Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Emotional intelligence and clinical symptoms in outpatients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
Emotional intelligence and GAD symptoms
November 25, 2024
author
Lizeretti NP, Extremera N
journal
Psychiatr Q
Date Published
2011 Sep
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study investigated the relationship between emotional intelligence (EI) and clinical symptoms in psychiatric patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) compared to a control group.
💡
What They Found
They found significant correlations between certain dimensions of emotional intelligence, such as clarity and repair, and symptoms of anxiety.
📚
What This Means
These findings emphasize that emotional intelligence deficits may increase vulnerability to developing generalized anxiety disorder, aligning with evidence that GAD often coexists with other mental health issues.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to explore how emotional intelligence (EI) relates to generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Researchers found that patients with GAD often struggle to perceive emotions clearly and tend to exaggerate negative feelings.
The findings suggest that fostering emotional intelligence could be a new approach to treating GAD. By improving how patients understand and manage their emotions, therapists might help them cope better with anxiety in the future.
The findings suggest that fostering emotional intelligence could be a new approach to treating GAD. By improving how patients understand and manage their emotions, therapists might help them cope better with anxiety in the future.
Abstract: background
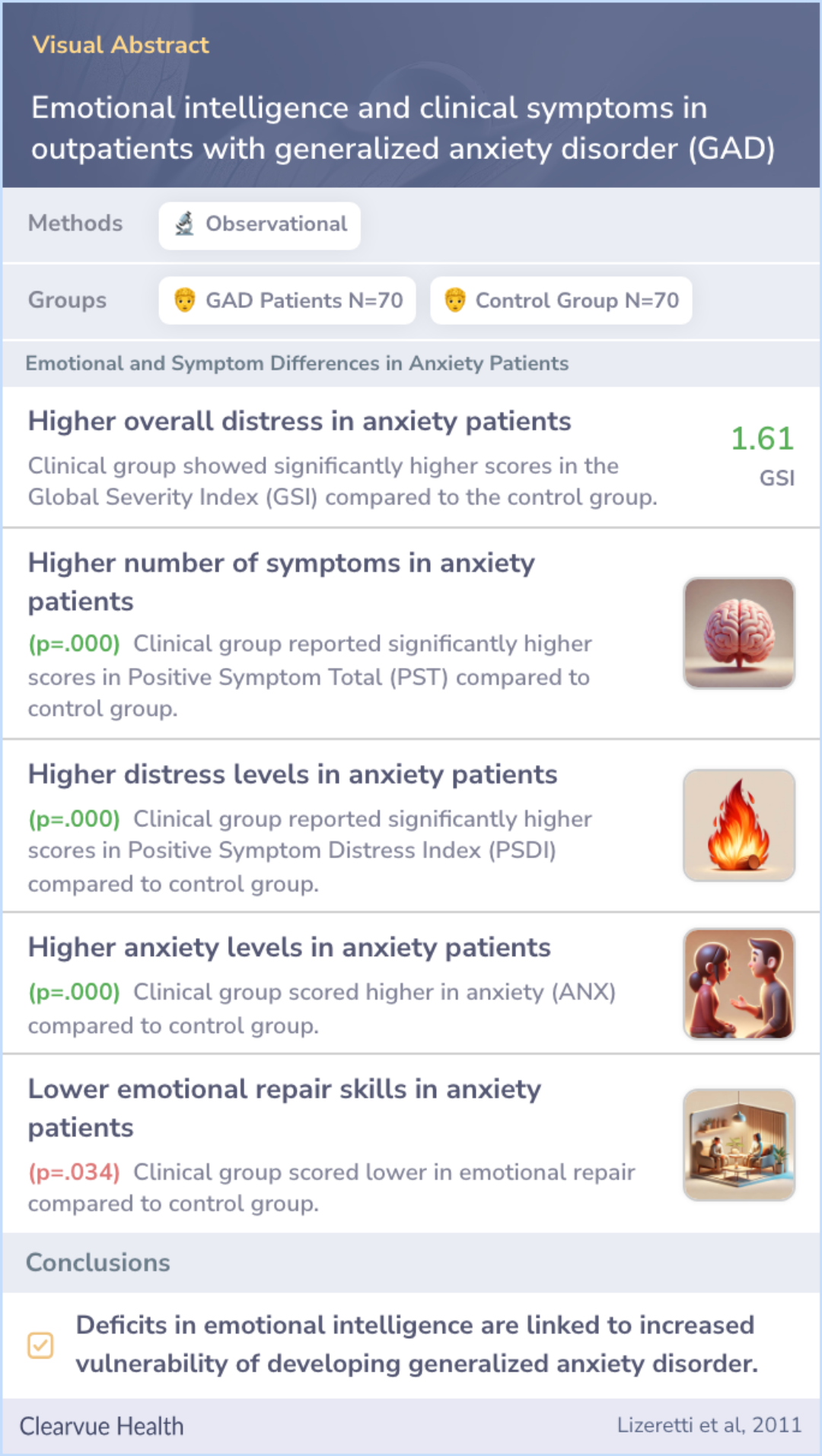
The present study aimed to investigate the relationship between EI and clinical symptoms in a group of psychiatric patients with GAD compared to the control group.

Emotional Regulation Issues
"The findings suggest that patients with GAD have difficulty in perceiving emotional experiences clearly and have a tendency to intensify the experience and expression of negative emotions, indicating considerable problems with emotional regulation."
Vulnerability Factor
"Our results provide preliminary evidence suggesting that deficit of the ability to attend to, discriminate among, and manage emotions might represent a vulnerability factor in the development of GAD, in accordance with other studies."
Therapeutic Implications
"One of the main advantages of the Salovey and Mayer EI model is that the authors proposed that EI abilities can be learned and developed, which has implications for prevention and treatment in clinical populations."
Study Summary
Methods
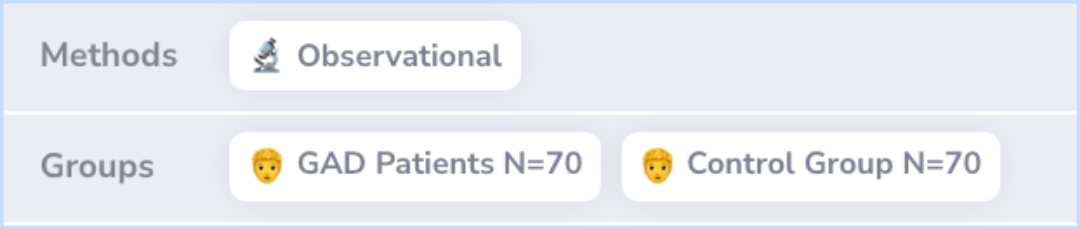
Researchers conducted a study with 140 participants, half of whom were patients diagnosed with GAD. These participants were mostly female. They completed questionnaires that measured their emotional intelligence and clinical symptoms.
This approach, known as a cross-sectional study, aims to capture a snapshot of these characteristics at one point in time, helping researchers see immediate relationships between EI and anxiety symptoms.
This approach, known as a cross-sectional study, aims to capture a snapshot of these characteristics at one point in time, helping researchers see immediate relationships between EI and anxiety symptoms.
Abstract: methods
Seventy outpatients (82.9% female) with a DSM-IV-TR diagnosis of GAD and 70 control individuals (72.9% female) completed self-report instruments assessing EI and clinical symptoms in a cross-sectional study.
Study Summary
Results
Findings revealed noticeable connections between specific areas of emotional intelligence, like clarity and repair, and anxiety symptoms. Specifically, abilities like understanding emotions clearly and addressing emotional distress stood out.
The study highlighted that those with lower EI abilities were more likely to display anxiety symptoms, suggesting these EI deficits could make individuals susceptible to GAD, offering a potential vulnerability link.
The study highlighted that those with lower EI abilities were more likely to display anxiety symptoms, suggesting these EI deficits could make individuals susceptible to GAD, offering a potential vulnerability link.
Abstract: results
Significant correlations were observed between EI dimensions such as clarity (r = .327) and repair (r = .405) and symptoms of anxiety. Also, the dimensions of attention and repair allowed a clear discrimination between clinical patients and control g...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
The research concluded that lacking emotional intelligence skills might play a role in developing Generalized Anxiety Disorder. This vulnerability can heighten the chances of experiencing anxiety-related issues.
These outcomes suggest bolstering EI skills could be beneficial in preventing or managing GAD, providing new directions for therapy and intervention aimed at improving emotional skills.
These outcomes suggest bolstering EI skills could be beneficial in preventing or managing GAD, providing new directions for therapy and intervention aimed at improving emotional skills.
Abstract: conclusions
The present study showed that deficits in EI abilities were a vulnerability factor in the development of GAD.

Background Information
Patient Guide
🧠
Emotional Intelligence in Mental Health
Deficits in EI can increase vulnerability to anxiety disorders, impacting diagnosis and treatment approaches.
🤕
Symptoms of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
GAD often presents with physical symptoms like fatigue and restlessness, complicating emotional regulation.
📅
Diagnosing GAD
DSM-5 criteria and tools like GAD-7 help identify excessive worry and other symptoms of anxiety disorders.
💊
Treatment of GAD
Effective management includes therapy and medications, addressing both emotional and physical symptoms.
🌍
Causes and Comorbidities in GAD
Genetics, environmental stressors, and related mental disorders contribute to the complex presentation of GAD.
Professional Guide
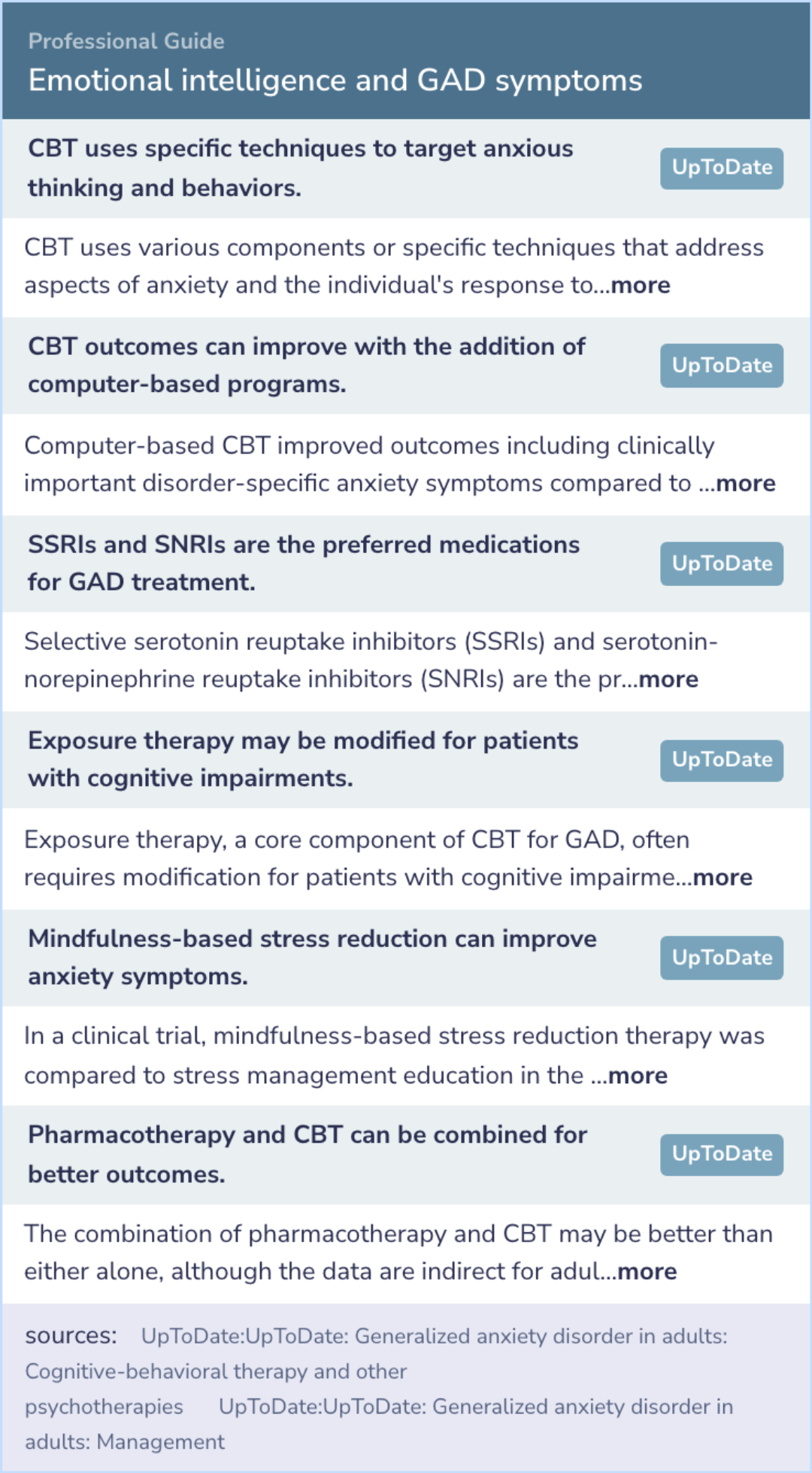
Expert Opinion: Emotional intelligence and GAD symptoms
The study highlights the role of emotional intelligence deficits in GAD, drawing attention to tailored psychotherapy techniques.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) incorporates patient education, relaxation training, and cognitive restructuring, efficiently targeting anxious thinking patterns.
Combining SSRIs or SNRIs with CBT enhances treatment efficacy.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction also yielded significant symptom improvements in clinical settings.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) incorporates patient education, relaxation training, and cognitive restructuring, efficiently targeting anxious thinking patterns.
Combining SSRIs or SNRIs with CBT enhances treatment efficacy.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction also yielded significant symptom improvements in clinical settings.
Evidence Summary
Emotion Regulation and Its Role in Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders often come with challenges in managing emotions. These difficulties can amplify the severity of anxiety symptoms, making it harder for individuals to cope. The relationship between emotional regulation and anxiety is significant.
Emotion regulation issues frequently contribute to worsening anxiety symptoms. Addressing these challenges may guide efforts to improve care and offer more effective treatments for those living with anxiety.
Emotion regulation issues frequently contribute to worsening anxiety symptoms. Addressing these challenges may guide efforts to improve care and offer more effective treatments for those living with anxiety.
Evidence Summary
Perseverative Thought Patterns in GAD and MDD
People with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) tend to engage in repetitive negative thinking, called perseverative thought. This pattern involves dwelling on negative topics repeatedly.
The research highlights a strong connection between perseverative thought and these mental health conditions, showing that individuals with GAD and MDD often get stuck in these thought loops, which may intensify their symptoms.
The research highlights a strong connection between perseverative thought and these mental health conditions, showing that individuals with GAD and MDD often get stuck in these thought loops, which may intensify their symptoms.
Evidence Summary
Exploring GAD: Symptoms and Coping Strategies
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) can manifest in many ways, from persistent worry to overwhelming stress that affects daily life. The article highlights how GAD impacts individuals, exploring common symptoms like restlessness and difficulty concentrating.
It also offers an overview of treatments and coping methods, focusing on therapeutic interventions and strategies that can help manage GAD's effects over time, including counseling and relaxation techniques.
It also offers an overview of treatments and coping methods, focusing on therapeutic interventions and strategies that can help manage GAD's effects over time, including counseling and relaxation techniques.