Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
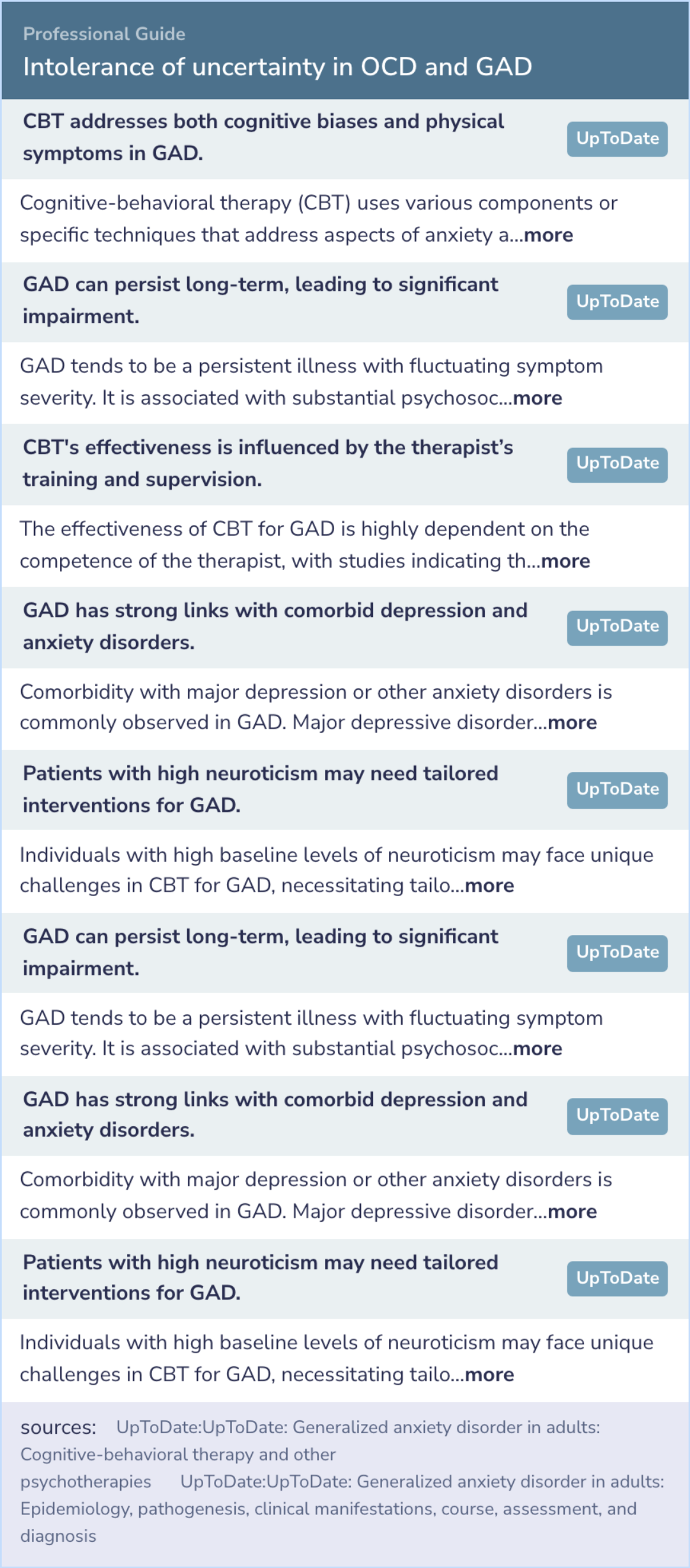
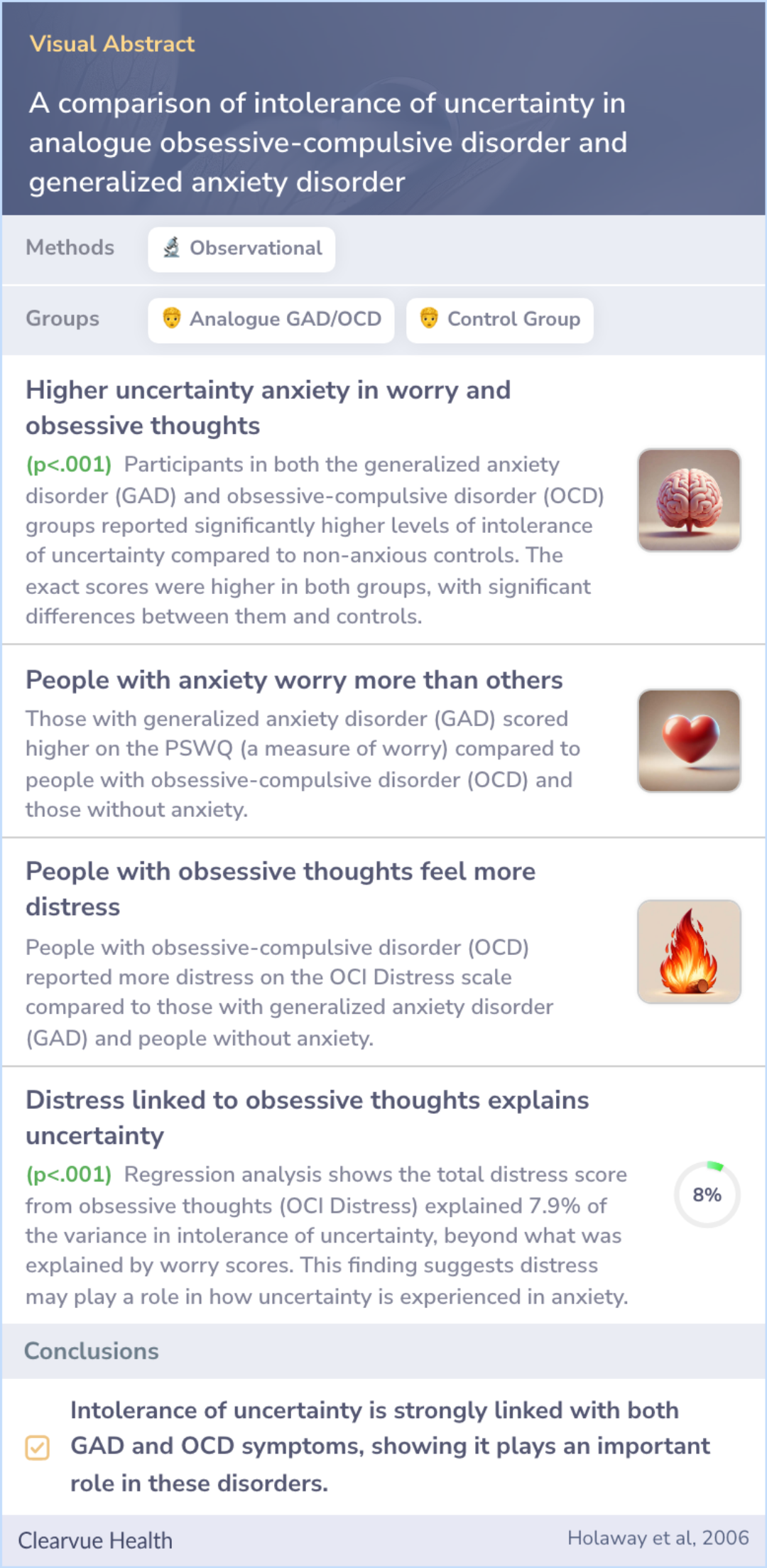
A comparison of intolerance of uncertainty in analogue obsessive-compulsive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder
Intolerance of uncertainty in OCD and GAD
November 25, 2024
author
Holaway RM, Heimberg RG, Coles ME
journal
J Anxiety Disord
Date Published
2006
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study explored the relationship between intolerance of uncertainty and symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
💡
What They Found
The research found a strong link between intolerance of uncertainty and symptoms of both GAD and OCD, with no significant difference in its impact between the two disorders.
📚
What This Means
This study suggests that intolerance of uncertainty is a central theme in both GAD and OCD, aligning with current evidence that recognizes shared characteristics in anxiety disorders.
Study Summary
Study Overview
The study explored how intolerance of uncertainty relates to anxiety disorders, especially Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). It noted that people with GAD might worry to control their feelings about uncertainty, while OCD rituals could serve as coping strategies for distress.
Overall, the research indicates that intolerance of uncertainty plays a significant role in both disorders, highlighting common threads in anxiety-related behaviors.
Overall, the research indicates that intolerance of uncertainty plays a significant role in both disorders, highlighting common threads in anxiety-related behaviors.
Abstract: background
Intolerance of uncertainty has been defined as the unwillingness to tolerate the possibility that negative events may occur in the future, no matter how low the probability.

Exploring Uncertainty
"Intolerance of uncertainty may be a central theme in a number of the anxiety disorders."
Understanding Behaviors
"Individuals may view rituals and compulsions as their only available strategy for reducing the distress associated with the possibility of a feared outcome."
Link Between Disorders
"This finding suggests that intolerance of uncertainty may not be specific to one disorder, but is, in fact, relevant to both GAD and OCD."
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers evaluated how intolerance of uncertainty compares between people with traits of GAD, OCD, or both, versus those without these traits.
A group of participants was formed, which included those displaying signs of GAD and OCD. Their levels of intolerance towards uncertainty were assessed and compared against a control group to understand any notable patterns or differences.
A group of participants was formed, which included those displaying signs of GAD and OCD. Their levels of intolerance towards uncertainty were assessed and compared against a control group to understand any notable patterns or differences.
Abstract: methods
The current study compared intolerance of uncertainty in individuals with analogue GAD and/or OCD.

Study Summary
Results
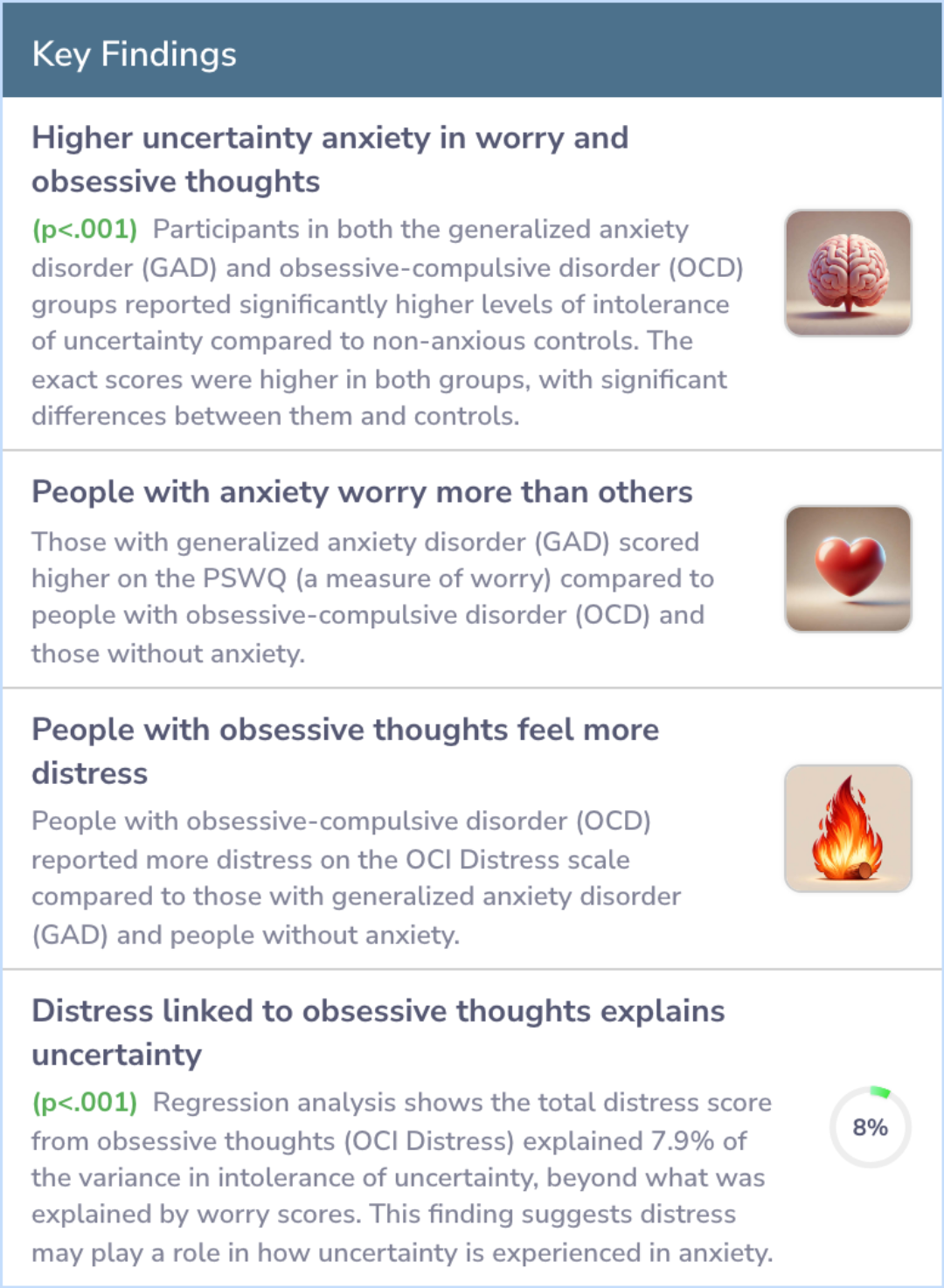
The study found a strong link between intolerance of uncertainty and symptoms of worrying, GAD, and OCD. Interestingly, neither GAD nor OCD was more linked to this intolerance than the other.
People with signs of GAD or OCD had higher levels of intolerance for uncertainty than those without such symptoms, indicating a shared characteristic, but those two groups were not significantly different from each other in this regard.
People with signs of GAD or OCD had higher levels of intolerance for uncertainty than those without such symptoms, indicating a shared characteristic, but those two groups were not significantly different from each other in this regard.
Abstract: results
Intolerance of uncertainty was strongly related to pathological worry, GAD symptoms, and OCD symptoms; however, neither worry nor GAD was found to be more strongly associated with intolerance of uncertainty than OCD. Further, individuals with analogu...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
The findings suggest that not being able to deal well with uncertainty is a common factor across various anxiety disorders. This intolerance might play a crucial role in how anxiety disorders like GAD and OCD develop.
Recognizing this shared trait could help tailor treatment approaches across different anxiety conditions, potentially leading to more effective management of these disorders.
Recognizing this shared trait could help tailor treatment approaches across different anxiety conditions, potentially leading to more effective management of these disorders.
Abstract: conclusions
These findings suggest that intolerance of uncertainty may be a central theme in a number of the anxiety disorders.

Background Information
Patient Guide
😟
Persistent Worry in GAD
Excessive worry in GAD impacts daily life, tying into intolerance of uncertainty themes.
🔗
OCD and Role of Intolerance
OCD linked with intolerance of uncertainty, suggesting shared features with GAD.
🧠
Biological Underpinnings
Genetic predisposition and neurotransmitter imbalances play roles in GAD, influencing uncertainty tolerance.
💭
Cross-Disorder Characteristics
GAD and OCD may share intolerance of uncertainty, highlighting cross-disorder themes.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Intolerance of uncertainty in OCD and GAD
Consistent with the abstract’s focus on intolerance of uncertainty in anxiety disorders, experts emphasize the comprehensive approach of CBT in addressing cognitive biases and physical symptoms of GAD.
GAD’s chronic nature leads to significant impairment across various life domains, necessitating effective long-term management strategies.
Therapist expertise significantly impacts CBT outcomes, highlighting the importance of professional training in treating GAD symptoms.
Given the high comorbidity between GAD and depression, integrated interventions could be crucial for comprehensive treatment.
GAD’s chronic nature leads to significant impairment across various life domains, necessitating effective long-term management strategies.
Therapist expertise significantly impacts CBT outcomes, highlighting the importance of professional training in treating GAD symptoms.
Given the high comorbidity between GAD and depression, integrated interventions could be crucial for comprehensive treatment.
Evidence Summary
Managing Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Its Symptoms
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) affects daily life with persistent worry. The article reviews GAD's symptoms, focusing on how overwhelming thoughts impact routine tasks and interactions. It highlights how worry shapes a person's experience of anxiety.
Several treatments and coping methods, such as therapy and lifestyle adjustments, are discussed as ways to manage GAD's symptoms and reduce its effect on everyday life.
Several treatments and coping methods, such as therapy and lifestyle adjustments, are discussed as ways to manage GAD's symptoms and reduce its effect on everyday life.
Evidence Summary
How GAD Leads to Overgeneralized Fear and Avoidance
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) can cause a person to spread fear from one situation to many others, leading them to avoid even safe situations. This avoidance is linked to an overgeneralization of threat. Ongoing research aims to explain why individuals with GAD tend to perceive threats in places where none exist.
Fear becomes amplified, making people react as if more situations are dangerous than they actually are. As a result, they stay away from situations unnecessarily, increasing their anxiety in the long run.
Fear becomes amplified, making people react as if more situations are dangerous than they actually are. As a result, they stay away from situations unnecessarily, increasing their anxiety in the long run.
Evidence Summary
Comparing CBT and Applied Relaxation for GAD
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) works by altering the negative thoughts and behaviors that often fuel anxiety, providing individuals with strategies to better manage their GAD symptoms. Applied Relaxation, on the other hand, helps individuals focus on muscle relaxation techniques to physically reduce anxiety levels, offering a more body-centered approach.
Both methods aim to reduce anxiety, but CBT targets thoughts while Applied Relaxation focuses on physical tension release.
Both methods aim to reduce anxiety, but CBT targets thoughts while Applied Relaxation focuses on physical tension release.