Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Metacognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder: an open trial
Metacognitive therapy for GAD
November 25, 2024
author
Wells A, King P
journal
J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry
Date Published
2006 Sep
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original

Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study investigated the effectiveness of a new metacognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder.
💡
What They Found
Patients experienced significant improvements in worry, anxiety, and depression with lasting changes at 6 and 12 months after treatment.
📚
What This Means
These findings align with current methods by adding a promising new therapy option for managing GAD symptoms, showing notable improvements similar to those seen with current cognitive-behavioral therapy and medications.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to explore a new therapy for generalized anxiety disorder, focusing on how people think about their worries. The researchers believed that changing these thoughts could help those struggling. They found that when treatment concentrated on metacognitions, patients experienced noticeable relief from anxiety and worry, suggesting a fresh approach to managing these challenges.
These findings highlight that understanding the thinking patterns behind anxiety could lead to effective treatments for people who feel overwhelmed.
These findings highlight that understanding the thinking patterns behind anxiety could lead to effective treatments for people who feel overwhelmed.
Abstract: background
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) responds only modestly to existing cognitive-behavioural treatments. This study investigated a new treatment based on an empirically supported metacognitive model.

Need for Effective Treatments
"There is a need for more effective treatments for generalized anxiety disorder, given the modest outcomes observed with current approaches."
Focusing on Metacognitions
"The current findings underscore the importance of a metacognitive approach that focuses on the mechanisms underlying pathological worry, rather than the content of worry."
Impact on Worry
"A specific focus on metacognitions has a general impact across components of worry."
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers enrolled ten individuals diagnosed with GAD, based on DSM-IV criteria, to undergo the new metacognitive therapy. Researchers evaluated the patients at the start, after the therapy, and again at 6 months and 12 months to track changes.
This progression helped determine the therapy's long-term impact and effectiveness, providing a comprehensive overview of patient outcomes over time.
This progression helped determine the therapy's long-term impact and effectiveness, providing a comprehensive overview of patient outcomes over time.
Abstract: methods
Ten consecutive patients fulfilling DSM-IV criteria for GAD were assessed before and after metacognitive therapy, and at 6, and 12-month follow-up.
Study Summary
Results
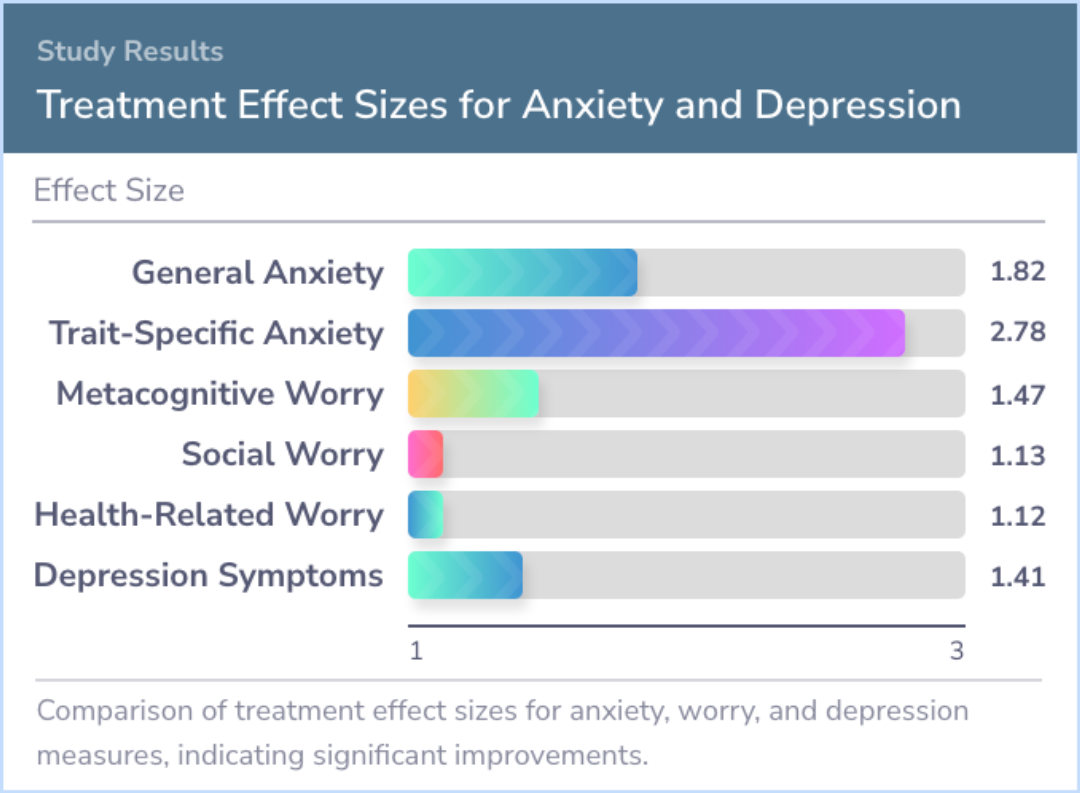
Patients showed notable improvements in levels of worry, anxiety, and depression following the treatment, with most experiencing significant relief. Importantly, these benefits persisted for nearly all participants.
Recovery was high, with 87.5% showing progress immediately post-treatment, and 75% maintaining it over the 6 to 12 months that followed, indicating lasting positive effects.
Recovery was high, with 87.5% showing progress immediately post-treatment, and 75% maintaining it over the 6 to 12 months that followed, indicating lasting positive effects.
Abstract: results
Patients were significantly improved at post-treatment, with large improvements in worry, anxiety, and depression (ESs ranging from 1.04-2.78). In all but one case these were lasting changes. Recovery rates were 87.5% at post treatment and 75% at 6 a...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
This innovative approach to GAD treatment shows promise, suggesting it could be more effective than current options. Its potential lasting benefits offer hope for individuals struggling with persistent anxiety.
Further rigorous evaluation is warranted to better establish the therapy's broad applicability and ensure it can reliably benefit a wider population.
Further rigorous evaluation is warranted to better establish the therapy's broad applicability and ensure it can reliably benefit a wider population.
Abstract: conclusions
The treatment appears promising and controlled evaluation is clearly indicated.
Background Information
Patient Guide
🌀
Suboptimal Response to Existing Treatments
Generalized anxiety disorder often shows limited improvement with current cognitive-behavioral therapy options.
🔍
Role of Metacognitive Therapy
New treatments exploring metacognitive models may offer alternative management options for generalized anxiety disorder.
😟
Characteristics of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
GAD involves persistent, unrealistic worry impacting daily activities, often managed with CBT and medications.
⚖️
Challenges in GAD Treatment
Treatment compliance issues and comorbidities with depression complicate generalized anxiety disorder management.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Metacognitive therapy for GAD
In line with the promising results of the metacognitive model for GAD, CBT proves effective when it targets specific anxious thoughts and behaviors through structured techniques.
The quality of therapist training enhances these outcomes, emphasizing the importance of expertise in treatment success.
Moreover, combining CBT with pharmacotherapy or incorporating mindfulness may augment these benefits.
Acknowledging often-overlooked physical symptoms further enriches diagnostic accuracy.
The quality of therapist training enhances these outcomes, emphasizing the importance of expertise in treatment success.
Moreover, combining CBT with pharmacotherapy or incorporating mindfulness may augment these benefits.
Acknowledging often-overlooked physical symptoms further enriches diagnostic accuracy.
Evidence Summary
Managing Anxiety: Understanding GAD Symptoms and Treatments
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is marked by persistent worry and anxiety, affecting daily life through constant unease and stress. Those with GAD may experience symptoms like restlessness, difficulty concentrating, and physical discomfort.
Various treatments and coping strategies, including therapy and lifestyle changes, can help manage these symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected by GAD.
Various treatments and coping strategies, including therapy and lifestyle changes, can help manage these symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected by GAD.
Evidence Summary
How Mindfulness-Based Therapy Eases Anxiety
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) combines meditation with therapeutic techniques to help those with Generalized Anxiety Disorder manage stress and anxiety. By emphasizing mindfulness and being present, MBCT encourages a focused awareness that can reduce anxious thoughts.
Participants learn practical skills, like breathing exercises, to better handle their symptoms, offering tools that help bring calm and control in moments of anxiety.
Participants learn practical skills, like breathing exercises, to better handle their symptoms, offering tools that help bring calm and control in moments of anxiety.
Evidence Summary
How CBT and Mindfulness Manage Anxiety
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps people with Generalized Anxiety Disorder by focusing on changing negative thought patterns, which are often linked to anxiety. This approach allows individuals to manage anxiety by reshaping their thoughts in a healthier way.
Mindfulness techniques are incorporated into CBT to enhance its effectiveness, helping people gain better control over their anxiety symptoms through consistent practice.
Mindfulness techniques are incorporated into CBT to enhance its effectiveness, helping people gain better control over their anxiety symptoms through consistent practice.
Evidence Summary
Managing Anxiety through Emotion Regulation Therapy
Emotion regulation therapy offers individuals with generalized anxiety disorder a structured way to manage and control their emotional responses. This therapy directly targets the anxiety by teaching strategies to help people stay in control of their reactions.
This approach is specifically tailored for those with GAD, addressing their unique challenges in understanding and handling emotions to help reduce anxiety levels.
This approach is specifically tailored for those with GAD, addressing their unique challenges in understanding and handling emotions to help reduce anxiety levels.