Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
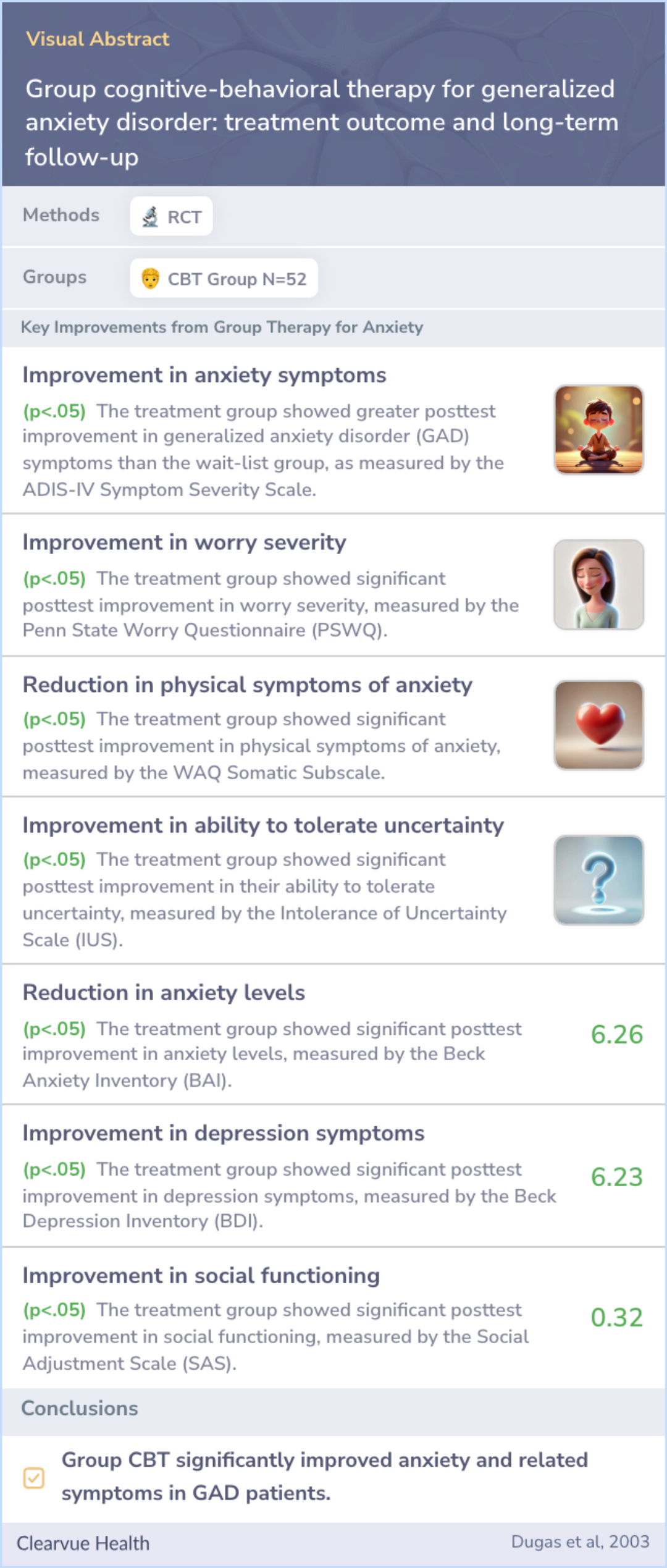
Group cognitive-behavioral therapy for generalized anxiety disorder: treatment outcome and long-term follow-up
Group CBT for Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Outcomes and Follow-up
November 25, 2024
author
Dugas MJ, Ladouceur R, Léger E, Freeston MH, Langlois F, Provencher MD, Boisvert JM
journal
J Consult Clin Psychol
Date Published
2003 Aug
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study investigated the effectiveness of a group format cognitive-behavioral therapy for treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
💡
What They Found
The study found that patients who participated in group therapy showed significant improvements in anxiety and related symptoms compared to those on a wait-list.
📚
What This Means
These findings align with current evidence that emphasizes cognitive-behavioral therapy as an effective treatment for generalized anxiety disorder.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to test the efficacy of group cognitive-behavioral therapy for GAD. It built on previous research showing the effectiveness of individual therapy. The study found that group therapy could be just as effective as individual therapy while being more accessible and cost-effective. Participants reported feeling less isolated and learned from others in the group, highlighting the social benefits of this treatment.
The findings confirm that addressing intolerance of uncertainty directly can significantly reduce worry and anxiety, core symptoms of GAD.
The findings confirm that addressing intolerance of uncertainty directly can significantly reduce worry and anxiety, core symptoms of GAD.
Abstract: background
A recently developed cognitive-behavioral treatment for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) targets intolerance of uncertainty by the reevaluation of positive beliefs about worry, problem-solving training, and cognitive exposure.

Efficacy of Group Therapy
"Our results suggest that group cognitive-behavioral therapy can be just as effective as individual therapy for GAD, despite the potential for higher dropout rates in group settings."
Social Connectedness
"These findings suggest that the benefits of group therapy extend beyond just symptom reduction, with participants reporting greater social connectedness and learning from others in the group."
Cost-Effectiveness
"The present study contributes to the growing body of evidence suggesting that group cognitive-behavioral therapy may be a viable alternative to individual therapy for GAD, especially in terms of cost-effectiveness."
Study Summary
Methods
The study explored whether group therapy could make this treatment more cost-effective compared to individual sessions. Fifty-two patients with GAD participated in 14 therapy sessions in small groups of 4 to 6 members.
Researchers used a wait-list control design, meaning some participants waited before starting therapy. They evaluated the therapy's effects using clinical assessments and self-reported questionnaires on anxiety and social adjustment.
Researchers used a wait-list control design, meaning some participants waited before starting therapy. They evaluated the therapy's effects using clinical assessments and self-reported questionnaires on anxiety and social adjustment.
Abstract: methods
As previous studies have established the treatment's efficacy when delivered individually, the present study tests the treatment in a group format as a way to enhance its cost-benefit ratio. A total of 52 GAD patients received 14 sessions of cognitiv...more
Study Summary
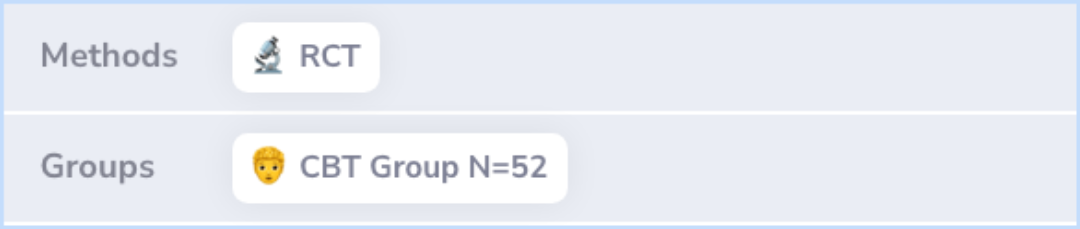
Results
The therapy group showed more significant improvements than those on the wait-list, showing the benefit of immediate treatment on all measures like anxiety and uncertainty. Participants continued to make progress in managing their symptoms even two years after the study ended.
This suggests that group therapy not only works in the short term but helps maintain longer-term gains in reducing anxiety and improving overall well-being.
This suggests that group therapy not only works in the short term but helps maintain longer-term gains in reducing anxiety and improving overall well-being.
Abstract: results
Results show that the treatment group, relative to the wait-list group, had greater posttest improvement on all dependent variables and that treated participants made further gains over the 2-year follow-up phase of the study.
Study Summary
Conclusions
The findings indicate that group cognitive-behavioral therapy effectively treats people with generalized anxiety disorder. It suggests that offering therapy in a group setting provides a valuable treatment option.
Therefore, this approach may benefit both health practitioners seeking effective treatments and patients looking for manageable ways to treat their anxiety symptoms in a supportive group environment.
Therefore, this approach may benefit both health practitioners seeking effective treatments and patients looking for manageable ways to treat their anxiety symptoms in a supportive group environment.
Abstract: conclusions
The results indicate the effectiveness of group cognitive-behavioral therapy for patients with generalized anxiety disorder, suggesting its value as a treatment option.

Background Information
Patient Guide
📚
Understanding GAD
Generalized Anxiety Disorder features excessive worry, impacting daily life and often managed with CBT.
💭
Role of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
CBT focuses on altering maladaptive thoughts and gradually confronting anxiety-provoking situations in those with GAD.
🔗
GAD's Connections
Often occurs with depression and other disorders, making it complex to treat, highlighting the value of integrated care.
🔄
Challenges in GAD Treatment
Patients face chronic symptoms and compliance issues, underlining the need for adaptable and sustainable treatment methods.
🔗
Therapeutic and Medication Balance
Combining CBT with medications often provides the most effective treatment outcomes for GAD sufferers.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Group CBT for Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Outcomes and Follow-up
In line with the study's findings, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) remains an effective approach for treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), helping to reduce symptoms through targeted exercises.
Group CBT is particularly beneficial for older adults, enhancing efficacy through social interaction.
Additionally, the combination of CBT and pharmacotherapy may offer improved outcomes over either treatment alone.
Group CBT is particularly beneficial for older adults, enhancing efficacy through social interaction.
Additionally, the combination of CBT and pharmacotherapy may offer improved outcomes over either treatment alone.
Evidence Summary
Transforming Anxiety: CBT vs. Applied Relaxation
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) shifts focus towards transforming negative thoughts and behaviors that fuel anxiety, helping individuals break free from cycles of worry. In contrast, Applied Relaxation offers practical techniques to ease muscle tension, providing immediate relief from anxiety symptoms. Both methods aim to address Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), yet they approach treatment from different angles, offering diverse strategies to support those struggling with anxiety.
Understanding these two approaches allows individuals to choose a path that resonates with their needs, whether through mental reframing or physical relaxation techniques.
Understanding these two approaches allows individuals to choose a path that resonates with their needs, whether through mental reframing or physical relaxation techniques.
Evidence Summary
How CBT and Mindfulness Help Manage Anxiety
CBT helps people manage their anxiety by changing the way they think about their worries. Through regular practice, it can help replace negative thought patterns with more balanced ones. Mindfulness techniques are sometimes combined with CBT to enhance these effects.
Incorporating mindfulness allows individuals to improve their control over anxiety symptoms, especially with continued use alongside traditional CBT methods.
Incorporating mindfulness allows individuals to improve their control over anxiety symptoms, especially with continued use alongside traditional CBT methods.
Evidence Summary
How Cognitive and Behavioral Therapies Reduce Anxiety
Cognitive and behavioral therapies focus on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. They use strategies like exposure therapy and cognitive restructuring to reduce anxiety symptoms.
These therapies lead to noticeable decreases in anxiety levels for many, often improving their quality of life.
Patients frequently report significant progress after undergoing these treatments, with long-lasting benefits over time.
These therapies lead to noticeable decreases in anxiety levels for many, often improving their quality of life.
Patients frequently report significant progress after undergoing these treatments, with long-lasting benefits over time.



