Ritalin Paper Database
Visual Abstract
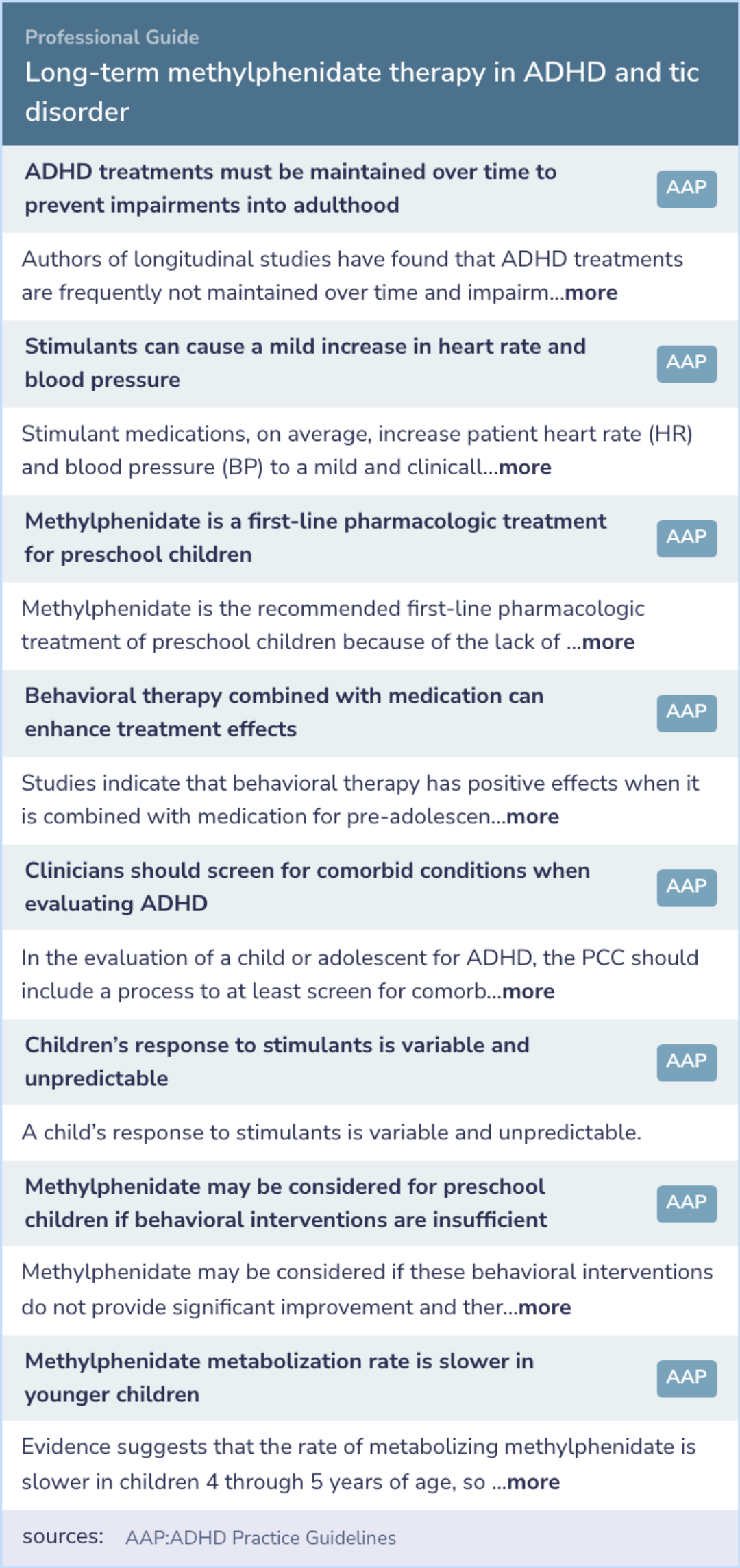
Long-term methylphenidate therapy in children with comorbid attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and chronic multiple tic disorder
Long-term methylphenidate therapy in ADHD and tic disorder
October 18, 2024
author
Gadow KD, Sverd J, Sprafkin J, Nolan EE, Grossman S
journal
Arch Gen Psychiatry
Date Published
1999 Apr
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study aimed to examine how methylphenidate (Ritalin) affects ADHD behaviors and motor and vocal tics during long-term treatment.
💡
What They Found
Researchers found that methylphenidate (Ritalin) maintained behavioral improvements without worsening tics, and did not have significant cardiovascular or growth adverse effects after two years.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that methylphenidate (Ritalin) can be a safe and effective long-term treatment for children with ADHD and mild to moderate tics, aligning with current evidence that supports its use.
Study Summary
Study Overview
A study examined how long-term treatment with a medication called methylphenidate affects children with ADHD and tic disorders.
During the study, researchers found that the frequency of motor and vocal tics did not change over time, even with ongoing treatment.
Children showed improved ADHD behaviors during a drug trial, and these gains were maintained in follow-up evaluations.
It was noted that substituting the medication with a placebo significantly worsened ADHD symptoms, while tics remained unchanged.
Overall, this research supports that methylphenidate is a safe and effective option for many children facing these challenges.
During the study, researchers found that the frequency of motor and vocal tics did not change over time, even with ongoing treatment.
Children showed improved ADHD behaviors during a drug trial, and these gains were maintained in follow-up evaluations.
It was noted that substituting the medication with a placebo significantly worsened ADHD symptoms, while tics remained unchanged.
Overall, this research supports that methylphenidate is a safe and effective option for many children facing these challenges.
Abstract: background
This study examined changes in attention-deficit hyperactivity (ADHD) behaviors and motor and vocal tics during long-term treatment with methylphenidate.

Implications of Medication
"It is now generally accepted that methylphenidate and dextroamphetamine are safe and effective treatments for ADHD in many (but not necessarily all) children with comorbid tic disorder."
Long-Term Outcomes
"Treatment gains that were experimentally demonstrated in an 8-week controlled drug trial were still present at 2-year follow-up, and were most dramatically documented in the simulated classroom setting."
Concerns Addressed
"The primary objective of the present study is to determine if long-term exposure to methylphenidate results in increased tic frequency or severity."
Study Summary
Methods
The study involved 34 children who had ADHD and a chronic multiple tic disorder. Previously, these children participated in an 8-week trial where they were randomly given either methylphenidate (Ritalin) or a placebo, without knowing which one they were receiving.
After this initial trial, the children were assessed every 6 months over a period of 2 years. Researchers watched the children in a simulated classroom setting and asked their parents and doctors to fill out behavior rating scales. The videos of the classroom sessions were reviewed by people unaware of whether the children were on medication or not, ensuring unbiased observations.
After this initial trial, the children were assessed every 6 months over a period of 2 years. Researchers watched the children in a simulated classroom setting and asked their parents and doctors to fill out behavior rating scales. The videos of the classroom sessions were reviewed by people unaware of whether the children were on medication or not, ensuring unbiased observations.
Abstract: methods
Thirty-four prepubertal children with ADHD and chronic multiple tic disorder (who had participated in an 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled methylphenidate evaluation) were evaluated at 6-month intervals for 2 years as part of a prospective, no...more
Study Summary
Results
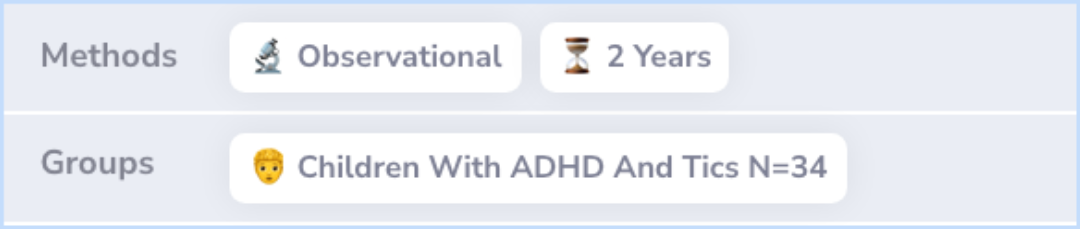
The findings indicated that there was no significant change in the frequency or severity of motor and vocal tics during the long-term use of methylphenidate (Ritalin) compared to initial evaluations. The behavioral improvements observed during the initial 8-week trial were maintained throughout the follow-up period.
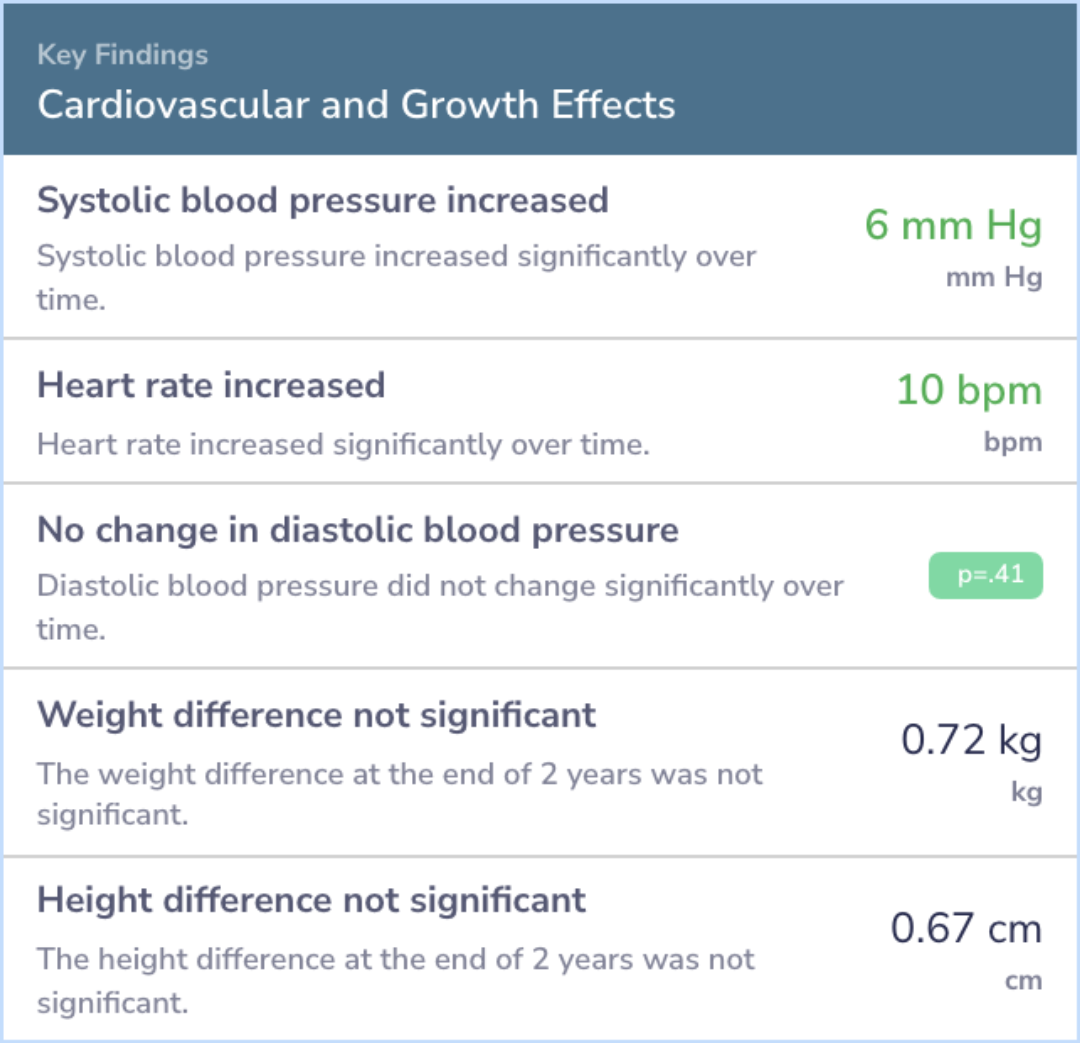
Additionally, the study did not find any clinically significant adverse effects on cardiovascular health or growth in these children over the two years of treatment. This suggests stability in physical health markers despite prolonged medication use.
Additionally, the study did not find any clinically significant adverse effects on cardiovascular health or growth in these children over the two years of treatment. This suggests stability in physical health markers despite prolonged medication use.
Abstract: results
There was no evidence (group data) that motor tics or vocal tics changed in frequency or severity during maintenance therapy compared with diagnostic or initial double-blind placebo evaluations. Behavioral improvements demonstrated during the acute d...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
The research concluded that long-term treatment with methylphenidate (Ritalin) appears to be both safe and effective for managing ADHD symptoms in children who also have mild to moderate tic disorders. However, the study emphasizes the necessity for ongoing clinical monitoring.
This is to ensure that the medication does not exacerbate tics in individual patients, despite the favorable group data outcomes. Continuous observation will help to promptly identify and manage any potential drug-induced complications.
This is to ensure that the medication does not exacerbate tics in individual patients, despite the favorable group data outcomes. Continuous observation will help to promptly identify and manage any potential drug-induced complications.
Abstract: conclusions
Long-term treatment with methylphenidate seems to be safe and effective for the management of ADHD behaviors in many (but not necessarily all) children with mild to moderate tic disorder. Nevertheless, careful clinical monitoring is mandatory to rule...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
👨⚕️
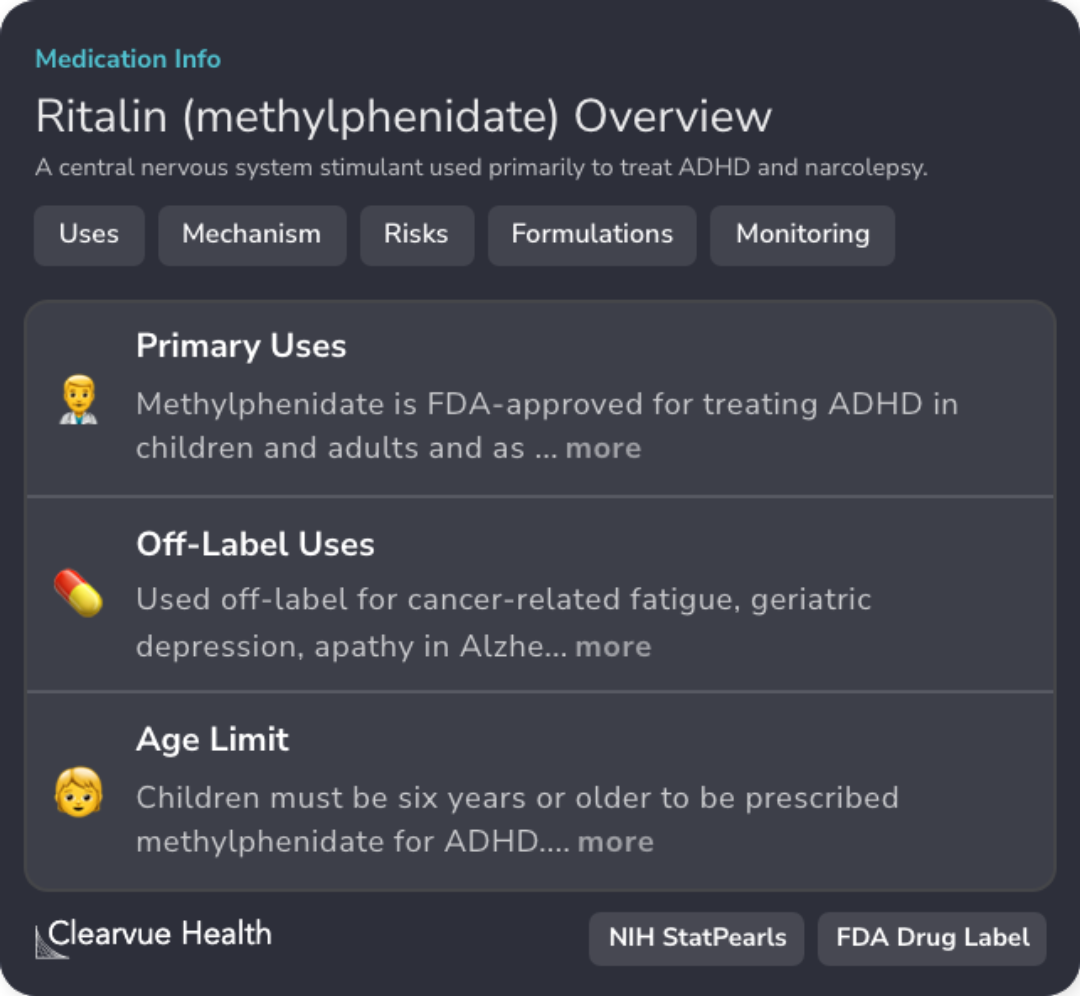
Primary Uses of Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate is FDA-approved for treating ADHD in children and adults, making it a common therapy for ADHD management.
🧠
Methylphenidate's Mechanism of Action
It blocks norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake, increasing their concentration in the synaptic cleft, which can help manage ADHD symptoms.
🧒
Age Limits for Medication
Methylphenidate can be prescribed to children aged six years or older for ADHD treatment, ensuring the pediatric focus of the study.
📉
Cardiovascular and Growth Risks
Monitoring for cardiovascular issues and growth suppression is crucial during long-term use due to potential side effects of methylphenidate.
👀
Monitoring and Side Effects
Regular monitoring is needed for side effects like cardiovascular issues and psychiatric reactions, which is vital for long-term treatment plans.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Long-term methylphenidate therapy in ADHD and tic disorder
The findings suggest that maintaining ADHD treatments over time is essential, as indicated by persistent impairments into adulthood when treatments are not sustained.
Stimulant medications, including methylphenidate, mildly increase heart rate and blood pressure, necessitating careful monitoring, especially since some individuals experience more significant changes.
Combining behavioral therapy with medication enhances treatment effects in pre-adolescent children, underscoring the importance of a multi-faceted approach.
Clinicians should also screen for comorbid conditions such as anxiety, depression, and developmental disorders during ADHD evaluations to ensure comprehensive care.
Stimulant medications, including methylphenidate, mildly increase heart rate and blood pressure, necessitating careful monitoring, especially since some individuals experience more significant changes.
Combining behavioral therapy with medication enhances treatment effects in pre-adolescent children, underscoring the importance of a multi-faceted approach.
Clinicians should also screen for comorbid conditions such as anxiety, depression, and developmental disorders during ADHD evaluations to ensure comprehensive care.
Evidence Summary
Behavior and Tic Outcomes During Long-term Methylphenidate Therapy
Thirty-four children with ADHD and chronic multiple tic disorder were assessed biannually for two years after an initial controlled trial of methylphenidate. Behavioral improvements noted during the acute trial were sustained. Motor and vocal tics did not worsen in frequency or severity. No significant adverse effects on cardiovascular function or growth were found.
Evidence Summary
Atomoxetine vs. Methylphenidate in ADHD Treatment
The article compares Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate, two medications used to treat ADHD.
It discusses the effectiveness, side effects, and patient response to each medication.
The information helps readers understand the differences and make informed choices based on their experiences and needs.
It discusses the effectiveness, side effects, and patient response to each medication.
The information helps readers understand the differences and make informed choices based on their experiences and needs.
Evidence Summary
Methylphenidate's Effect on Brain Activity in ADHD
This article explores how methylphenidate, a medication for ADHD, impacts brain activity related to attention.
By using brain imaging, researchers observed changes in attention-related regions of the brain in individuals with ADHD after taking the medication.
Methylphenidate is a medication commonly used to treat ADHD by improving focus and attention.
Researchers used brain imaging techniques to observe changes in brain regions linked to attention after taking the medication.
By using brain imaging, researchers observed changes in attention-related regions of the brain in individuals with ADHD after taking the medication.
Methylphenidate is a medication commonly used to treat ADHD by improving focus and attention.
Researchers used brain imaging techniques to observe changes in brain regions linked to attention after taking the medication.
Evidence Summary
Methylphenidate Effects on Cognitive Functions in ADHD
Methylphenidate is commonly used to treat ADHD. It improves cognitive functions like attention, focus, and mental performance. Research shows that this medication benefits those diagnosed with ADHD. The article illustrates these improvements with evidence from studies on cognitive gains in individuals with ADHD.