Adderall
Evidence Based Answers
How do ADHD medications affect driving performance in adolescents?
ADHD medications like methylphenidate help improve focus and reaction times, but potential side effects like nervousness or insomnia may influence driving safety.
Published: October 24, 2024
Click to explore a section:
ADHD medications can improve focus and reaction times but may cause side effects that affect driving.
Studies Summary
🚗
Study: OROS Methylphenidate Enhances Driving Performance
In a study examining ADHD medications, OROS methylphenidate improved driving performance in adolescents by reducing time spent off-road and enhancing speed control, unlike mixed amphetamine salts.
🕵️♂️
Driving Focus with ADHD Medications
ADHD medications like methylphenidate enhance levels of brain neurotransmitters, improving focus and attention, key for driving, particularly by maintaining sustained attention during long trips.
⏱️
Adderall XR and Sustained Focus for Driving
Adderall XR provides all-day effectiveness, helping maintain focus and control throughout the day, which can be beneficial for driving activities that require prolonged attention.
Highly Cited Studies
Long term Effects of Methylphenidate in Adults
Peer Reviewed Study 1
Effect of ADHD Medications on Adolescent Driving Performance
Peer Reviewed Study 2
Comparing Cardiac Risks of ADHD Medications and Driving
Peer Reviewed Study 3
Adderall XR's All-Day Effectiveness and Its Implications for Driving Performance
Peer Reviewed Study 4
Comparison of Adderall and Methylphenidate on ADHD Symptoms
Background: ADHD Medications and Driving in Adolescents
ADHD medications, such as methylphenidate, are commonly prescribed to adolescents to manage symptoms of ADHD. These medications increase levels of specific neurotransmitters in the brain, which can help improve focus and reduce impulsive behaviors.
Methylphenidate might affect driving performance, as driving requires sustained attention and quick decision-making.
Methylphenidate might affect driving performance, as driving requires sustained attention and quick decision-making.
“
Source Quotes:
Methylphenidate blocks the reuptake of two neurotransmitters, norepinephrine (NE) and dopamine, in presynaptic neurons.
Many studies have shown that methylphenidate improves cognition, vigilance, reaction time, short-term memory and the learning of verbal and non-verbal material.
Background: Methylphenidate's Impact on Reaction Time
Driving demands quick reaction times, especially in situations requiring sudden stops or fast maneuvers. ADHD medications like methylphenidate can influence reaction times.
These medications are effective at improving attention and reducing impulsivity, which may impact how quickly an adolescent can respond to road hazards.
These medications are effective at improving attention and reducing impulsivity, which may impact how quickly an adolescent can respond to road hazards.
“
Source Quotes:
The response inhibition (the probability and speed with which the patient could inhibit responses to a primary task) is better reflected by a modified measurement method, supporting the hypothesis that the function for improvement in behavior is linear with increasing doses.
Background: Adverse Effects of ADHD Medications on Driving
ADHD medications can improve focus and attention, but they also come with side effects that could impact driving performance. Common side effects include insomnia, nervousness, and changes in blood pressure, all of which may affect an adolescent's ability to drive safely.
These potential adverse effects should be considered when evaluating the overall impact on driving performance.
These potential adverse effects should be considered when evaluating the overall impact on driving performance.
“
Source Quotes:
Insomnia and nervousness are the most commonly reported adverse effects in patients using methylphenidate.
When children or adolescents who are being treated with stimulant medications develop adverse effects, it is important to determine the timing of the effect in relation to medication administration.
Peer Reviewed Study
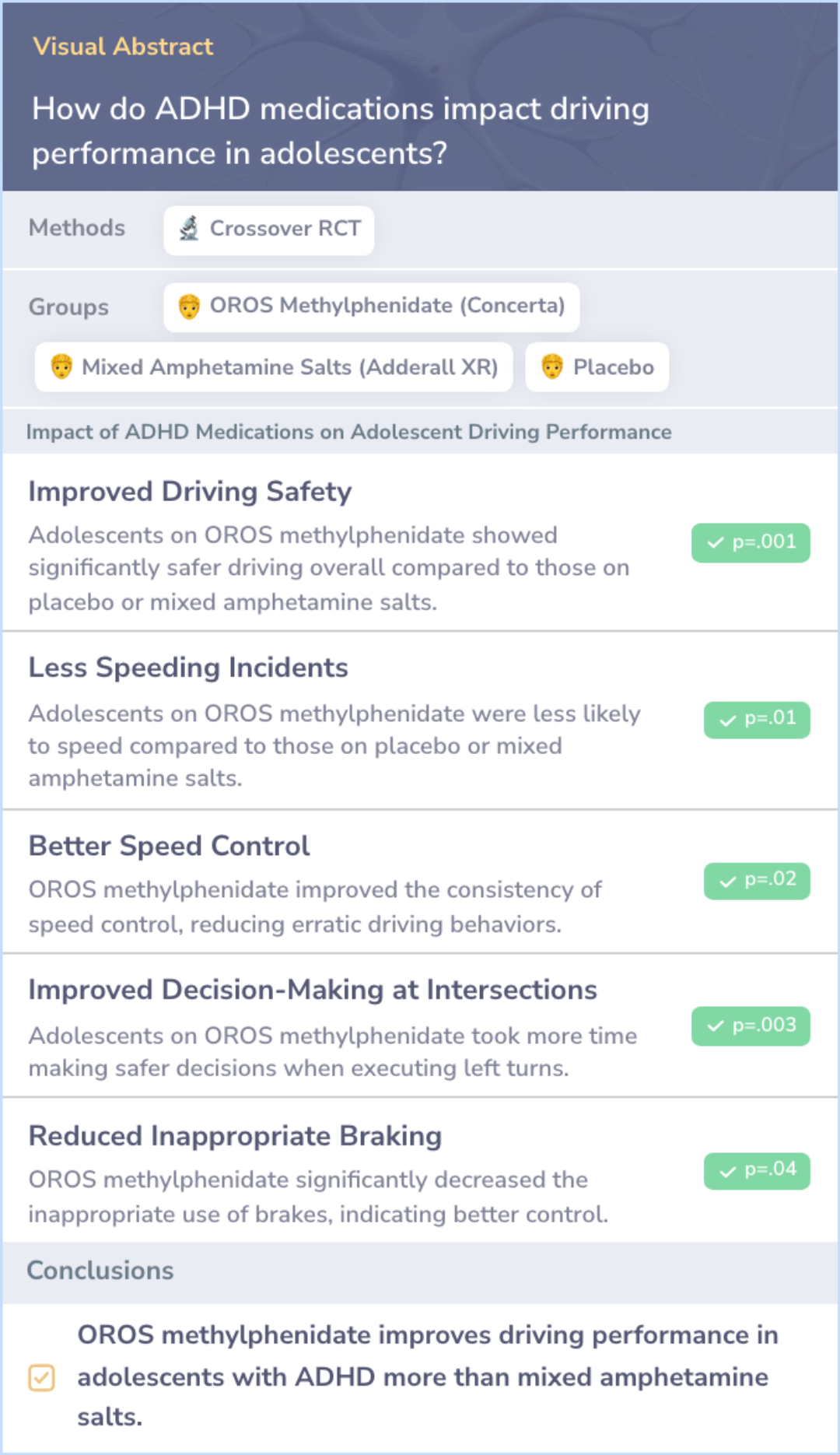
Study: Effect of ADHD Medications on Adolescent Driving Performance
This study examined how two long-acting stimulant medications, OROS methylphenidate and mixed amphetamine salts extended release, affect driving performance in adolescents with ADHD. The study used a driving simulator at different times of the day: 5:00 pm, 8:00 pm, and 11:00 pm. Results showed that OROS methylphenidate led to better driving performance, reducing time spent driving off the road, speeding, erratic speed control, and inappropriate use of brakes.
Mixed amphetamine salts extended release did not show significant improvement over placebo in these areas.
Mixed amphetamine salts extended release did not show significant improvement over placebo in these areas.
author
Cox DJ, Merkel RL, Moore M, Thorndike F, Muller C, Kovatchev B
journal
Pediatrics
Date Published
2006 Sep
Peer Reviewed Study
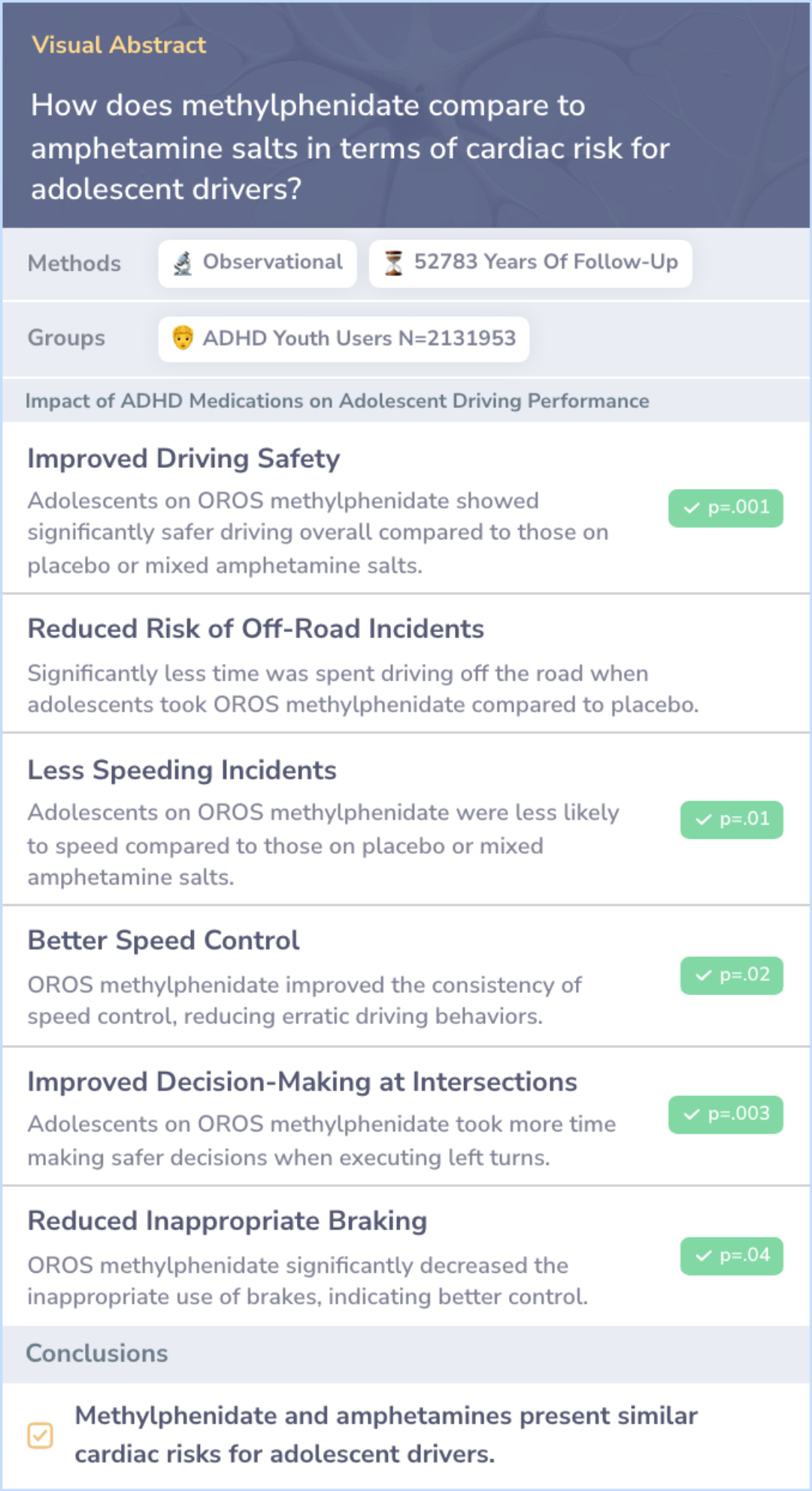
Study: Comparing Cardiac Risks of ADHD Medications and Driving
This study compared the risk of cardiac events between adolescents using methylphenidate and those using amphetamine salts, both common ADHD medications. The analysis involved over 2 million youth, focusing on emergency department visits related to cardiac issues during the use of these stimulants.
Results indicated that the risk of cardiac emergency visits was similar between current users of methylphenidate and amphetamine salts, with no significant difference during periods of former use.
Results indicated that the risk of cardiac emergency visits was similar between current users of methylphenidate and amphetamine salts, with no significant difference during periods of former use.
author
Winterstein AG, Gerhard T, Shuster J, Saidi A
journal
Pediatrics
Date Published
July 2009
Peer Reviewed Study
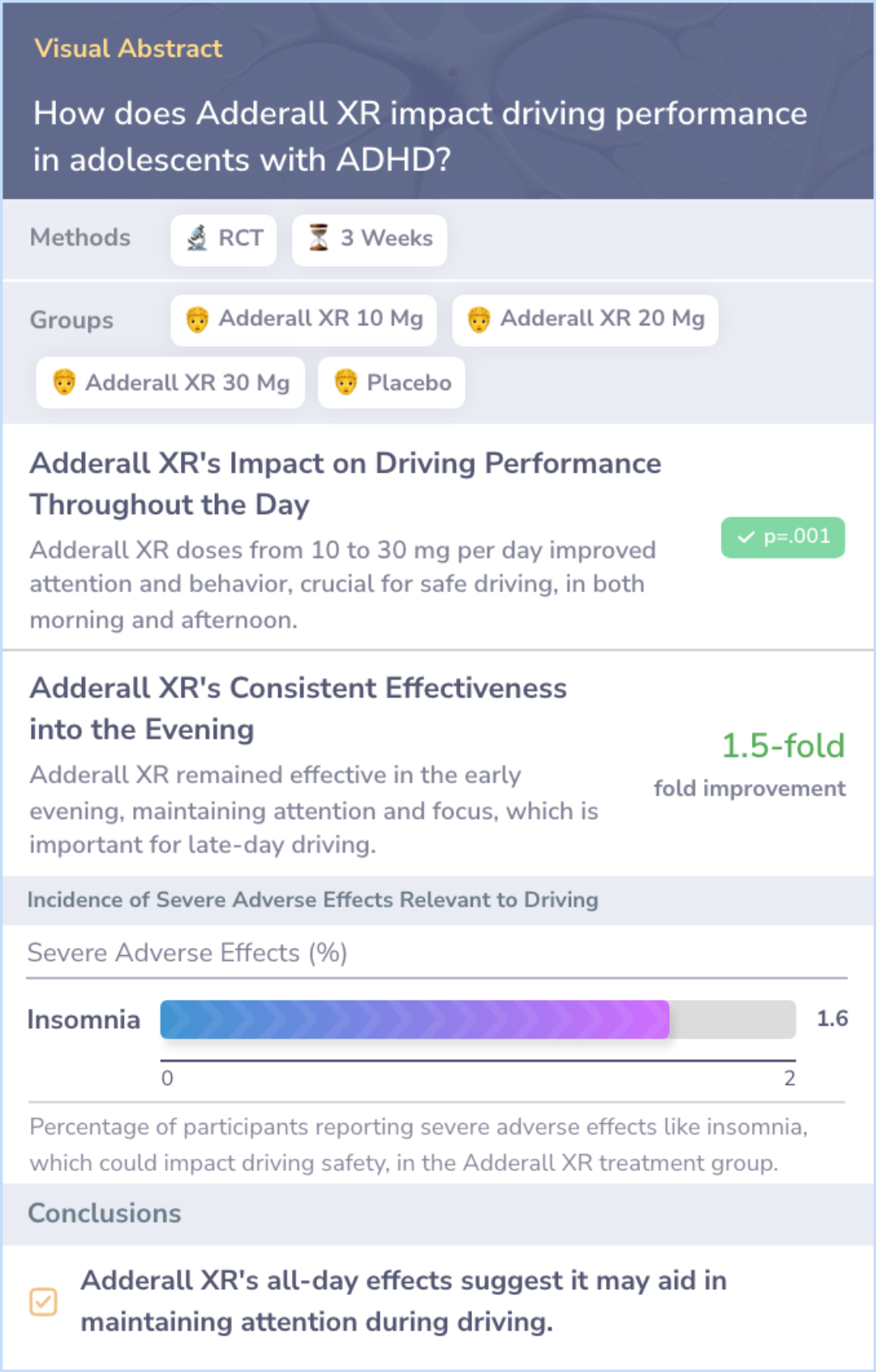
Study: Adderall XR's All-Day Effectiveness and Its Implications for Driving Performance
This study evaluated Adderall XR, a medication designed to last throughout the day with one morning dose, in children with ADHD. It showed consistent improvements in behavior across the day, as reported by both teachers and parents. The extended-release nature of the medication resulted in sustained effects into the afternoon and late afternoon.
These findings suggest that the medication may help maintain focus and control throughout the day, which could be beneficial for activities like driving that require sustained attention.
These findings suggest that the medication may help maintain focus and control throughout the day, which could be beneficial for activities like driving that require sustained attention.
author
Biederman J, Lopez FA, Boellner SW, Chandler MC
journal
Pediatrics
Date Published
2002 Aug
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Comparison of Adderall and Methylphenidate on ADHD Symptoms
This abstract compares the effects of Adderall and the standard-release form of methylphenidate, two common ADHD medications. Adderall shows a small but statistically significant advantage over methylphenidate in symptom measures and global ratings, particularly in clinician and parent ratings.
This comparison is important for understanding the effectiveness of ADHD medications, which can impact areas such as driving performance in adolescents.
This comparison is important for understanding the effectiveness of ADHD medications, which can impact areas such as driving performance in adolescents.
author
Faraone SV, Biederman J, Roe C
journal
J Clin Psychopharmacol
Date Published
October 2002

Key Takeaways
Conclusions
ADHD medications play a notable role in improving driving performance among adolescents by enhancing focus, attention, and reducing impulsivity, thus potentially mitigating driving errors. Studies show that OROS methylphenidate offers significant benefits in these areas, while mixed amphetamine salts do not demonstrate the same level of improvement. Additionally, long-acting formulations like Adderall XR extend their benefits throughout the day. However, one must also consider potential side effects that may negatively affect driving abilities.
Research highlights the importance of tailored medication plans for ADHD adolescents who drive, balancing the enhancements in attentiveness against possible adverse outcomes. Effective management of ADHD with apt medication thus appears vital for safe adolescent driving.
Research highlights the importance of tailored medication plans for ADHD adolescents who drive, balancing the enhancements in attentiveness against possible adverse outcomes. Effective management of ADHD with apt medication thus appears vital for safe adolescent driving.

Evidence Summary
Driving Variability and Distractions for Teens with ADHD
Newly licensed teens with ADHD show more variability in speed and lane position, even after accounting for driving experience. Distractions such as texting worsen these issues for all adolescents. Although braking reaction time remains unaffected, teens with ADHD commit more driving violations. The study highlights how texting exacerbates existing challenges in teens with ADHD, emphasizing safety concerns during distracted driving episodes.
Evidence Summary
ADHD Drivers: How Distractions Vary by Context
Young adults with ADHD face higher risks in driving, especially when distracted by in-car tech like infotainment systems. How they handle secondary tasks, such as phone calls during urban drives or memory tasks on highways, varies. While they're vulnerable in low-stimulus settings, their distraction levels match others in busier environments, highlighting how context impacts attention distribution.
Evidence Summary
ADHD and Driving Risks in Teens
ADHD affects driving abilities, leading to more crashes and citations. Teens with ADHD face higher risks of reckless driving, unlicensed driving, and license suspensions compared to their peers. Driving records highlight their increased traffic violations and costly crashes. Behind the wheel and on simulators, they show impulsive errors, slower reactions, and unsafe driving practices, indicating ongoing risks.