Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Cross-sectional Comparison of the Epidemiology of DSM-5 Generalized Anxiety Disorder Across the Globe
Epidemiology of DSM-5 Generalized Anxiety Disorder Globally
November 25, 2024
author
Ruscio AM, Hallion LS, Lim CCW, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Al-Hamzawi A, Alonso J, Andrade LH, Borges G, Bromet EJ, Bunting B, Caldas de Almeida JM, Demyttenaere K, Florescu S, de Girolamo G, Gureje O, Haro JM, He Y, Hinkov H, Hu C, de Jonge P, Karam EG, Lee S, Lepine JP, Levinson D, Mneimneh Z, Navarro-Mateu F, Posada-Villa J, Slade T, Stein DJ, Torres Y, Uda H, Wojtyniak B, Kessler RC, Chatterji S, Scott KM
journal
JAMA Psychiatry
Date Published
May 1, 2017
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The research focused on understanding the prevalence, course, and impact of DSM-5-defined generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) across different countries.
💡
What They Found
The study found that generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is more common than previously thought, varies widely between countries, and is particularly prevalent and impairing in high-income countries.
📚
What This Means
The findings align with current evidence noting the impact of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) on daily life and underscore the serious nature of GAD, highlighting the need for global attention and research on how socioeconomic factors influence GAD.
Study Summary
Study Overview
The study aimed to deepen understanding of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), which has often been overlooked compared to other anxiety disorders. Concerned about its impact, researchers sought data across different countries, revealing that GAD is widespread and can be especially challenging in high-income nations due to competitive pressures and high expectations.
Their findings suggest that GAD is tied to socioeconomic factors, calling attention to its prevalence in various global contexts and signaling the need for more comprehensive research.
Their findings suggest that GAD is tied to socioeconomic factors, calling attention to its prevalence in various global contexts and signaling the need for more comprehensive research.
Abstract: background
To provide the first epidemiologic data on DSM-5 GAD and explore cross-national differences in its prevalence, course, correlates, and impact.

Understanding GAD
"Understanding of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) has lagged behind understanding of other anxiety disorders."
Global Context
"Attention to GAD has been especially limited outside a small number of industrialized, affluent countries in which nearly all research on the disorder has been conducted."
Public Health Significance
"These results underscore the public health significance of GAD across the globe while uncovering cross-national differences in prevalence, course, and impairment that require further investigation."
Study Summary
Methods
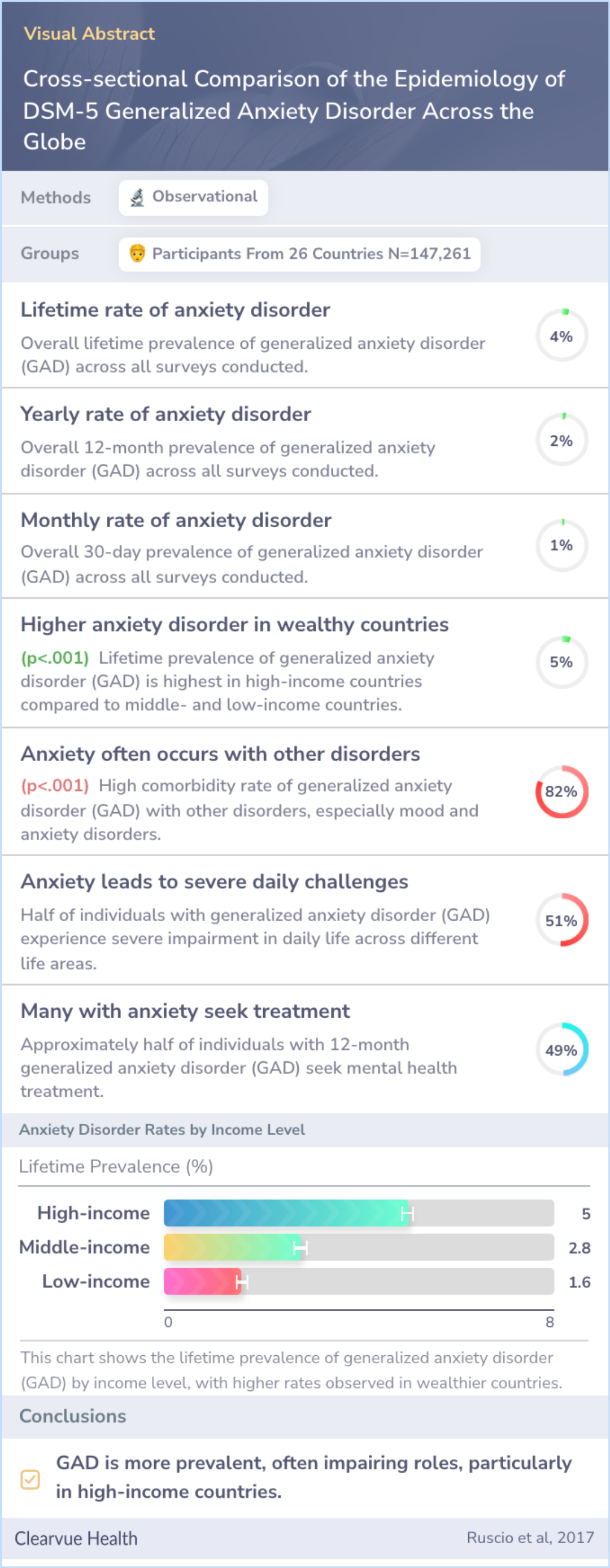
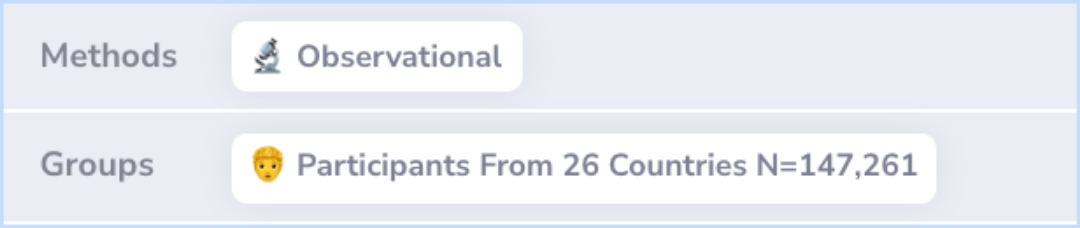
The study analyzed information from the World Health Organization’s World Mental Health Survey Initiative. Surveys were conducted in 26 different nations using standardized methods and tools. These surveys reached 147,261 adults who were interviewed in person.
The surveys took place between 2001 and 2012, with data analyzed from July 2015 to December 2016. This extensive data collection aimed to ensure a comprehensive understanding of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) across diverse populations.
The surveys took place between 2001 and 2012, with data analyzed from July 2015 to December 2016. This extensive data collection aimed to ensure a comprehensive understanding of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) across diverse populations.
Abstract: methods
Data come from the World Health Organization World Mental Health Survey Initiative. Cross-sectional general population surveys were carried out in 26 countries using a consistent research protocol and assessment instrument. A total of 147 261 adults ...more
Study Summary
Results
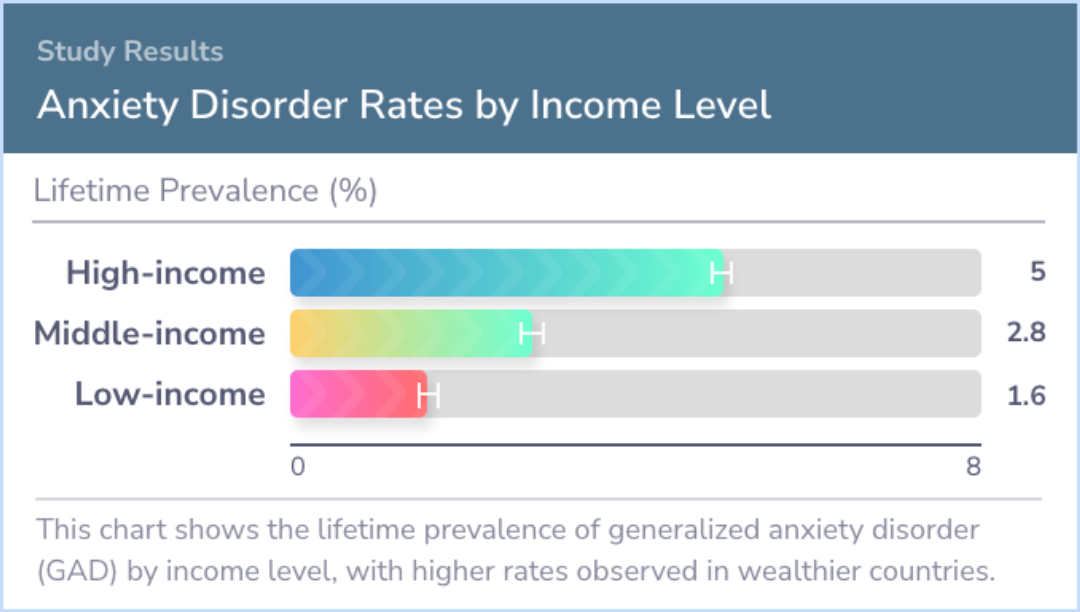
The study involved 147,261 adults aged 18 to 99, with a response rate of nearly 70%. Across the surveys, the lifetime prevalence of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) was found to be 3.7%, meaning this percentage of respondents had experienced it at some point. High-income nations reported higher rates, while low-income regions showed lower prevalence.
GAD often starts in adulthood and lingers over time, especially in less affluent countries. A high number of individuals with GAD also experience other mental health issues, and half of those affected seek treatment, with rates higher in wealthier areas.
GAD often starts in adulthood and lingers over time, especially in less affluent countries. A high number of individuals with GAD also experience other mental health issues, and half of those affected seek treatment, with rates higher in wealthier areas.
Abstract: results
Respondents were 147 261 adults aged 18 to 99 years. The surveys had a weighted mean response rate of 69.5%. Across surveys, DSM-5 GAD had a combined lifetime prevalence (SE) of 3.7% (0.1%), 12-month prevalence of 1.8% (0.1%), and 30-day prevalence o...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
The study reveals that DSM-5 GAD occurs more frequently than its predecessor and leads to significant challenges in everyday life. High-income countries, paradoxically, see more cases despite GAD often affecting those with lower socioeconomic status within these countries.
The research highlights the pressing health concern that GAD represents internationally, while also identifying different ways it manifests in various social and economic contexts, pointing to the need for targeted further research.
The research highlights the pressing health concern that GAD represents internationally, while also identifying different ways it manifests in various social and economic contexts, pointing to the need for targeted further research.
Abstract: conclusions
The findings of this study show that DSM-5 GAD is more prevalent than DSM-IV GAD and is associated with substantial role impairment. The disorder is especially common and impairing in high-income countries despite a negative association between GAD a...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
🌍
Prevalence Awareness
GAD affects millions worldwide, indicated by data from multiple countries and consistent research protocols.
📝
Diagnostic Tools
Tools like DSM-5 and GAD-7 are employed for GAD diagnosis, focusing on prolonged anxiety symptoms.
🤕
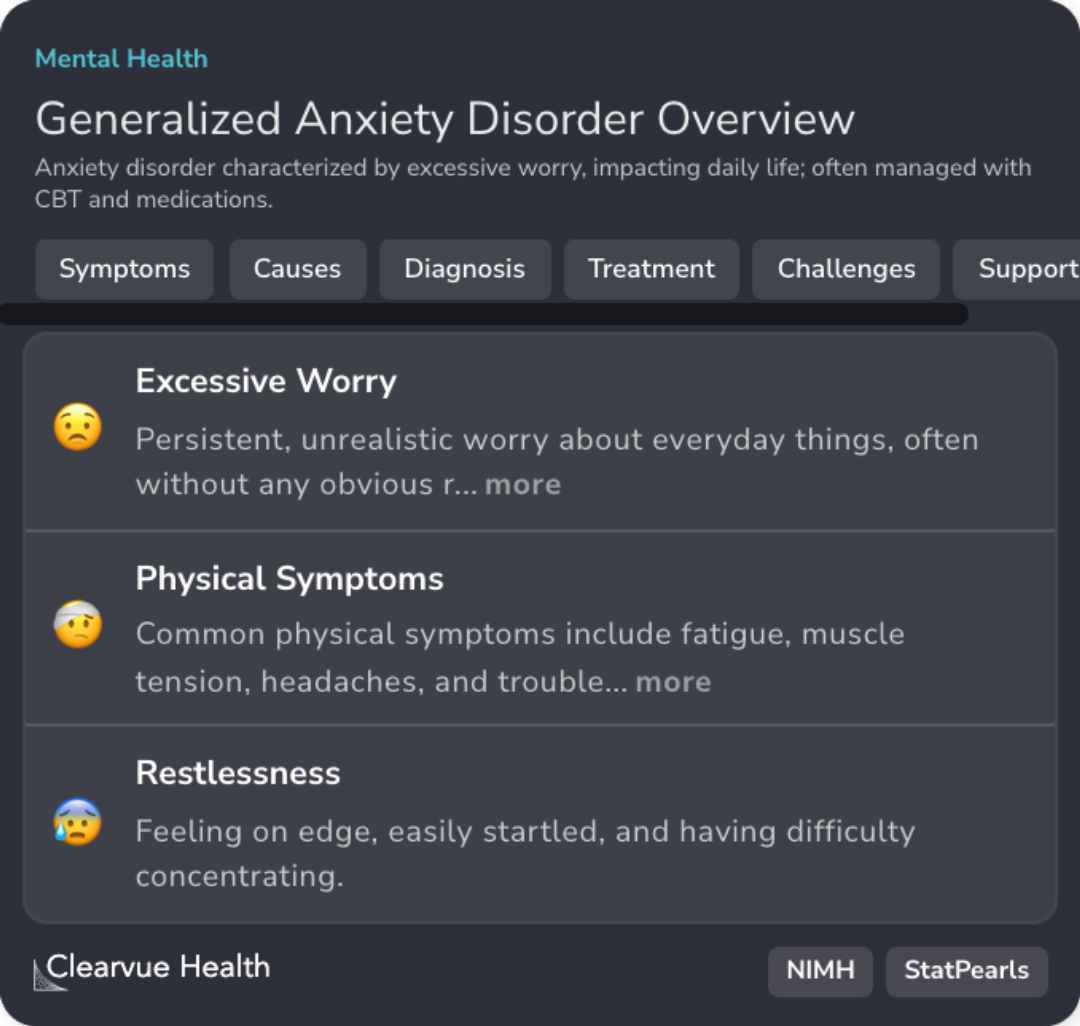
Symptoms and Impact
Physical symptoms include fatigue and muscle tension, impacting daily life and role functioning.
🧠
Complex Causes
GAD arises from genetic predispositions, neurotransmitter imbalances, and stressful environments.
💊
Treatment Approaches
Combination of CBT and medications like SSRIs is commonly recommended for managing GAD.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Epidemiology of DSM-5 Generalized Anxiety Disorder Globally
The data emphasize the global prevalence of DSM-5-defined generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), particularly its significant impact and role impairment.
GAD's chronic nature and excessive worry, often leading to severe distress, are well-documented.
This aligns with the recognition of a higher prevalence among females.
Pharmacotherapy with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), alongside cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), forms the foundation of treatment, often involving shared decision-making.
Screening is advocated yearly using tools like the GAD-7 to address frequent comorbidity with disorders such as major depressive disorder (MDD).
GAD's chronic nature and excessive worry, often leading to severe distress, are well-documented.
This aligns with the recognition of a higher prevalence among females.
Pharmacotherapy with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), alongside cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), forms the foundation of treatment, often involving shared decision-making.
Screening is advocated yearly using tools like the GAD-7 to address frequent comorbidity with disorders such as major depressive disorder (MDD).
Evidence Summary
Gender-Based Insights into Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) affects men and women differently, with notable variations in how the condition presents and persists. This analysis sheds light on gender-based differences, using comprehensive data from the NESARC to reveal unique aspects of GAD’s prevalence and characteristics across genders.
The findings underline how men and women may experience and report symptoms in distinct ways, contributing to broader insights into the disorder’s impact on each gender.
The findings underline how men and women may experience and report symptoms in distinct ways, contributing to broader insights into the disorder’s impact on each gender.
Evidence Summary
The Widespread Impact of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized Anxiety Disorder affects many people in the U.S., often making everyday tasks harder to handle. The disorder’s prevalence highlights the need to better support those facing these daily challenges.
The impact on routine activities can be significant, affecting individuals' ability to fulfill responsibilities. Awareness of this condition’s widespread reach can guide efforts in creating resources and treatments.
The impact on routine activities can be significant, affecting individuals' ability to fulfill responsibilities. Awareness of this condition’s widespread reach can guide efforts in creating resources and treatments.
Evidence Summary
Widespread Impact of Subthreshold Generalized Anxiety
Subthreshold Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) affects a significant number of individuals, presenting challenges in their daily lives. It is characterized by symptoms that don’t fully meet the diagnostic criteria for GAD but still impact well-being.
This disorder’s prevalence highlights the difficulties many face in managing persistent anxiety symptoms that interfere with routine activities without reaching full clinical severity.
This disorder’s prevalence highlights the difficulties many face in managing persistent anxiety symptoms that interfere with routine activities without reaching full clinical severity.