Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Escitalopram in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: double-blind, placebo controlled, flexible-dose study
Escitalopram for generalized anxiety disorder
October 25, 2024
author
Davidson JR, Bose A, Korotzer A, Zheng H
journal
Depress Anxiety
Date Published
2004
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The main research question focused on evaluating the efficacy and tolerability of escitalopram in treating generalized anxiety disorder.
💡
What They Found
The study found that escitalopram (Lexapro) was significantly more effective than a placebo in reducing anxiety symptoms, with higher response rates and better improvement in scores for patients with generalized anxiety disorder.
📚
What This Means
The findings are aligned with current clinical evidence that supports the use of medications like SSRIs, such as escitalopram (Lexapro), to manage symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder effectively.
Study Summary
Study Overview
The study aimed to explore how well escitalopram works in preventing relapse for patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). It monitored patients for an extended period and highlighted that two-thirds of those on escitalopram completed the study, indicating high satisfaction.
The findings suggest a consistent effectiveness of escitalopram in long-term therapy, with minimal side effects, which could influence how GAD treatments are viewed and managed in different healthcare settings.
The findings suggest a consistent effectiveness of escitalopram in long-term therapy, with minimal side effects, which could influence how GAD treatments are viewed and managed in different healthcare settings.
Abstract: background
Escitalopram has been shown in clinical trials to improve anxiety symptoms associated with depression, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. This study was designed to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of escitalopram in the treatment of ...more

Efficacy and Satisfaction
"An indirect measure of the satisfaction of the participating patients is that two-thirds of the patients randomized to continued escitalopram remained in the study until its completion."
Long-Term Effectiveness
"In brief, there was no loss of efficacy during long-term maintenance therapy. The side-effect burden was minimal and did not constitute a clinical issue."
First Comprehensive Study
"This is the first reported controlled study that goes beyond 6 months of GAD treatment; in fact patients were monitored for up to 76 weeks."
Study Summary
Methods
Participants aged 18 and over meeting specific anxiety criteria were chosen for this study. Initially, they were given a placebo (an inactive substance) to account for psychological effects.
After this lead-in period, they received either escitalopram, starting at 10 mg per day, or a placebo for eight weeks. The key measure was the change in anxiety scores, assessed by a standardized scale.
After this lead-in period, they received either escitalopram, starting at 10 mg per day, or a placebo for eight weeks. The key measure was the change in anxiety scores, assessed by a standardized scale.
Abstract: methods
Outpatients (18 years or older) who met DSM-IV criteria for GAD, with baseline Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety (HAMA) scores > or = 18, were randomly assigned to double blind treatment with escitalopram (10 mg/day for the first 4 weeks and then fle...more
Study Summary
Results
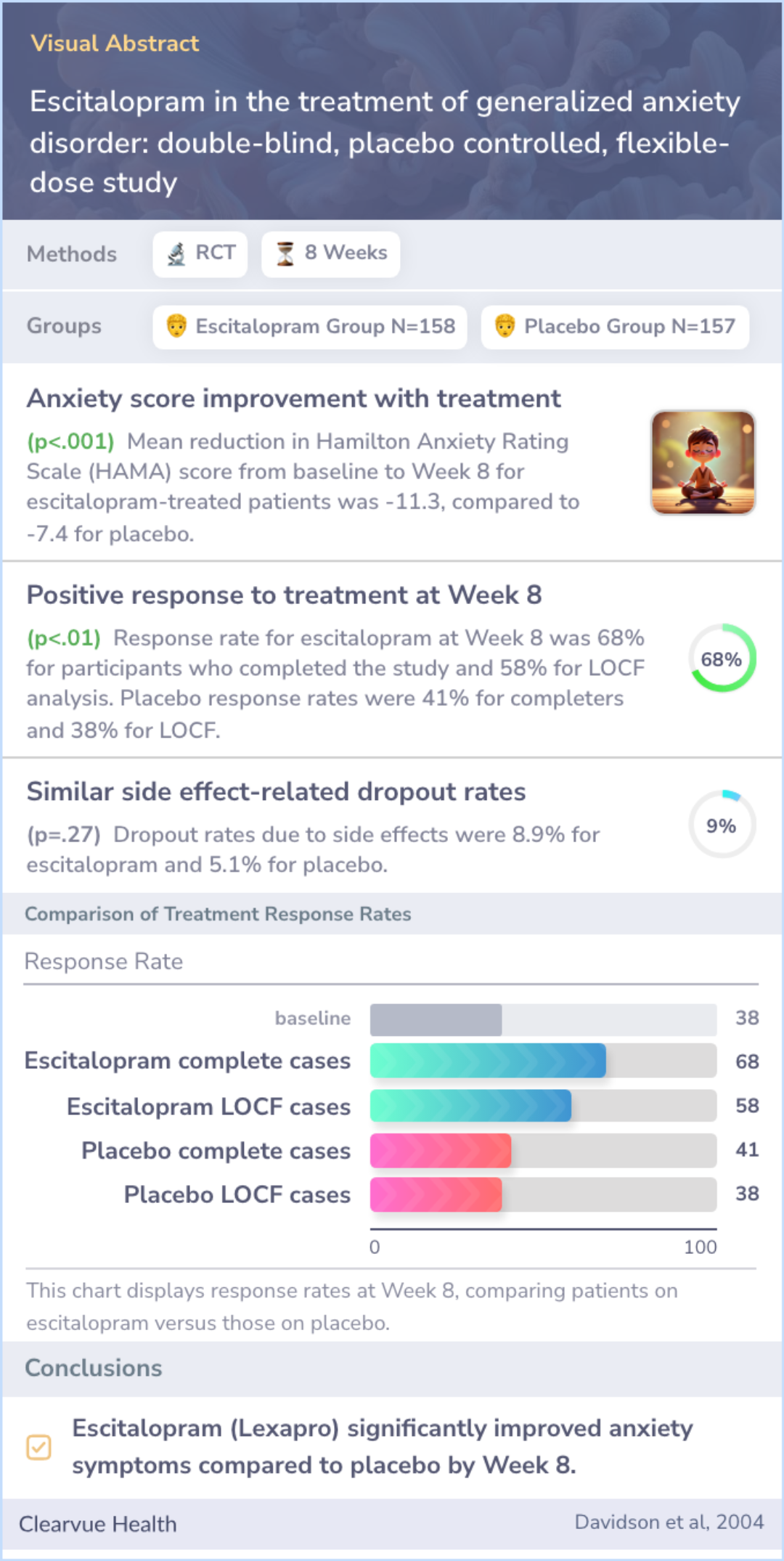
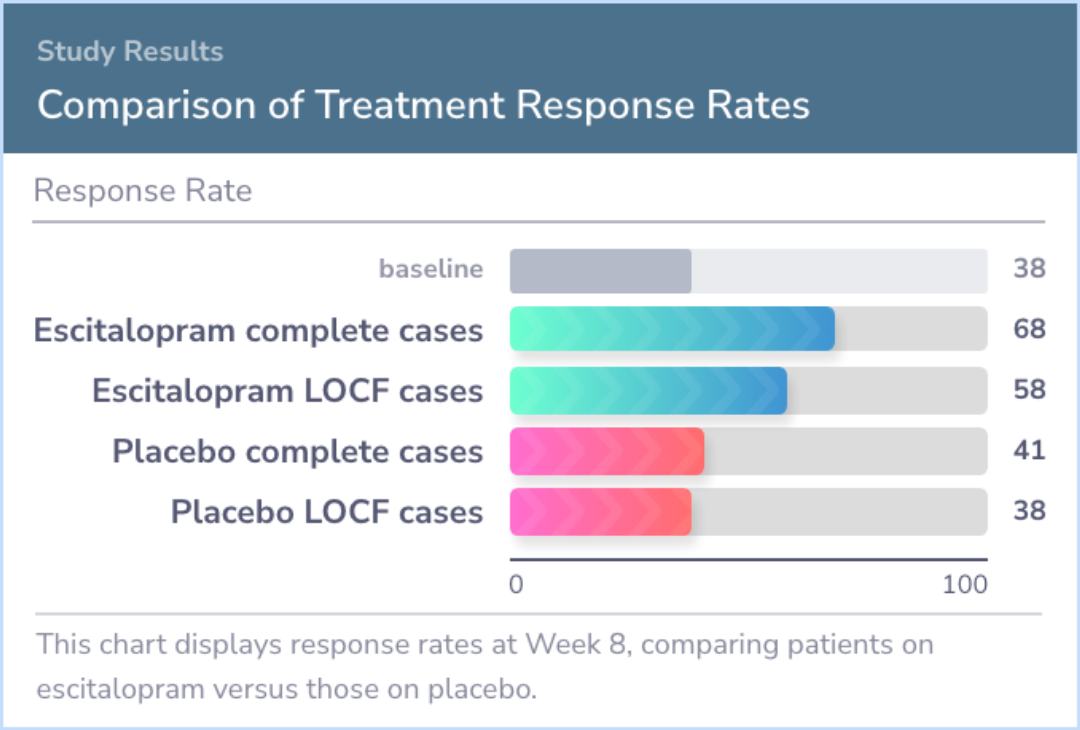
The research revealed that escitalopram led to marked improvements in anxiety compared with the placebo group. Participants taking escitalopram showed noticeable improvements in anxiety levels as early as the first week.
After eight weeks, those using escitalopram demonstrated higher response rates, with 68% showing improvement versus 41% in the placebo group. The drug was generally well-tolerated, with no significant difference in side effects causing participants to leave the study.
After eight weeks, those using escitalopram demonstrated higher response rates, with 68% showing improvement versus 41% in the placebo group. The drug was generally well-tolerated, with no significant difference in side effects causing participants to leave the study.
Abstract: results
The escitalopram group (N = 158) showed a statistically significant, and clinically relevant, greater improvement at endpoint compared with placebo (N = 157) in all prospectively defined efficacy parameters. Significant improvement in HAMA total scor...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
Escitalopram, at doses of 10 to 20 mg a day, is proven to be an effective treatment for generalized anxiety disorder. It also exhibits a favorable safety profile, with few severe side effects.
The study concludes that escitalopram provides a reliable choice for managing GAD, offering both efficacy and tolerance in patients.
The study concludes that escitalopram provides a reliable choice for managing GAD, offering both efficacy and tolerance in patients.
Abstract: conclusions
Escitalopram 10-20 mg/day is effective, safe, and well tolerated in the treatment of patients with GAD.

Background Information
Patient Guide
😟
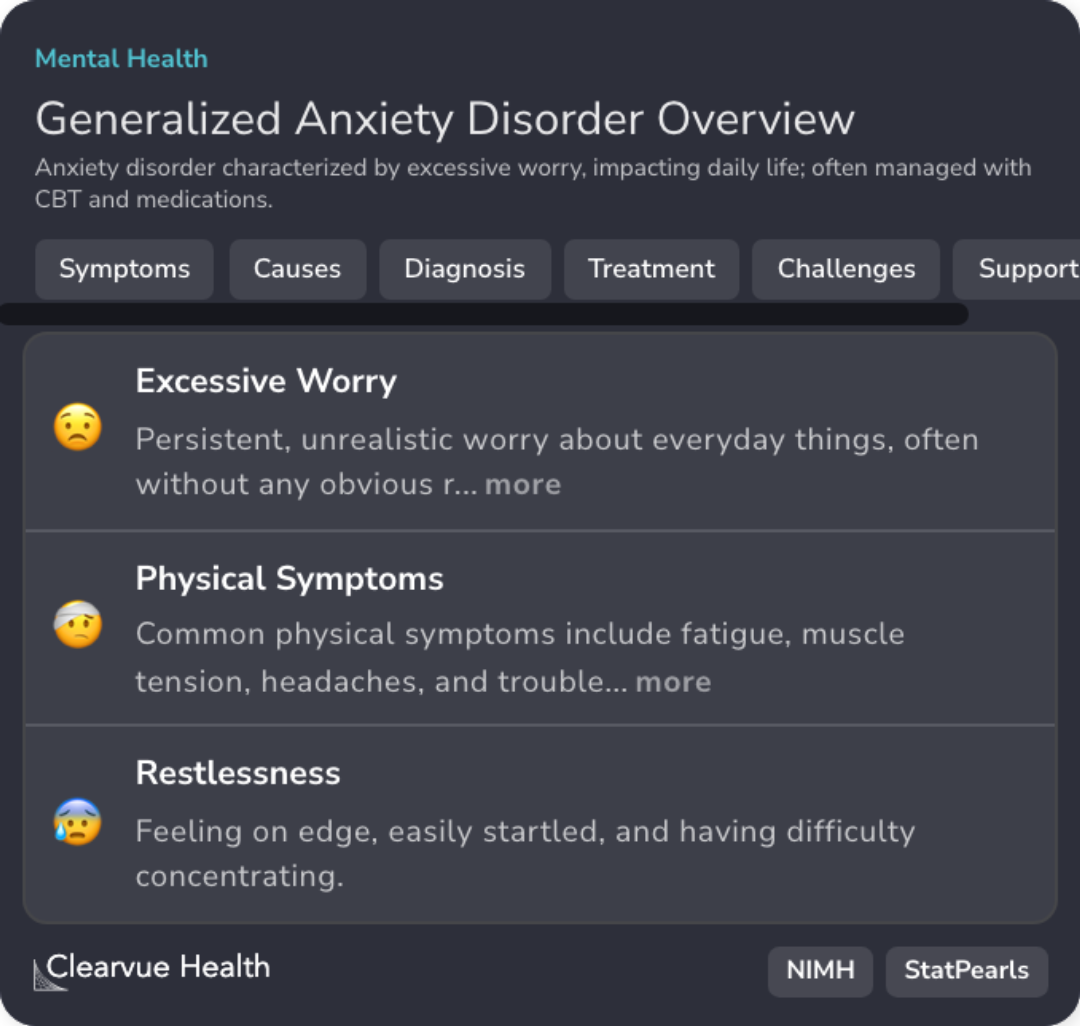
GAD Symptoms Overview
Excessive, persistent worry in GAD impacts daily life; symptoms include fatigue, tension, and restlessness.
🧠
Biological Links in GAD
Genetics and neurotransmitter imbalances play a role in GAD's biological underpinnings.
📝
GAD Diagnosis Tools
GAD-7 and DSM-5 help evaluate and diagnose GAD severity and occurrence in patients.
💊
Medications for GAD
SSRIs are common treatments for GAD, requiring management of potential side effects.
🔗
GAD and Comorbidities
GAD often coexists with depression and other disorders, complicating its treatment landscape.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Escitalopram for generalized anxiety disorder
In line with findings on escitalopram's efficacy, SSRIs and SNRIs are favored for GAD due to their tolerability and reduced side effects compared to other antidepressants.
Escitalopram, alongside other SSRIs, demonstrates effectiveness in reducing anxiety symptoms.
Pharmacotherapy, while recommended for those unable to fully engage in CBT, may benefit from buspirone augmentation when partial response is observed.
Continued SSRI treatment for a minimum of 12 months is advised to prevent relapse.
Escitalopram, alongside other SSRIs, demonstrates effectiveness in reducing anxiety symptoms.
Pharmacotherapy, while recommended for those unable to fully engage in CBT, may benefit from buspirone augmentation when partial response is observed.
Continued SSRI treatment for a minimum of 12 months is advised to prevent relapse.
Evidence Summary
Medications for Managing Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A Comparative Review
This review examines various medications for managing Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), drawing from clinical evidence and expert guidelines to assess their effectiveness and safety.
It provides insights into how each drug compares in addressing GAD symptoms, highlighting strengths and potential limitations identified in studies.
The discussion centers on treatment recommendations based on clinical data, offering a grounded perspective on the options available.
It provides insights into how each drug compares in addressing GAD symptoms, highlighting strengths and potential limitations identified in studies.
The discussion centers on treatment recommendations based on clinical data, offering a grounded perspective on the options available.
Evidence Summary
Sertraline: Benefits and Risks in Anxiety Management
Sertraline is highlighted as an option for managing generalized anxiety disorder, aiming to reduce symptoms and improve well-being. The discussion offers a straightforward look at how sertraline works to ease anxiety.
Alongside its benefits, the medication's potential side effects are outlined, providing a balanced view of its effectiveness in anxiety management.
By considering both advantages and risks, the overview delivers a complete picture of sertraline for treating anxiety.
Alongside its benefits, the medication's potential side effects are outlined, providing a balanced view of its effectiveness in anxiety management.
By considering both advantages and risks, the overview delivers a complete picture of sertraline for treating anxiety.
Evidence Summary
Transforming Anxiety: Two Effective Approaches
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers a structured approach to tackling anxiety by transforming negative thought patterns and behaviors, providing individuals with tools to challenge their anxious thoughts. In contrast, Applied Relaxation emphasizes physical techniques that promote muscle relaxation, helping to ease anxiety symptoms through controlled breathing and relaxation exercises.
Both methods provide distinct strategies for managing Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), catering to different preferences and therapeutic needs, highlighting the varied ways to address anxiety effectively.
Both methods provide distinct strategies for managing Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), catering to different preferences and therapeutic needs, highlighting the varied ways to address anxiety effectively.