Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Emotion Regulation Therapy for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Emotion Regulation Therapy for GAD
September 30, 2024
author
Fresco DM, Mennin DS, Heimberg RG, Ritter M
journal
Cogn Behav Pract
Date Published
2013 Aug
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
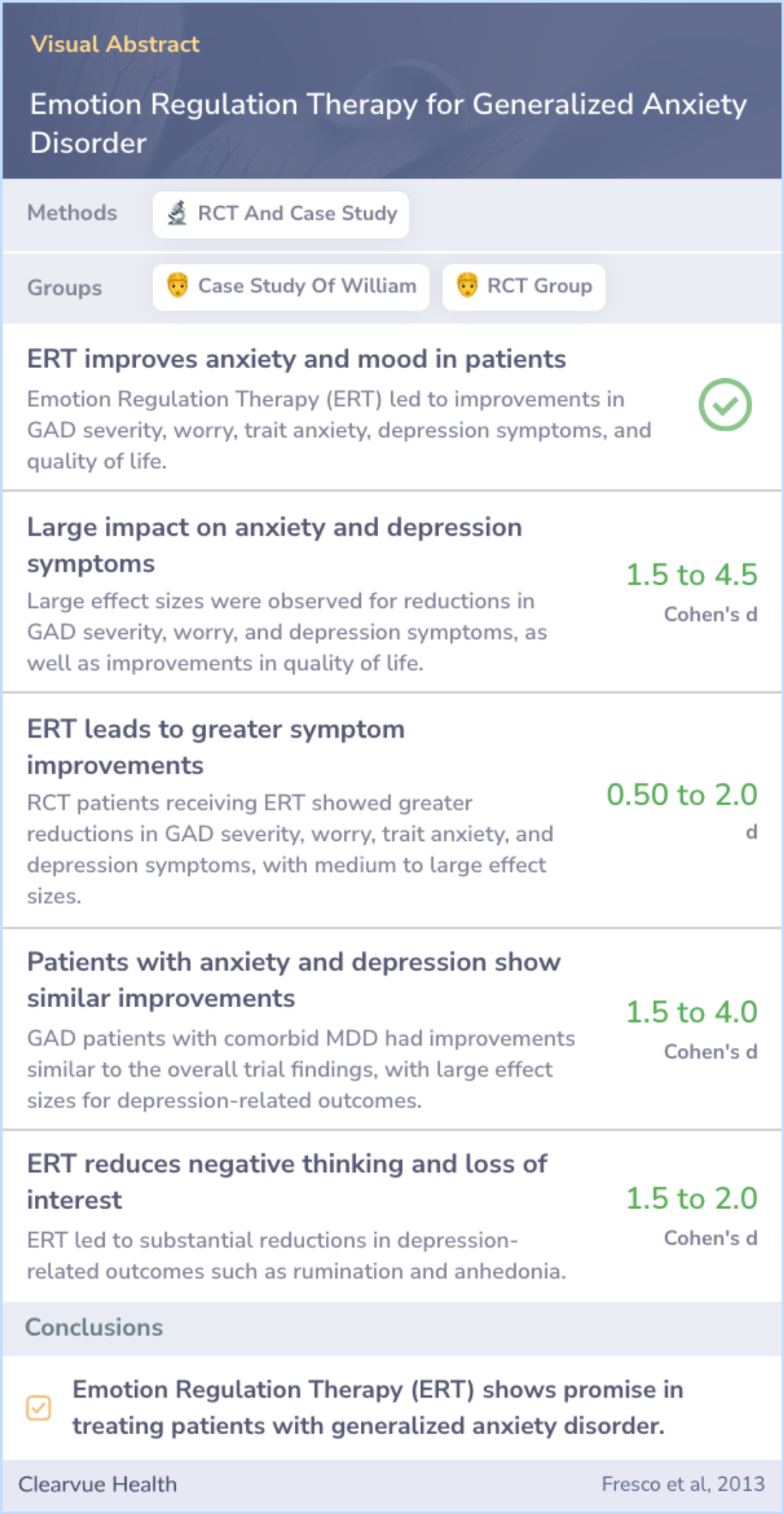
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers studied the effectiveness of Emotion Regulation Therapy (ERT) for patients with generalized anxiety disorder who do not respond well to traditional cognitive behavioral therapies (CBT).
💡
What They Found
They found considerable preliminary evidence supporting the utility of Emotion Regulation Therapy (ERT) for treating patients with generalized anxiety disorder.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that Emotion Regulation Therapy (ERT) may be a useful alternative for patients with generalized anxiety disorder who do not benefit from traditional CBT, aligning with current guidelines that recommend multiple treatment approaches for GAD.
Study Summary
Study Overview
Emotion Regulation Therapy (ERT) combines different methods to help people manage their emotions better, especially those with anxiety and depression. The study shows that emotions can serve important purposes, but sometimes they can be overwhelming. By understanding how emotions work and teaching new skills, ERT aims to help individuals respond better to their feelings, promoting a more balanced, fulfilling life.
The findings highlight how ERT targets the root issues behind these distressing feelings and offers hope for improved mental health treatment.
The findings highlight how ERT targets the root issues behind these distressing feelings and offers hope for improved mental health treatment.
Abstract: background
Despite the success of cognitive behavioral therapies (CBT) for emotional disorders, a sizable subgroup of patients with complex clinical presentations, such as patients with generalized anxiety disorder, fails to evidence adequate treatment response...more

Understanding ERT's Framework
"Emotion Regulation Therapy (ERT) integrates facets of traditional and contemporary cognitive behavioral therapies (CBTs), mindfulness, and emotion-focused interventions within a framework that reflects basic and translational findings in affect science."
The Core of ERT
"The goal of ERT is to teach clients to improve attendance to their motivational states and learn alternatives to reactive responses including worry, rumination, self-criticism, compulsive behaviors, and reassurance seeking."
Comprehensive Approach
"The integration of mindfulness and emotion-focused interventions with CBT offers a more comprehensive approach to treating emotional disorders like GAD."
Study Summary
Methods
ERT targets specific patterns of motivational dysfunction and helps patients develop emotion regulation skills. Preliminary evidence for this approach comes from both open and randomized controlled psychotherapy trials.
These trials have shown promising results in terms of ERT's utility and effectiveness, as well as the mechanisms underlying its therapeutic benefits.
These trials have shown promising results in terms of ERT's utility and effectiveness, as well as the mechanisms underlying its therapeutic benefits.
Abstract: methods
ERT is a mechanism-targeted intervention focusing on patterns of motivational dysfunction while cultivating emotion regulation skills. Open and randomized controlled psychotherapy trials have demonstrated considerable preliminary evidence for the uti...more

Study Summary
Results
The article illustrates the application of ERT through the case study of 'William.' It provides a detailed case-conceptualization of William from an ERT standpoint.
Additionally, it outlines the stages and progress of ERT in William's treatment, showcasing how ERT addresses his specific emotional and motivational challenges.
Additionally, it outlines the stages and progress of ERT in William's treatment, showcasing how ERT addresses his specific emotional and motivational challenges.
Abstract: results
This article provides an illustration of ERT through the case of “William.” In particular, this article includes a case-conceptualization of William from an ERT perspective while describing the flow and progression of the ERT treatment approach.
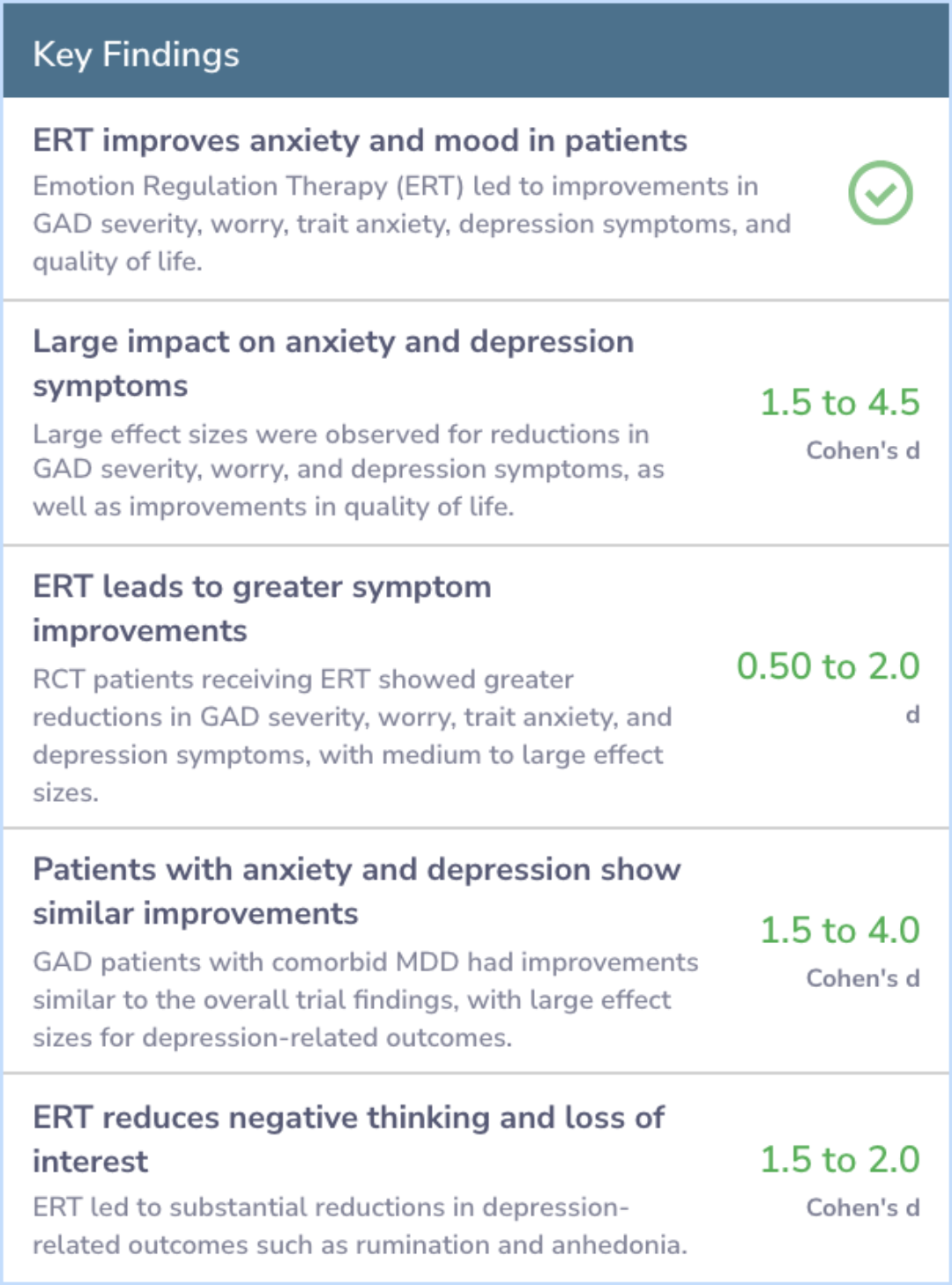
Study Summary
Conclusions
The article serves as a practical demonstration of ERT using the example of 'William.' It offers insights into how ERT can be tailored to individual cases.
By describing William's case in detail, the article highlights the flow and progression of the ERT treatment approach, emphasizing its potential benefits for patients with complex emotional disorders.
By describing William's case in detail, the article highlights the flow and progression of the ERT treatment approach, emphasizing its potential benefits for patients with complex emotional disorders.
Abstract: conclusions
This article provides an illustration of ERT through the case of 'William.' In particular, this article includes a case-conceptualization of William from an ERT perspective while describing the flow and progression of the ERT treatment approach.

Background Information
Patient Guide
😟
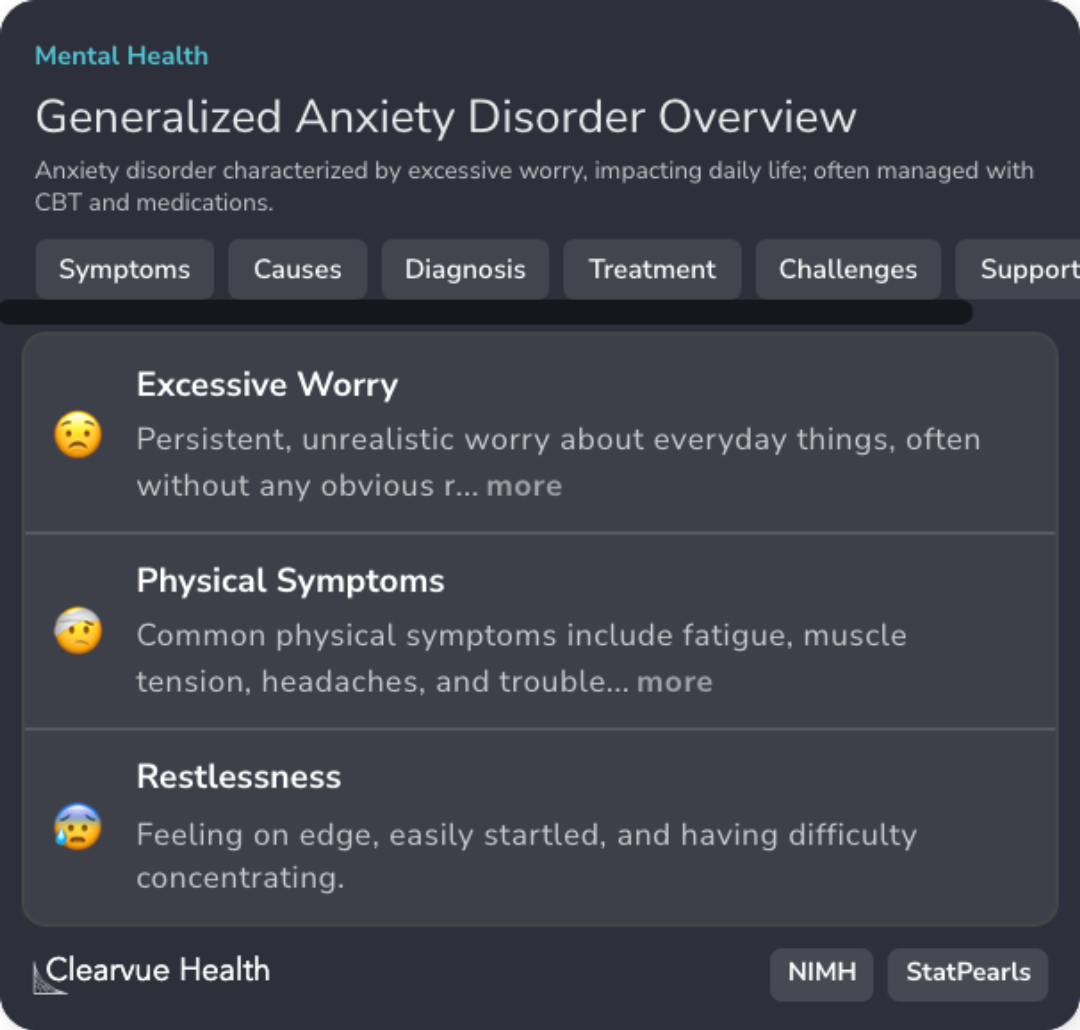
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Overview
Anxiety disorder characterized by excessive worry, impacting daily life; often managed with CBT and medications.
🧠
Biological and Environmental Causes
GAD arises from genetic predispositions, neurotransmitter imbalances, and environmental factors such as trauma and substance use.
📅
DSM-5 and Screening Tools
Diagnosing GAD requires excessive anxiety for 6 months, aided by tools like the GAD-7 for symptom severity.
🔗
Multimodal Treatment Approaches
Effective GAD management often involves a combination of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and medications such as SSRIs.
⚖️
Challenges in Managing GAD
Treatment compliance issues, comorbidities like depression, and the chronic nature of GAD complicate effective management.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Emotion Regulation Therapy for GAD
In line with current research, diagnosing generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) requires at least six months of persistent and uncontrollable worry.
SSRIs and SNRIs often serve as the first line of pharmacological treatment.
GAD's frequent comorbidity with major depression necessitates careful assessment.
Combining CBT techniques like cognitive restructuring with pharmacotherapy may offer superior outcomes.
Recognizing physical symptoms such as muscle tension is essential in treatment planning.
SSRIs and SNRIs often serve as the first line of pharmacological treatment.
GAD's frequent comorbidity with major depression necessitates careful assessment.
Combining CBT techniques like cognitive restructuring with pharmacotherapy may offer superior outcomes.
Recognizing physical symptoms such as muscle tension is essential in treatment planning.
Evidence Summary
CBT and Mindfulness: Boosting Anxiety Control Through Practice
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is shown to help manage anxiety by actively changing negative thought patterns. Integrating mindfulness into therapy boosts its impact, leading to better control over symptoms when practiced regularly.
Together, CBT and mindfulness empower individuals to improve anxiety management through consistent practice, allowing them to build more effective coping strategies over time.
Together, CBT and mindfulness empower individuals to improve anxiety management through consistent practice, allowing them to build more effective coping strategies over time.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Thought-Based and Relaxation Techniques for GAD
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) targets negative thought patterns that fuel anxiety, teaching individuals to reshape how they think and act. On the other hand, Applied Relaxation provides muscle relaxation techniques, focusing on physical responses to stress. Both therapies aim to reduce anxiety symptoms, but each approaches the problem from different angles.
CBT reshapes thoughts, while Applied Relaxation emphasizes physical calmness to manage Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD).
CBT reshapes thoughts, while Applied Relaxation emphasizes physical calmness to manage Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD).
Evidence Summary
Mindfulness for Emotional Regulation in Anxiety
Practicing mindfulness can help manage and control emotions, which is particularly beneficial for those experiencing generalized anxiety disorder. Persistent worry is a defining feature of this condition, and mindfulness offers a way to reduce symptoms by encouraging emotional regulation.
By focusing on present-moment awareness, mindfulness helps individuals address the constant worry that often accompanies generalized anxiety disorder.
By focusing on present-moment awareness, mindfulness helps individuals address the constant worry that often accompanies generalized anxiety disorder.



