side effects, are generally reserved for second or third-line use.
Interestingly, combined treatment with CBT and SSRIs displays superior efficacy to either approach alone in children.
However, SSRIs necessitate careful dose titration and monitoring because of potential side effects.
There is also an associated risk of increased suicidality in children on antidepressants, which underscores the importance of monitoring.
Additionally, studies have shown meaningful symptom reduction in children with GAD treated with fluoxetine compared to placebo, emphasizing its utility in clinical settings.
SNRIs, due to their side effects, are generally reserved for second or third-line use.
Interestingly, combined treatment with CBT and SSRIs displays superior efficacy to either approach alone in children.
However, SSRIs necessitate careful dose titration and monitoring because of potential side effects.
There is also an associated risk of increased suicidality in children on antidepressants, which underscores the importance of monitoring.
Additionally, studies have shown meaningful symptom reduction in children with GAD treated with fluoxetine compared to placebo, emphasizing its utility in clinical settings.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Treatment Effectiveness for Anxiety Relief
The slide examines various treatments for generalized anxiety disorder, highlighting how studies compare the effectiveness of different methods in reducing anxiety symptoms. It uses data to see which treatments show the most promise in symptom relief.
Studies have compared treatments, including medications, to understand which ones lead to the most significant improvements for patients dealing with anxiety symptoms.
Studies have compared treatments, including medications, to understand which ones lead to the most significant improvements for patients dealing with anxiety symptoms.
Evidence Summary
Mindfulness and Emotional Acceptance in GAD Management
Acceptance-based therapy helps people manage anxiety by focusing on mindfulness and emotional acceptance. Instead of trying to eliminate anxiety, it encourages patients to accept their thoughts and feelings.
This therapeutic approach reduces anxiety symptoms by teaching skills that help individuals live alongside their anxiety, making it easier to cope with daily challenges without avoiding emotions or sensations.
This therapeutic approach reduces anxiety symptoms by teaching skills that help individuals live alongside their anxiety, making it easier to cope with daily challenges without avoiding emotions or sensations.
Evidence Summary
Comparing CBT and Applied Relaxation for GAD
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Applied Relaxation offer two distinct approaches to treating Generalized Anxiety Disorder. CBT aims to reshape negative thought patterns and behaviors that fuel anxiety. In contrast, Applied Relaxation focuses on teaching individuals techniques to relax their muscles and reduce anxiety symptoms. Both methods target anxiety relief, but through different mechanisms.
While CBT addresses the root of anxious thinking, Applied Relaxation prioritizes physical relaxation, offering patients diverse paths to manage their symptoms.
While CBT addresses the root of anxious thinking, Applied Relaxation prioritizes physical relaxation, offering patients diverse paths to manage their symptoms.