Trending ADHD Papers
Visual Abstract
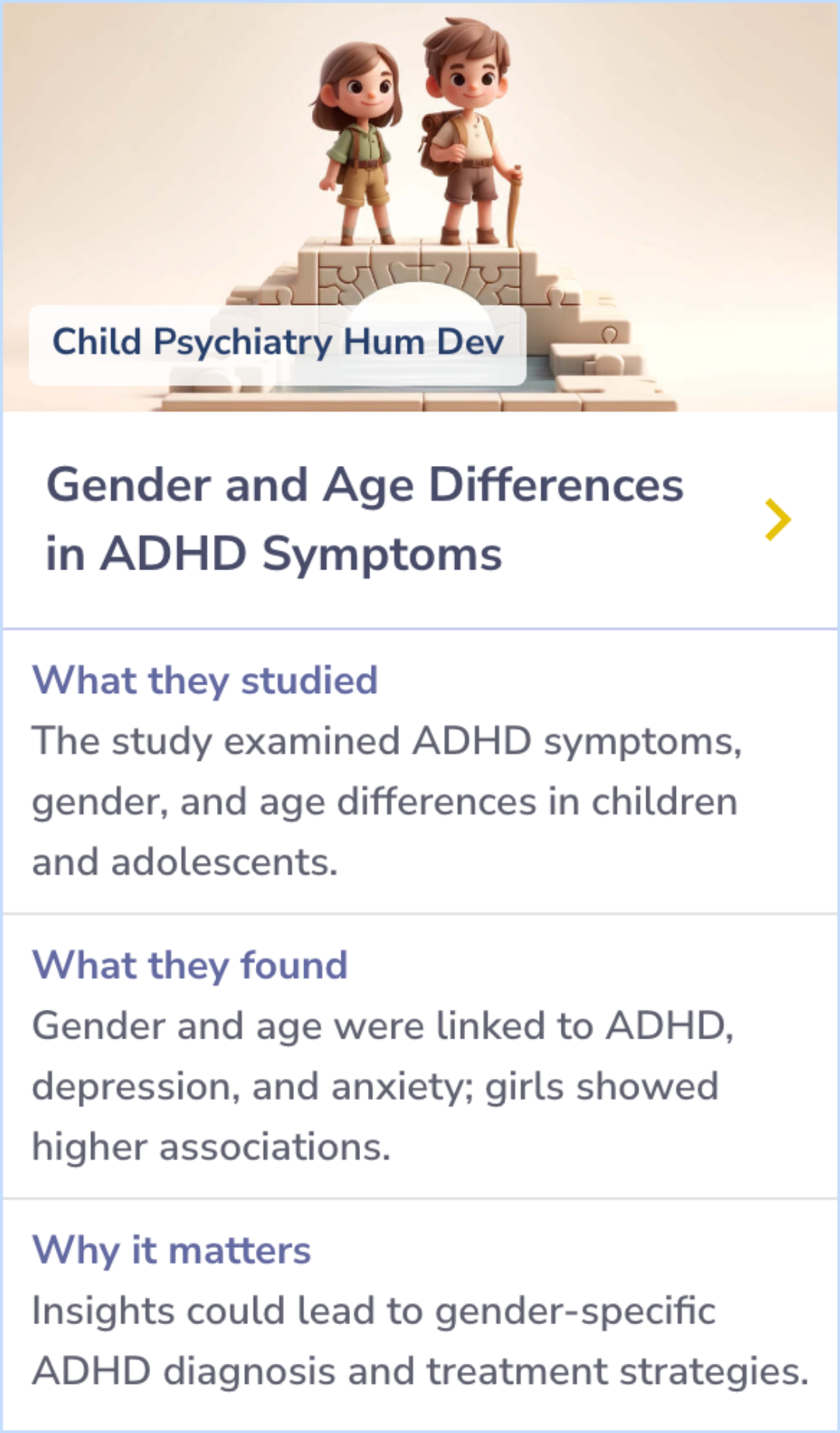
Gender and Age Differences in ADHD Symptoms and Co-occurring Depression and Anxiety Symptoms Among Children and Adolescents in the BELLA Study
Gender and Age Differences in ADHD Symptoms
December 9, 2024
author
Gilbert M, Boecker M, Reiss F, Kaman A, Erhart M, Schlack R, Westenhöfer J, Döpfner M, Ravens-Sieberer U
journal
Child Psychiatry Hum Dev
Date Published
2023 Oct 18
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
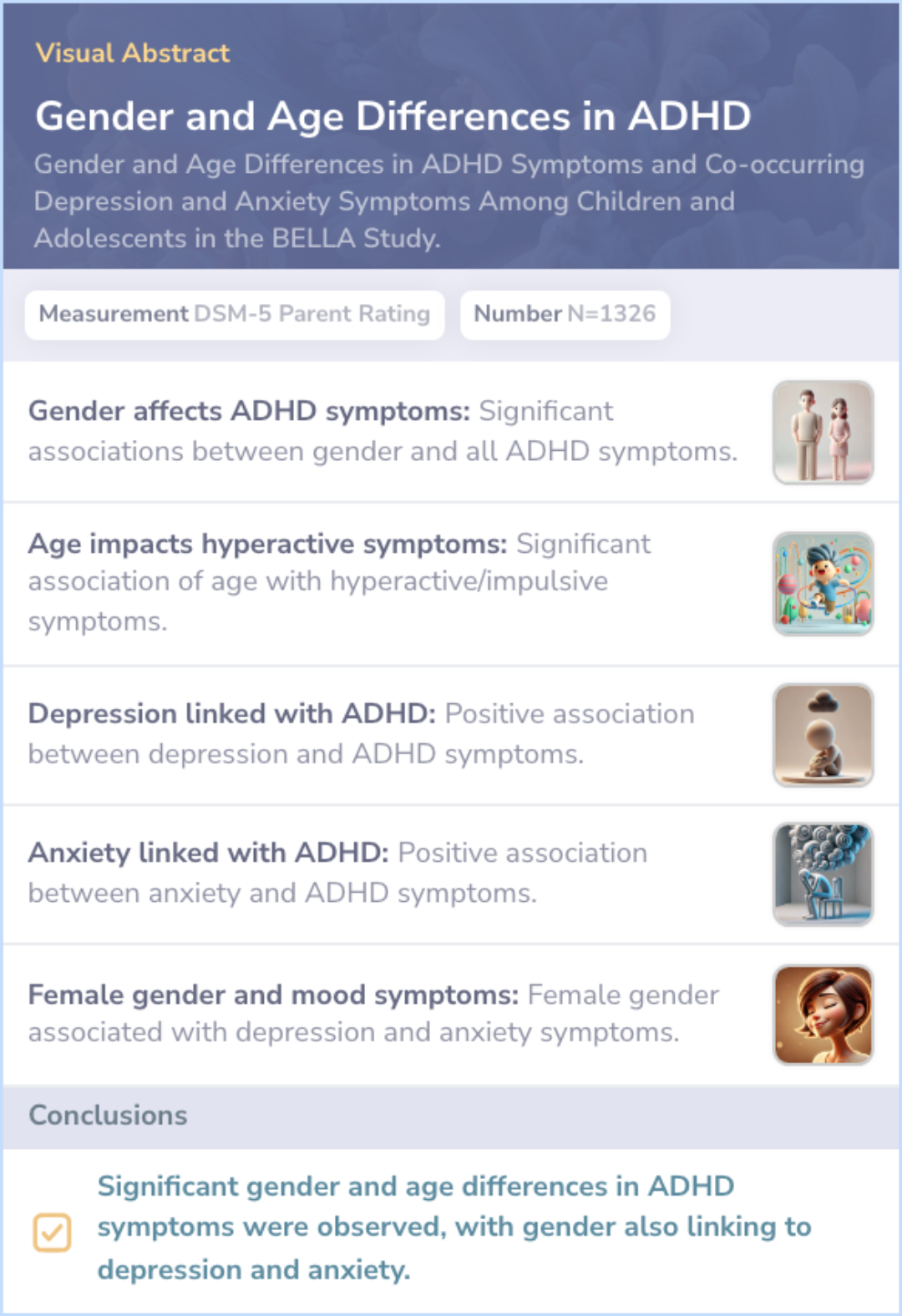
The researchers investigated gender and age differences in ADHD symptoms and their links to depression and anxiety among children and adolescents.
💡
What They Found
The study found significant associations between gender and ADHD symptoms, with age influencing hyperactive/impulsive symptoms. Depression and anxiety symptoms were more common in females with ADHD.
📚
What This Means
This research highlights the importance of considering gender-specific and age-related factors in ADHD diagnosis and treatment. Compared to other studies, this paper uniquely emphasizes the interplay of depression and anxiety with ADHD in girls.
Study Overview
Background & Objectives
ADHD, a common behavioral disorder, often appears during childhood and adolescence. Typically identified through symptoms like inattentiveness and impulsivity, ADHD varies across gender and age.
This study delves into how these symptoms manifest differently in boys and girls of various ages, complementing the BELLA study. A parent rating scale based on DSM-5 criteria helps measure these symptoms, aiming to close knowledge gaps in ADHD research.
This study delves into how these symptoms manifest differently in boys and girls of various ages, complementing the BELLA study. A parent rating scale based on DSM-5 criteria helps measure these symptoms, aiming to close knowledge gaps in ADHD research.
Abstract: background
The present study aims to fill this research gap by dimensionally evaluating gender and age differences in ADHD symptoms, as measured b...more
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers investigated the relationship between ADHD symptoms and symptoms of depression and anxiety. They used multiple linear regressions, a statistical method, to find patterns and associations. It was observed that gender has a noticeable impact on all ADHD symptoms.
Additionally, age influenced hyperactive and impulsive behaviors. The analysis revealed significant positive links between symptoms of depression, anxiety, and ADHD, with girls more likely to experience both anxiety and depression.
Additionally, age influenced hyperactive and impulsive behaviors. The analysis revealed significant positive links between symptoms of depression, anxiety, and ADHD, with girls more likely to experience both anxiety and depression.
Abstract: methods
Associations between ADHD symptoms and depression symptoms and anxiety symptoms were also examined. Multiple linear regressions reveale...more
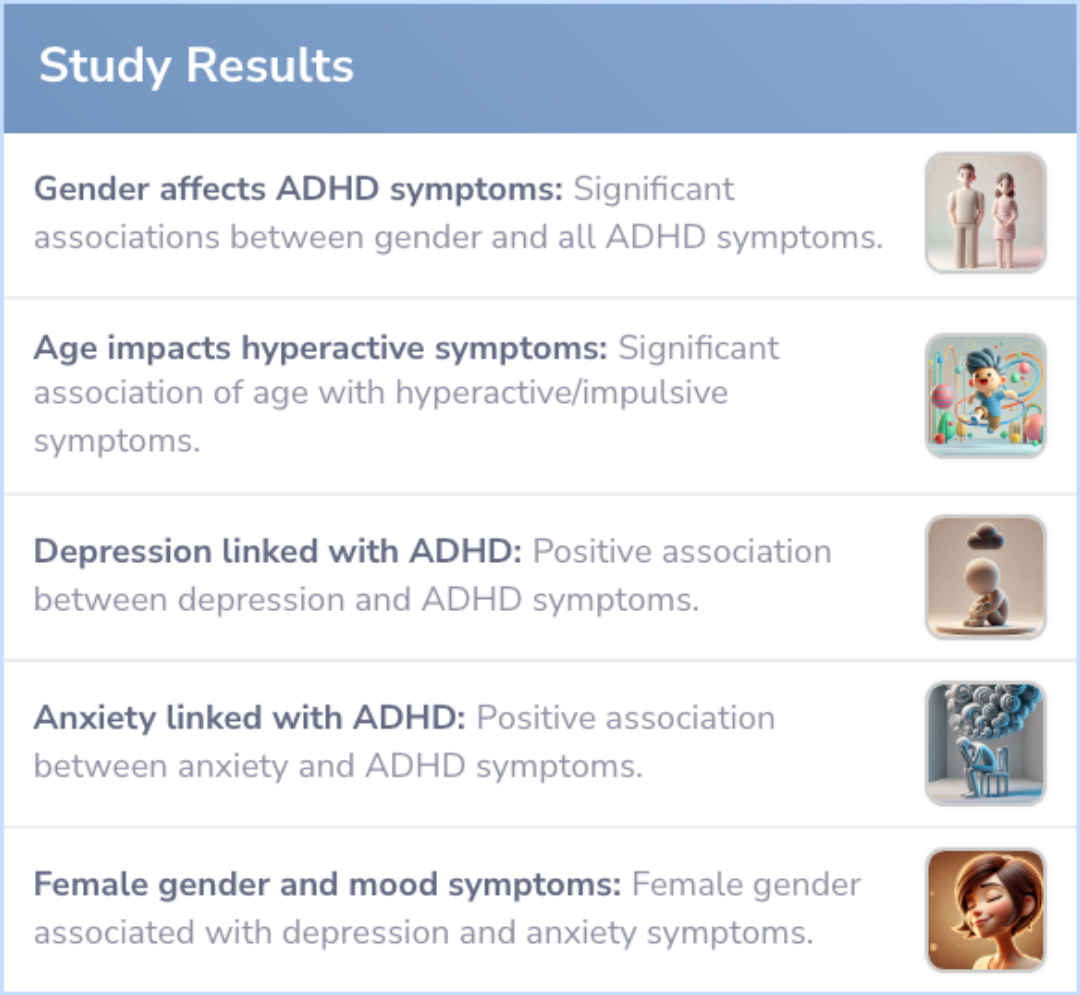
Study Results
Results
The study suggests that there is a potential need for gender-specific diagnosis and treatment approaches for ADHD. This is because males and females may exhibit ADHD symptoms differently. It also highlights the intersection of ADHD with depression and anxiety symptoms.
The evidence indicates that girls might experience these overlapping conditions more frequently, prompting a consideration for tailored therapeutic strategies.
The evidence indicates that girls might experience these overlapping conditions more frequently, prompting a consideration for tailored therapeutic strategies.
Abstract: results
These findings may suggest a need for more gender-specific approaches to ADHD diagnosis and treatment, as well as more research into th...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
The findings emphasize the value of considering gender differences when diagnosing and treating ADHD in children and adolescents. This approach might lead to better management and more effective interventions.
Furthermore, the research stresses the need for deeper investigations into how ADHD correlates with depression and anxiety to fully understand how these conditions interact and impact young individuals.
Furthermore, the research stresses the need for deeper investigations into how ADHD correlates with depression and anxiety to fully understand how these conditions interact and impact young individuals.
Abstract: conclusions
These findings may suggest a need for more gender-specific approaches to ADHD diagnosis and treatment, as well as more research into the intersections of ADHD and depression and anxiety symptoms in children and adolescents.
Clinical Guidelines
Guidelines suggest that screening for comorbid conditions like anxiety and depression is essential for children with ADHD.
Both boys and girls with ADHD often meet criteria for additional mental disorders.
Combining behavioral therapy with medication can improve treatment outcomes.
Both boys and girls with ADHD often meet criteria for additional mental disorders.
Combining behavioral therapy with medication can improve treatment outcomes.
Literature Review
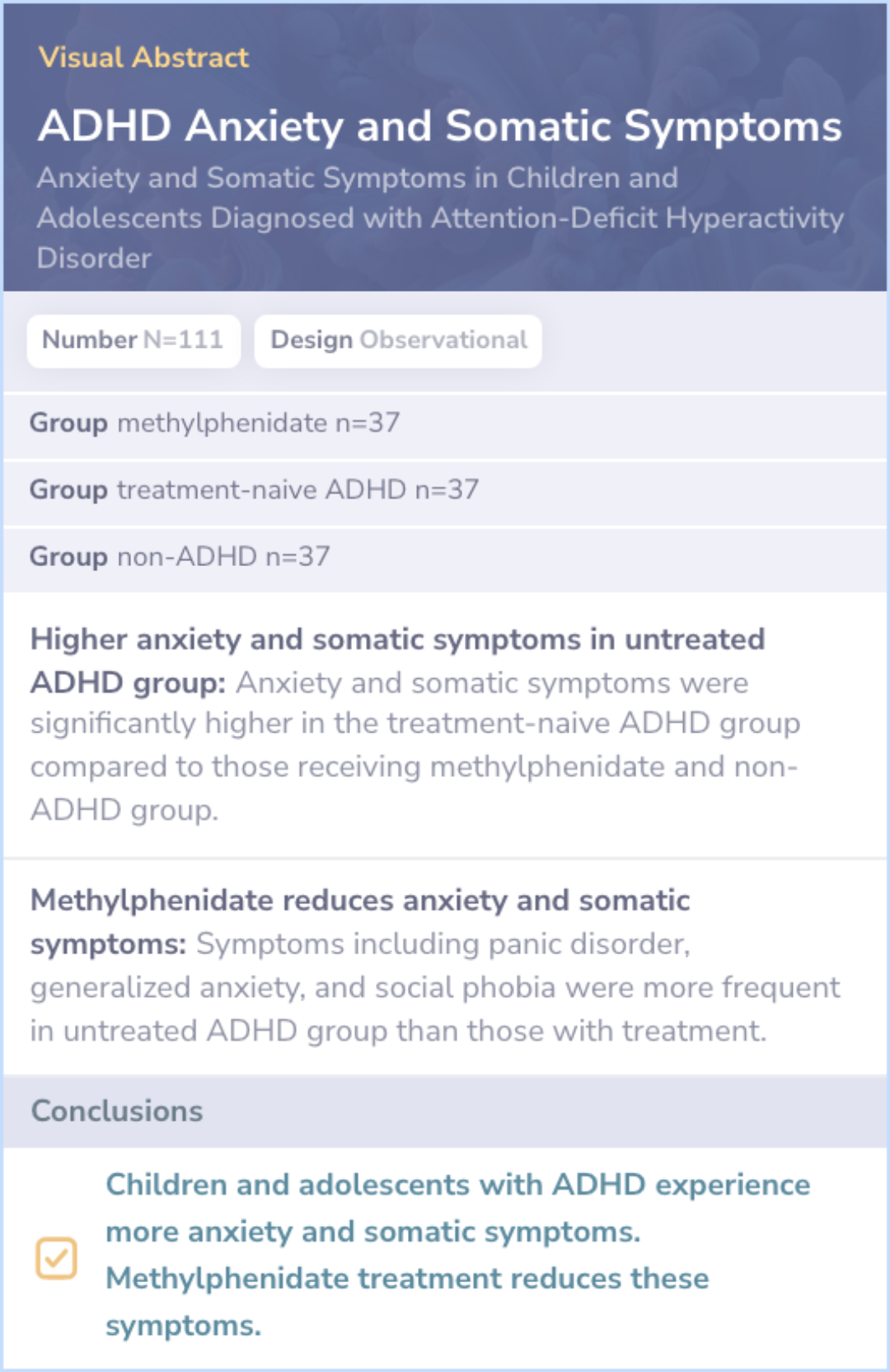
Okyar et al, 2023
Core Insight:The comparison paper underscores the prevalence of anxiety and somatic symptoms in children and adolescents with ADHD and highlights how methylphenidate treatment can reduce these symptoms. This complements the main paper's focus on gender and age differences, particularly by emphasizing how anxiety symptoms manifest alongside ADHD.
What It Adds:
Treatment Impact: Highlights methylphenidate reducing anxiety symptoms.
Somatic Symptoms: Clarifies somatic symptoms are prevalent with ADHD.
Key Differences:The main paper focuses on gender and age differences in ADHD symptoms, while this paper examines the impact of medication on anxiety and somatic symptoms.
Literature Review
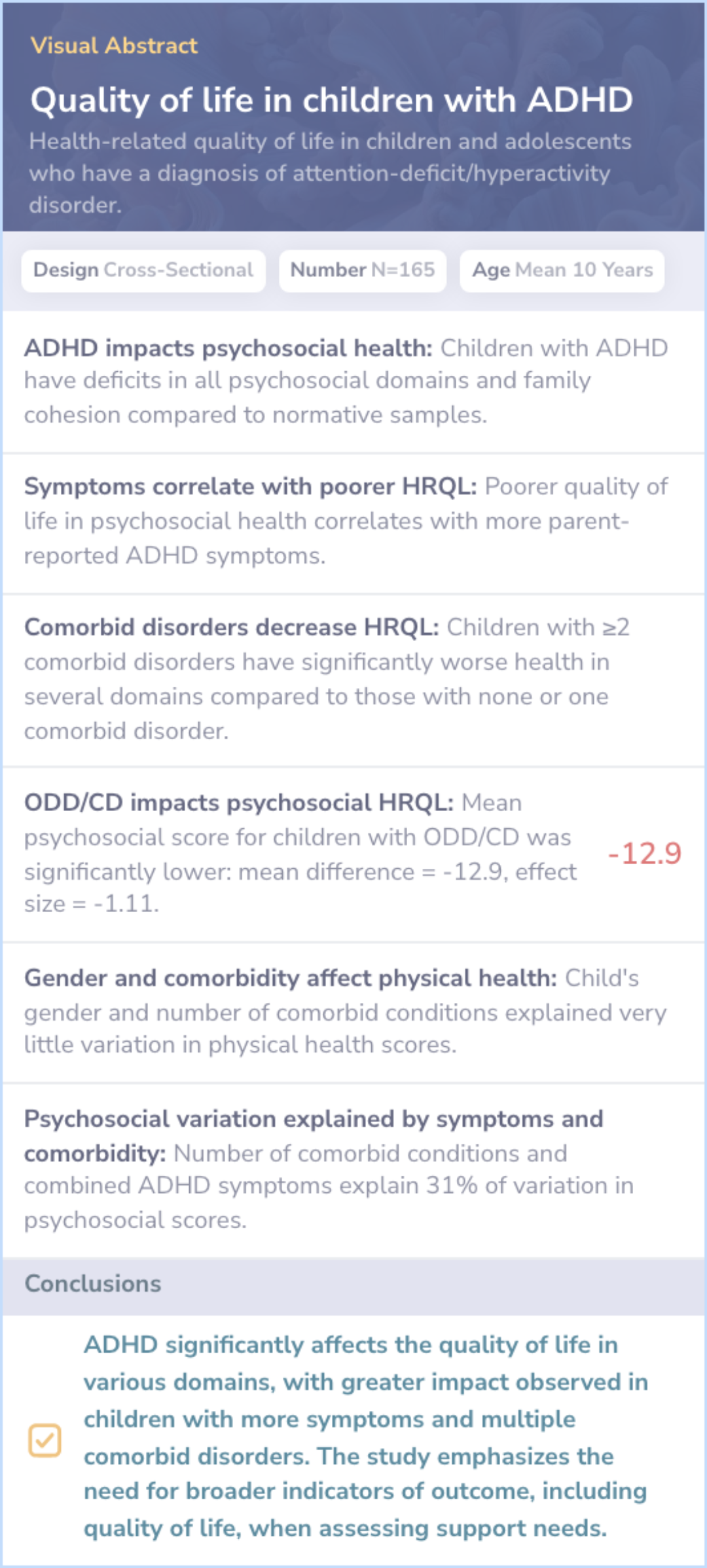
Klassen et al, 2004
Core Insight:The main paper explores gender and age differences in ADHD symptoms, while the comparison paper examines the impact of ADHD on health-related quality of life, focusing on symptom severity and comorbid conditions.
What It Adds:
HRQL Measurement: Comparison paper shows ADHD's impact on physical and psychosocial health.
Comorbidity Focus: Comparison paper links ADHD symptoms with comorbid disorders' effect on life quality.
Shared Themes:Both papers acknowledge the complexity of ADHD, involving various symptoms and conditions, and suggest improvements in diagnosis and treatment approaches.
Literature Review
[Lundervold] et al, 2016
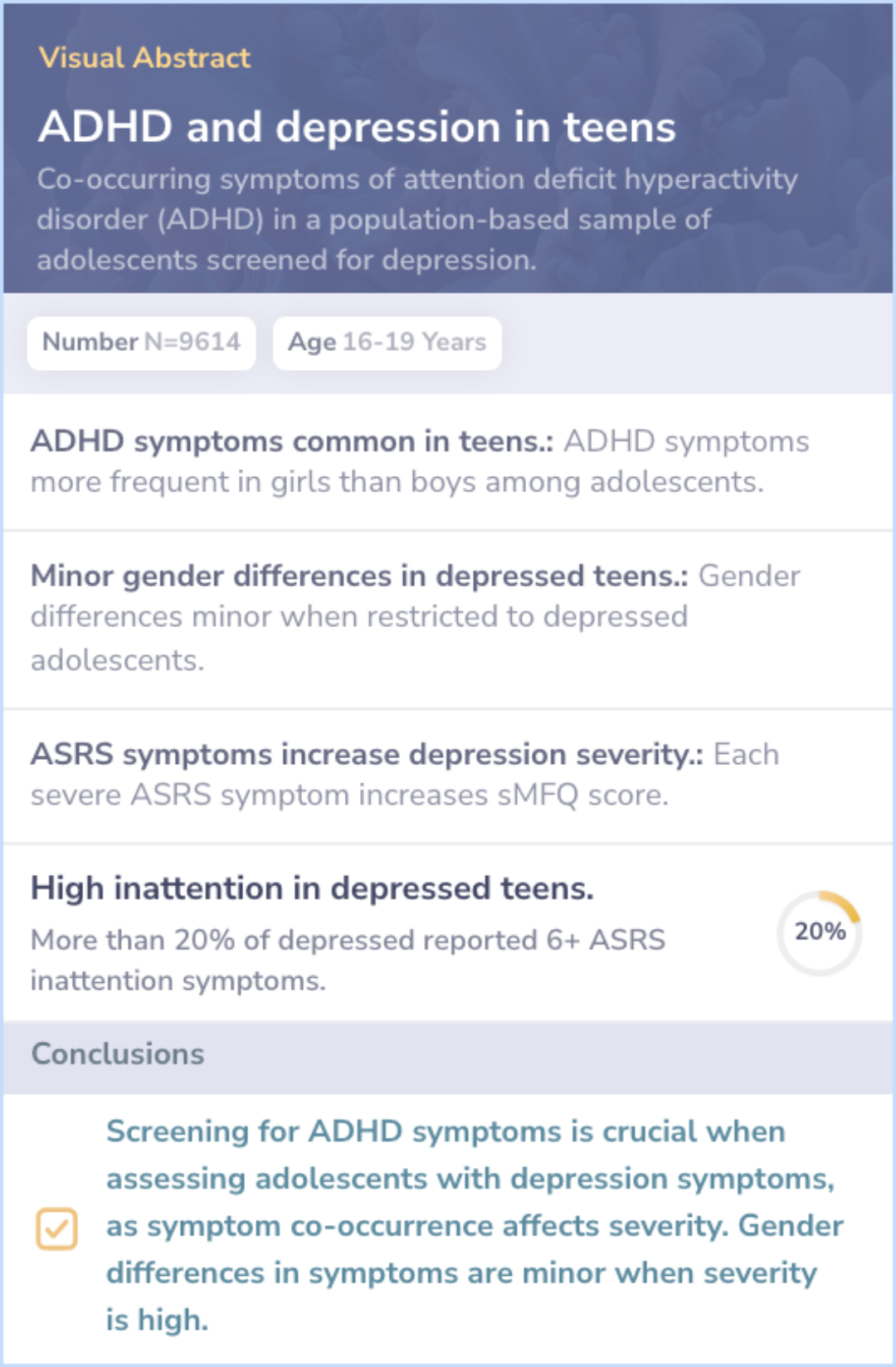
Core Insight:Both studies explore ADHD and its association with depression, highlighting the importance of investigating gender differences.
What It Adds:
Gender and ADHD: Both papers find higher ADHD symptoms in girls, but the comparison paper shows smaller differences in those with depression.
Symptom Co-occurrence: The comparison paper stresses the need to consider ADHD when evaluating depression severity in adolescents.
Shared Themes:Both papers address ADHD, gender differences, and overlap with depression, emphasizing screening requirements for accurate assessment.