Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Interpersonal pathoplasticity in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder
Pathoplasticity in GAD
November 25, 2024
author
Przeworski A, Newman MG, Pincus AL, Kasoff MB, Yamasaki AS, Castonguay LG, Berlin KS
journal
J Abnorm Psychol
Date Published
2011 May
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers investigated the variety of interpersonal problems in individuals with Generalized Anxiety Disorder.
💡
What They Found
The study found diverse interpersonal problems among people with GAD, forming four subtypes labeled as intrusive, exploitable, cold, and nonassertive.
📚
What This Means
These findings align with current evidence on GAD, suggesting that understanding interpersonal subtypes might influence treatment choices.
Study Summary
Study Overview
The study examined how interpersonal problems relate to Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). Researchers aimed to identify specific interpersonal subtypes and their effects on treatment. They found that interpersonal functioning is a major concern for GAD patients and can change depending on therapy types. This suggests that understanding interpersonal issues might improve treatment outcomes. The study opens doors to assessing these dimensions in GAD further.
By identifying the relationship between interpersonal behaviors and GAD, the findings may enhance treatment strategies. The focus on interpersonal subtypes also illuminates the complexities of GAD, hinting at a need for tailored therapeutic approaches that address individual interpersonal challenges.
By identifying the relationship between interpersonal behaviors and GAD, the findings may enhance treatment strategies. The focus on interpersonal subtypes also illuminates the complexities of GAD, hinting at a need for tailored therapeutic approaches that address individual interpersonal challenges.
Abstract: background
Recent theories of Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) have emphasized interpersonal and personality functioning as important aspects of the disorder.

Implications for Treatment Planning
"The presence of interpersonal subtypes in GAD may have important implications for treatment planning and efficacy."
Emphasis on Interpersonal Functioning
"Recent theories of Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) have emphasized interpersonal and personality functioning as important aspects of the disorder."
Contribution to Understanding GAD
"The current series of studies contribute to our understanding of the interplay between interpersonal behaviors and GAD and provide support for the application of the interpersonal pathoplasticity model to individuals with this diagnosis."
Study Summary
Methods
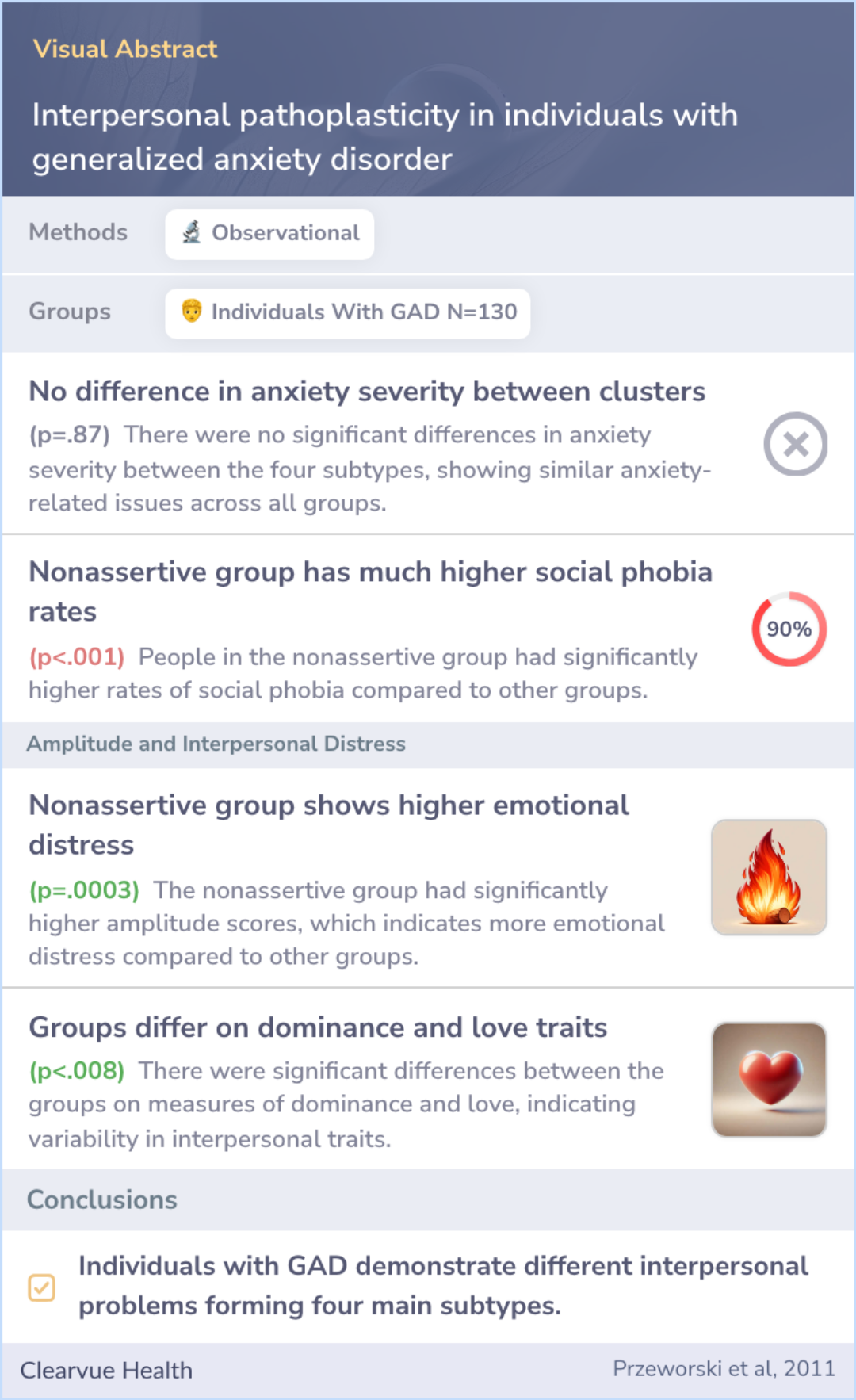
The research investigated interpersonal problems in two separate groups of individuals diagnosed with GAD, totaling 130 participants. These interpersonal issues were assessed using a tool called the Inventory of Interpersonal Problems (IIP-C), which classifies different types of social and personal difficulties.
Each group was analyzed to identify distinct interpersonal subtypes among the participants, giving insight into the various issues faced by those with GAD.
Each group was analyzed to identify distinct interpersonal subtypes among the participants, giving insight into the various issues faced by those with GAD.
Abstract: methods
The current paper examines heterogeneity in interpersonal problems in two studies of individuals with GAD (n = 47 and n = 83). Interpersonal subtypes were assessed using the Inventory of Interpersonal Problems (IIP-C; Alden, Wiggins, & Pincus, 1990).

Study Summary
Results
The findings showed that people with GAD experience a variety of interpersonal problems. The analysis revealed four main subtypes of interpersonal issues: intrusive, exploitable, cold, and nonassertive.
Importantly, these subtypes did not differ in terms of GAD severity, anxiety levels, or depression severity. However, one group of participants did show different rates of personality disorders, like avoidant personality disorder, supporting the validity of these identified subtypes.
Importantly, these subtypes did not differ in terms of GAD severity, anxiety levels, or depression severity. However, one group of participants did show different rates of personality disorders, like avoidant personality disorder, supporting the validity of these identified subtypes.
Abstract: results
Across both studies, individuals with GAD exhibited heterogeneous interpersonal problems, and cluster analyses of these patients' interpersonal characteristics yielded four replicable clusters identified as intrusive, exploitable, cold, and nonassert...more


Study Summary
Conclusions
The discovery of distinct interpersonal subtypes in people with GAD suggests that treatment approaches could be improved by considering these variations.
Recognizing these subtypes might help tailor treatment plans more effectively, potentially increasing their success in addressing the specific interpersonal issues faced by individuals with GAD.
Recognizing these subtypes might help tailor treatment plans more effectively, potentially increasing their success in addressing the specific interpersonal issues faced by individuals with GAD.
Abstract: conclusions
The presence of interpersonal subtypes in GAD may have important implications for treatment planning and efficacy.

Background Information
Patient Guide
🔄
Diverse Interpersonal Challenges in GAD
Individuals with GAD face varied interpersonal problems, affecting social interactions and relationships.
🧠
The Role of Personality in GAD
Personality functioning significantly impacts GAD, with implications on treatment and prognosis.
🔗
Complex Interplay of Comorbidities
GAD commonly coexists with conditions like avoidant personality disorder, complicating diagnosis and management.
🔍
Variation in GAD Treatment Approaches
Therapies for GAD such as CBT and medications need tailoring to address interpersonal issues.

Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Pathoplasticity in GAD
In line with the heterogeneity in interpersonal problems among individuals with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) effectively reduces GAD symptoms.
Given the diverse symptom manifestations, treatment decisions for GAD involve shared decision making to cater to individual preferences.
Patients with comorbid depressive symptoms may require pharmacotherapy before engaging in CBT.
After initiating treatment, regular follow-up is important for monitoring symptoms and adjusting care plans.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly recommended as initial pharmacotherapy.
Combining pharmacotherapy with CBT may enhance treatment outcomes.
Additionally, mindfulness practices, such as yoga, provide supplementary benefits in managing anxiety.
Given the diverse symptom manifestations, treatment decisions for GAD involve shared decision making to cater to individual preferences.
Patients with comorbid depressive symptoms may require pharmacotherapy before engaging in CBT.
After initiating treatment, regular follow-up is important for monitoring symptoms and adjusting care plans.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly recommended as initial pharmacotherapy.
Combining pharmacotherapy with CBT may enhance treatment outcomes.
Additionally, mindfulness practices, such as yoga, provide supplementary benefits in managing anxiety.
Evidence Summary
How CBT and Mindfulness Support Anxiety Management
CBT helps individuals manage their anxiety by shifting negative thought patterns that often fuel worry. Mindfulness techniques, integrated into this therapeutic approach, can enhance its effectiveness by promoting a greater sense of control over anxious thoughts and reactions.
Regular practice of these techniques has been shown to improve the ability to manage anxiety symptoms over time, offering long-term benefits for those with GAD.
Regular practice of these techniques has been shown to improve the ability to manage anxiety symptoms over time, offering long-term benefits for those with GAD.
Evidence Summary
Mindfulness for Managing GAD Symptoms
Mindfulness can help individuals with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) better regulate their emotions and reduce persistent worry. GAD involves constant, excessive anxiety, making mindfulness techniques particularly helpful in calming the mind and reducing symptoms.
By practicing mindfulness, individuals can gain more control over their emotions, ultimately managing the continuous anxiety that characterizes GAD.
By practicing mindfulness, individuals can gain more control over their emotions, ultimately managing the continuous anxiety that characterizes GAD.
Evidence Summary
Emotional Management in Anxiety and Treatment Potential
Emotion regulation is a common struggle for individuals with anxiety disorders. Difficulty managing emotions often intensifies anxiety symptoms, making it more challenging to cope.
Focusing on these emotional difficulties opens the door to more targeted approaches for alleviating anxiety. This insight aligns with broader research on tailoring treatments to the specific needs of those with anxiety-related challenges.
Focusing on these emotional difficulties opens the door to more targeted approaches for alleviating anxiety. This insight aligns with broader research on tailoring treatments to the specific needs of those with anxiety-related challenges.