Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
A meta-analysis of the relation of intolerance of uncertainty to symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder, major depressive disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder
Meta-analysis of intolerance of uncertainty and anxiety disorders
November 25, 2024
author
Gentes EL, Ruscio AM
journal
Clin Psychol Rev
Date Published
2011 Aug
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original

Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study examined how intolerance of uncertainty (IU) is related to symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), major depressive disorder (MDD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
💡
What They Found
They found that IU is more strongly associated with GAD than with OCD according to the GAD-specific definition, while for both MDD and OCD, IU shows moderate associations using the OCD-specific definition.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that IU might be a more specific risk factor for GAD compared to OCD, aligning with current knowledge that GAD tends to involve significant worry about uncertainty.
Study Summary
Study Overview
The study explored the role of intolerance of uncertainty (IU) in anxiety and mood disorders, examining its connections to generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), major depressive disorder (MDD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). It aimed to determine whether IU could be a specific risk factor for these conditions.
Researchers found that IU might affect various emotional disorders, suggesting a need for more unified treatment approaches that consider IU's role across multiple conditions.
Researchers found that IU might affect various emotional disorders, suggesting a need for more unified treatment approaches that consider IU's role across multiple conditions.
Abstract: background
Intolerance of uncertainty (IU) has been suggested to reflect a specific risk factor for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), but there have been no systematic attempts to evaluate the specificity of IU to GAD.

Role of IU in Emotional Disorders
"Several early psychological theories proposed that the experience of uncertainty and the tendency to avoid uncertain states may play a central role in the development and maintenance of anxiety and mood psychopathology."
Shared Feature of Disorders
"Theories linking IU to multiple emotional disorders suggest that IU may constitute a shared feature for these disorders."
Implications for Treatment
"Increased knowledge of the relationship of IU to GAD and OCD, as well as to MDD, may encourage further development and utilization of transdiagnostic interventions (if shared), or help researchers and clinicians tailor interventions to the features most relevant to each disorder (if specific)."
Study Summary
Methods
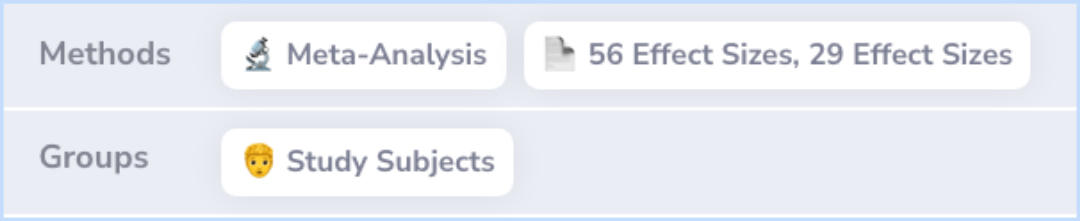
The researchers conducted a meta-analysis to investigate the relationship between IU and symptoms of GAD, MDD, and OCD. They used random effects analyses to examine two IU definitions.
One definition is commonly used in relation to GAD, while another is associated with OCD, reflecting diverse study focuses. These analyses were based on 56 and 29 effect sizes, respectively.
One definition is commonly used in relation to GAD, while another is associated with OCD, reflecting diverse study focuses. These analyses were based on 56 and 29 effect sizes, respectively.
Abstract: methods
This meta-analysis examined the cross-sectional association of IU with symptoms of GAD, major depressive disorder (MDD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Random effects analyses were conducted for two common definitions of IU, one that has pr...more
Study Summary
Results
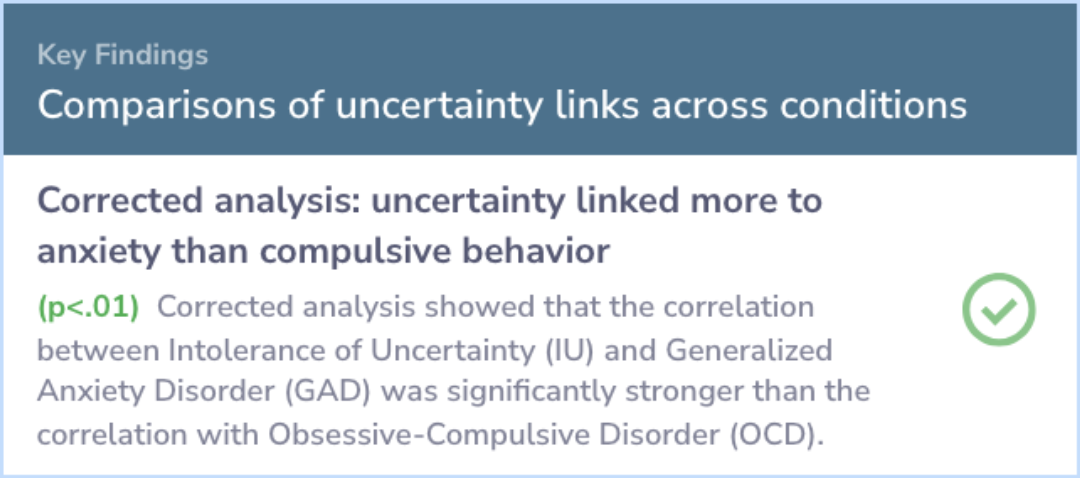
When IU was assessed through the GAD-specific lens, it correlated significantly with GAD. It showed moderate correlations with MDD and OCD as well. For the OCD-focused definition, stronger ties emerged with MDD and OCD, with no available studies for GAD.
Significance tests later confirmed that IU aligns more closely with GAD under the first definition compared to OCD. Other comparisons of IU's relationships with these disorders showed no notable differences.
Significance tests later confirmed that IU aligns more closely with GAD under the first definition compared to OCD. Other comparisons of IU's relationships with these disorders showed no notable differences.
Abstract: results
Using the definition of IU developed for GAD, IU shared a mean correlation of .57 with GAD, .53 with MDD, and .50 with OCD. Using the alternate definition developed for OCD, IU shared a mean correlation of .46 with MDD and .42 with OCD, with no studi...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
The study's results suggest specific and shared features in emotional disorders related to IU. These insights open pathways for developing more nuanced models of emotional disorders, enhancing understanding and treatment.
Such findings emphasize the importance of considering unique characteristics across disorders, paving the way for targeted research initiatives and potential interventions.
Such findings emphasize the importance of considering unique characteristics across disorders, paving the way for targeted research initiatives and potential interventions.
Abstract: conclusions
We discuss implications of these findings for models of shared and specific features of emotional disorders and for future research efforts.

Background Information
Patient Guide
🔄
Shared Symptoms Across Disorders
Mental health conditions like GAD, MDD, and OCD share symptoms, influencing diagnostic accuracy and treatment strategies.
🧩
Defining Intolerance of Uncertainty
IU is explored in mental disorders to understand its role as a potential risk factor or shared feature.
🔗
GAD's Comorbidity with Major Depression
GAD frequently coexists with depression, complicating diagnosis and management.
💭
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy's Role
CBT addresses cognitive distortions and maladaptive thought patterns in conditions like GAD and MDD.
🧬
Impact of Neurotransmitter Imbalances
Imbalances in neurotransmitter systems are associated with anxiety and depression, guiding pharmacological interventions.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Meta-analysis of intolerance of uncertainty and anxiety disorders
The examination of intolerance of uncertainty in emotional disorders underlines the importance of tailored therapeutic approaches.
Current professional recommendations state that CBT effectively addresses GAD by utilizing reasoning exercises and real experiences.
Shared decision-making emerges as a cornerstone in selecting suitable treatments, accommodating individual preferences.
Additionally, a suboptimal response to CBT may necessitate pharmacologic augmentation.
Recognizing the frequent comorbidity with major depressive disorder aids in comprehensive management.
Moreover, the link between neuroticism and GAD highlights genetic susceptibilities, informing targeted interventions.
Current professional recommendations state that CBT effectively addresses GAD by utilizing reasoning exercises and real experiences.
Shared decision-making emerges as a cornerstone in selecting suitable treatments, accommodating individual preferences.
Additionally, a suboptimal response to CBT may necessitate pharmacologic augmentation.
Recognizing the frequent comorbidity with major depressive disorder aids in comprehensive management.
Moreover, the link between neuroticism and GAD highlights genetic susceptibilities, informing targeted interventions.
Evidence Summary
How Uncertainty Complicates OCD and GAD
Difficulty with uncertainty affects how people manage OCD and GAD. For many, the inability to tolerate not knowing the future makes it harder to cope with these conditions.
This challenge complicates treatment efforts, but it also points to a pathway for improving care as research continues to explore ways to reduce this intolerance for better outcomes.
This challenge complicates treatment efforts, but it also points to a pathway for improving care as research continues to explore ways to reduce this intolerance for better outcomes.
Evidence Summary
Understanding Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Symptoms and Management
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) brings overwhelming worry and fear that can disrupt everyday life. The text highlights how this condition manifests and provides a clear overview of its symptoms and impact.
It also outlines the various treatment options available to those suffering from GAD, as well as coping strategies that can help people manage these symptoms effectively.
It also outlines the various treatment options available to those suffering from GAD, as well as coping strategies that can help people manage these symptoms effectively.
Evidence Summary
Depression and Anxiety: Strong Connections and Compounding Challenges
Depression and anxiety frequently co-occur, creating a complex interaction where symptoms are heightened, and treatment becomes more difficult. The strong connection between these conditions suggests that many individuals face both at the same time. This overlap often makes it harder to manage and can lead to worsening symptoms for those affected.
Research consistently shows this close relationship between the two, emphasizing how often depression and anxiety present together and interact in meaningful ways.
Research consistently shows this close relationship between the two, emphasizing how often depression and anxiety present together and interact in meaningful ways.