Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Insomnia in older adults with generalized anxiety disorder
Insomnia in Older Adults with GAD
November 25, 2024
author
Brenes GA, Miller ME, Stanley MA, Williamson JD, Knudson M, McCall WV
journal
Am J Geriatr Psychiatry
Date Published
2009 Jun
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The main research question was to study the frequency and severity of insomnia symptoms in older adults with GAD compared to those without GAD, and to see how comorbid depression and age affect these symptoms.
💡
What They Found
The study found that older adults with GAD, with or without depression, reported greater sleep disturbance severity than those without psychiatric diagnoses.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that older adults with GAD experience more severe sleep disturbances compared to those without GAD. This aligns with current evidence that GAD often comes with significant sleep-related issues.
Study Summary
Study Overview
The study aimed to explore the levels of insomnia in older adults with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). It found that many of these individuals experience significant sleep problems similar to those diagnosed with insomnia. The research highlights that sleep disturbances are not only common among older adults but also prevalent in those with GAD, irrespective of additional conditions like depression.
These findings point to the need for regular assessment and potential treatment of sleep issues in this population to improve overall well-being.
These findings point to the need for regular assessment and potential treatment of sleep issues in this population to improve overall well-being.
Abstract: background
The purposes of this study are to determine the frequency and severity of insomnia symptoms and related complaints experienced by older adults with GAD and compare them with older adults without GAD; compare insomnia symptoms among older adults with ...more

Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Sleep Disturbances
"Sleep disturbances are common in patients with anxiety disorders, particularly Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), as well as in older adults."
Purpose of the Study
"The primary purpose of this study is to determine the frequency and severity of insomnia symptoms and related complaints in older adults with and without GAD."
Assessing Sleep Disturbances
"Given the high rates of sleep disturbance and dissatisfaction with sleep reported by adults with GAD, sleep disturbances should be routinely assessed and treated when warranted among older adults with GAD."
Study Summary
Methods
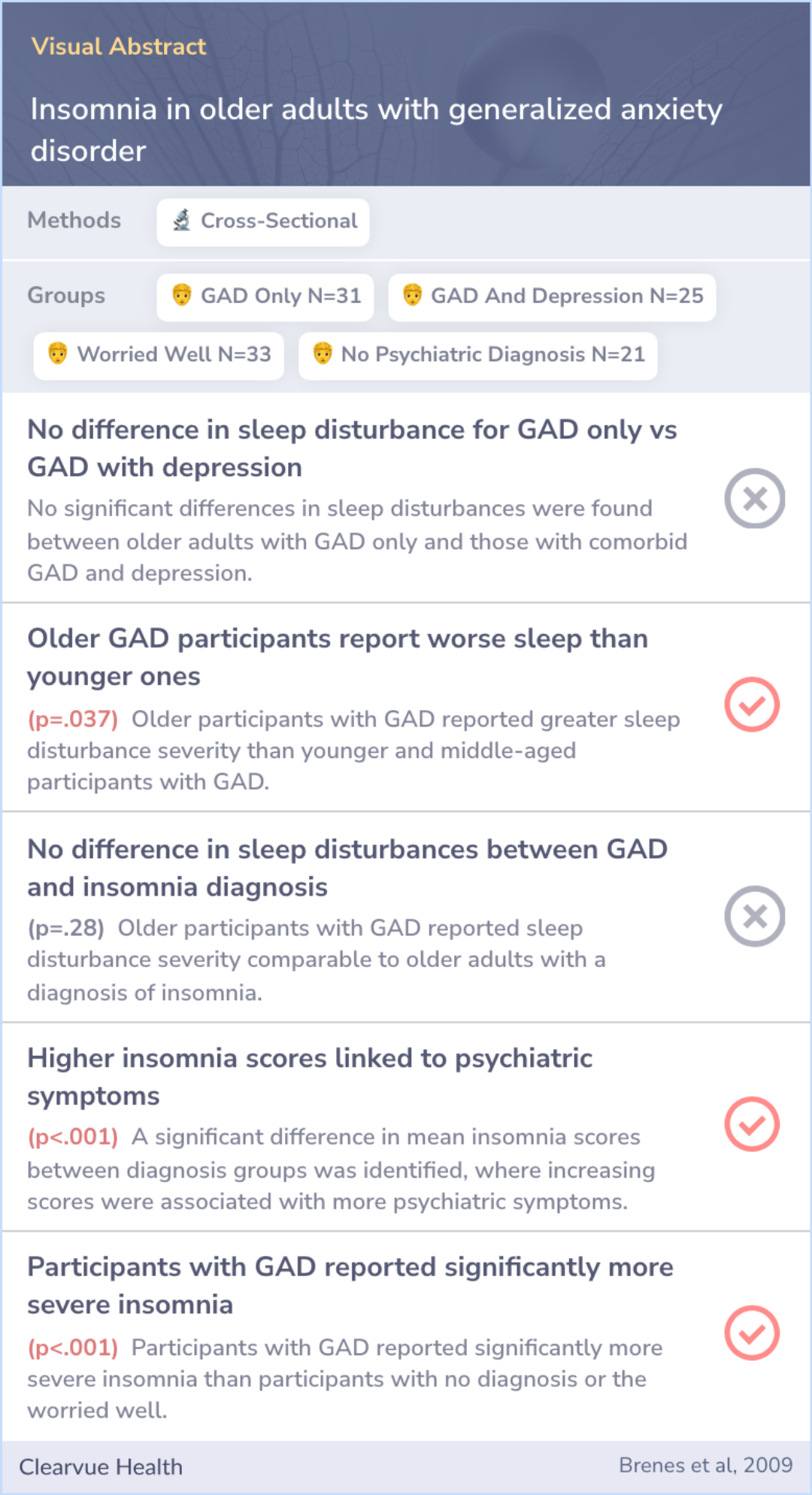
This study was cross-sectional, meaning it looked at data from a specific point in time. Participants were gathered through primary care clinics, ads, and mailings. There were 110 older adults in total.
The group included 31 with GAD, 25 with both GAD and depression, 33 classified as 'worried well,' and 21 with no psychiatric diagnosis. The key measures were psychiatric diagnosis, sleep disturbance, and overall health.
The group included 31 with GAD, 25 with both GAD and depression, 33 classified as 'worried well,' and 21 with no psychiatric diagnosis. The key measures were psychiatric diagnosis, sleep disturbance, and overall health.
Abstract: methods
Cross-sectional. Participants were recruited through primary care clinics, advertisements, and mass mailings. 110 older adults; 31 with GAD, 25 with GAD and depression, 33 worried well, and 21 with no psychiatric diagnosis. Psychiatric diagnosis, sle...more

Study Summary
Results
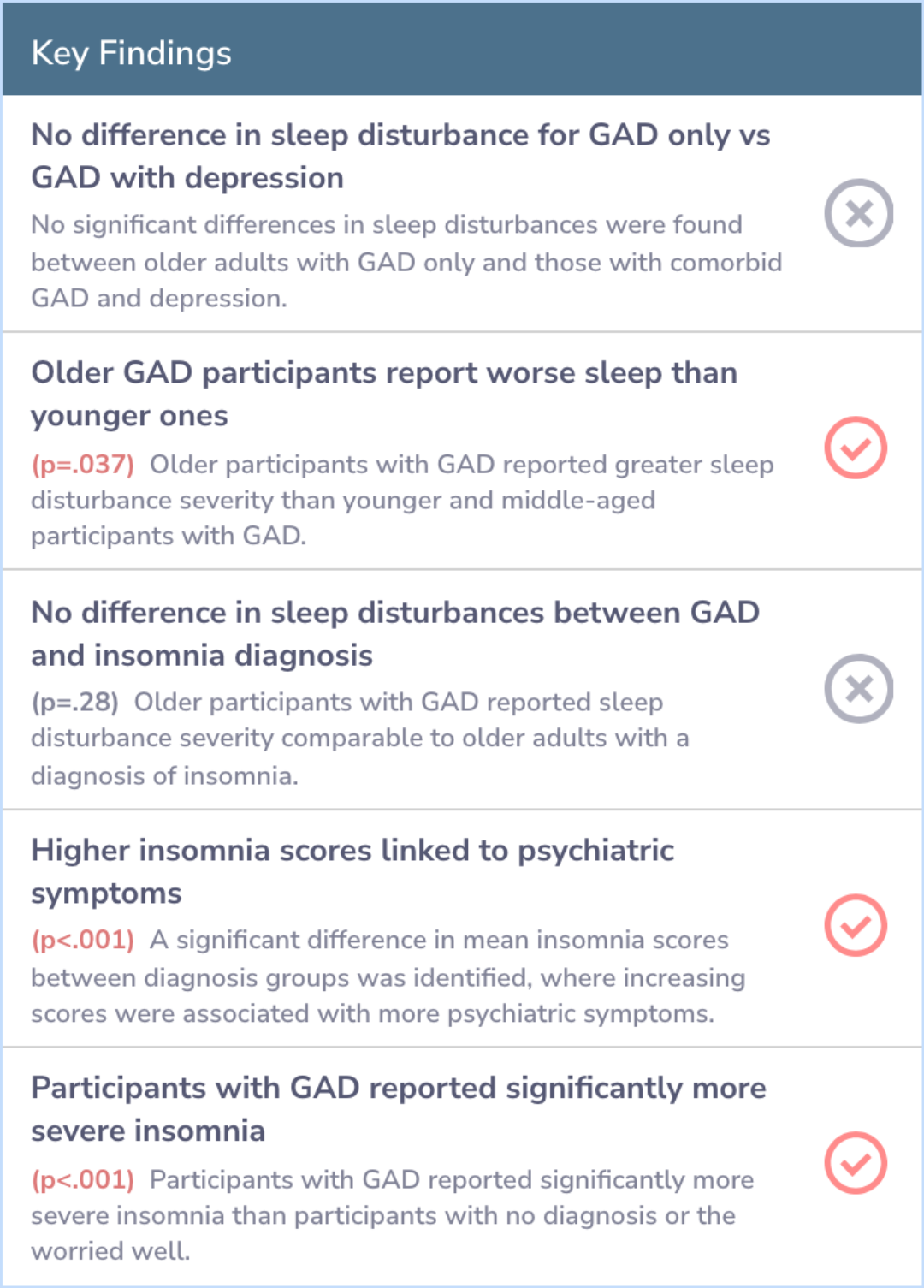
The study found that participants with GAD, whether they had depression or not, reported much more severe sleep problems than those without psychiatric issues or the 'worried well.' Interestingly, there was no difference in sleep disturbances between those with just GAD and those with both GAD and depression.
Older adults with GAD reported more severe sleep issues than younger and middle-aged GAD patients. Their sleep problems were similar to those with a diagnosed insomnia disorder. Moreover, 90% of older GAD patients were dissatisfied with their sleep, with most experiencing moderate to severe insomnia.
Older adults with GAD reported more severe sleep issues than younger and middle-aged GAD patients. Their sleep problems were similar to those with a diagnosed insomnia disorder. Moreover, 90% of older GAD patients were dissatisfied with their sleep, with most experiencing moderate to severe insomnia.
Abstract: results
Participants with GAD with and without comorbid depression reported significantly greater sleep disturbance severity than participants with no psychiatric diagnosis and the worried well. There were no differences in sleep disturbances between older a...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
These findings indicate the importance of evaluating sleep disturbances in older adults who have GAD. If untreated, these sleep issues could worsen their overall quality of life.
Given the high frequency and severity of insomnia among older adults with GAD, healthcare providers should include sleep assessments as part of the routine evaluation for these patients.
Given the high frequency and severity of insomnia among older adults with GAD, healthcare providers should include sleep assessments as part of the routine evaluation for these patients.
Abstract: conclusions
These findings support the assessment of sleep disturbances within the context of late-life GAD.

Background Information
Patient Guide
🛌
High Prevalence of Insomnia
Older adults with GAD frequently report high levels of sleep disturbance affecting daily function.
🤕
Physical Symptoms of GAD
Fatigue and trouble sleeping are common physical symptoms among individuals with GAD.
🔗
Comorbidity With Depression
Older adults with GAD often experience comorbid depression, complicating treatment strategies.
👵
Age-Related Differences
Insomnia severity can vary by age among those with GAD, affecting older adults more significantly.
Professional Guide
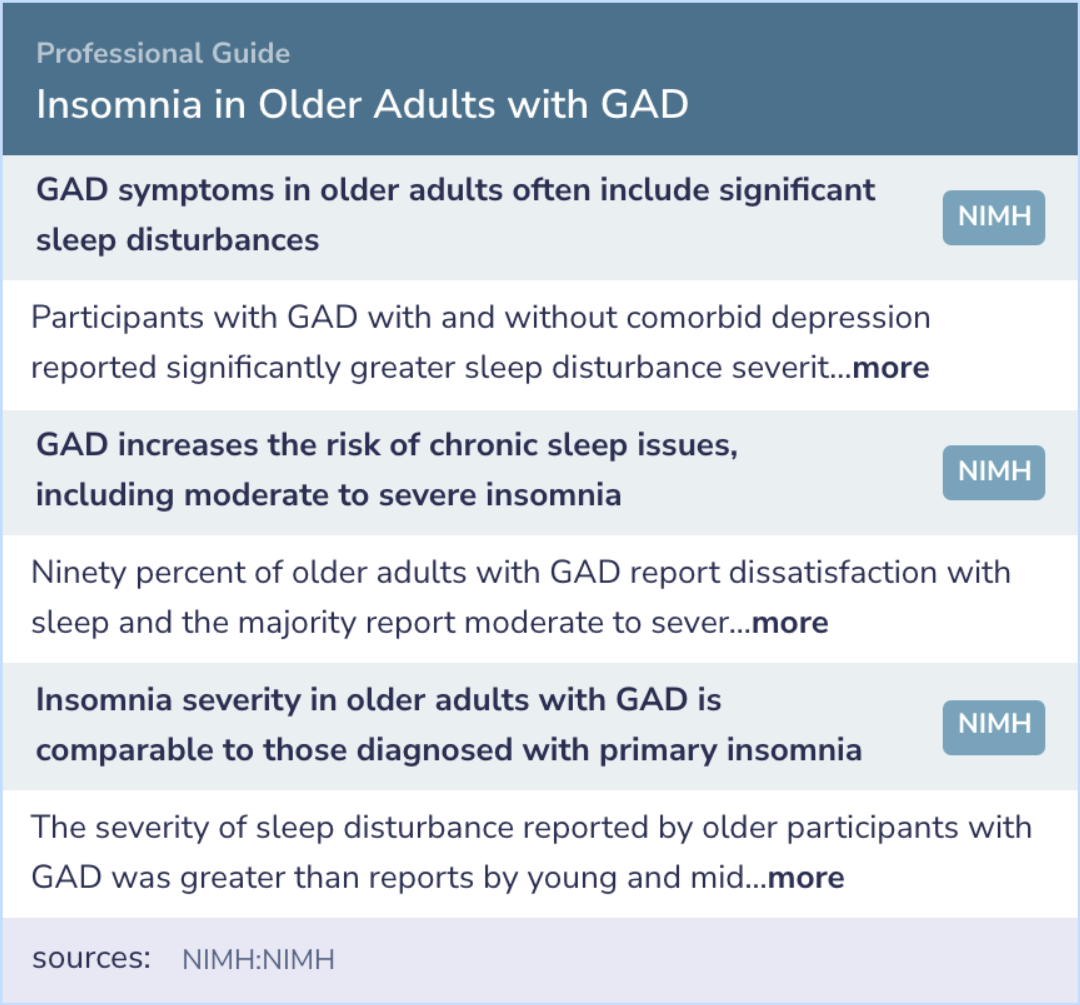
Expert Opinion: Insomnia in Older Adults with GAD
In line with the study's focus, GAD symptoms in older adults often include significant sleep disturbances.
This population also faces an increased risk of chronic sleep issues, including moderate to severe insomnia.
Interestingly, sleep issues do not differ significantly between those with GAD alone and those with comorbid depression.
Moreover, insomnia severity in older adults with GAD is comparable to those diagnosed with primary insomnia.
This population also faces an increased risk of chronic sleep issues, including moderate to severe insomnia.
Interestingly, sleep issues do not differ significantly between those with GAD alone and those with comorbid depression.
Moreover, insomnia severity in older adults with GAD is comparable to those diagnosed with primary insomnia.
Evidence Summary
Worry and Sleep Issues in Older Adults with GAD
Older adults with GAD often deal with persistent worry, sleep issues, and irritability, all of which can interfere with their day-to-day life. These symptoms can be especially tough to manage without proper diagnosis.
Sleep problems are a common feature, and irritability often goes hand in hand with the anxiety, making effective treatment an important step in improving quality of life for those affected by late-life GAD.
Sleep problems are a common feature, and irritability often goes hand in hand with the anxiety, making effective treatment an important step in improving quality of life for those affected by late-life GAD.
Evidence Summary
CBT vs Applied Relaxation: Different Approaches to Managing Anxiety
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Applied Relaxation are two approaches used for treating Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). CBT works by helping individuals recognize and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to their anxiety.
On the other hand, Applied Relaxation uses muscle relaxation techniques, teaching individuals how to physically relax their bodies, which helps reduce anxiety symptoms over time.
On the other hand, Applied Relaxation uses muscle relaxation techniques, teaching individuals how to physically relax their bodies, which helps reduce anxiety symptoms over time.
Evidence Summary
Depression and Anxiety: A Close Connection
Depression and anxiety often come hand in hand, amplifying symptoms and complicating treatment. Many individuals struggle with both conditions at the same time, creating a complex relationship between the two. The research indicates a strong overlap, making it clear that these conditions frequently go together.
When depression and anxiety co-occur, symptoms worsen, and the path to effective treatment becomes more difficult for those affected.
When depression and anxiety co-occur, symptoms worsen, and the path to effective treatment becomes more difficult for those affected.