Ritalin Paper Database
Visual Abstract
Meta-analysis of the efficacy of methylphenidate for treating adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
Efficacy of Methylphenidate for Adult ADHD
July 23, 2024
author
Faraone SV, Spencer T, Aleardi M, Pagano C, Biederman J
journal
J Clin Psychopharmacol
Date Published
2004 Feb
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers studied the effectiveness of methylphenidate (Ritalin) for treating adult ADHD.
💡
What They Found
They found that methylphenidate (Ritalin) is highly effective for treating adult ADHD, especially at higher doses.
📚
What This Means
These findings align with current evidence that supports the use of methylphenidate (Ritalin) for ADHD in adults, providing further assurance to clinicians about its effectiveness.
Study Summary
Background
Abstract: background
This article reviews the efficacy of methylphenidate (MPH) for adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
👨⚕️
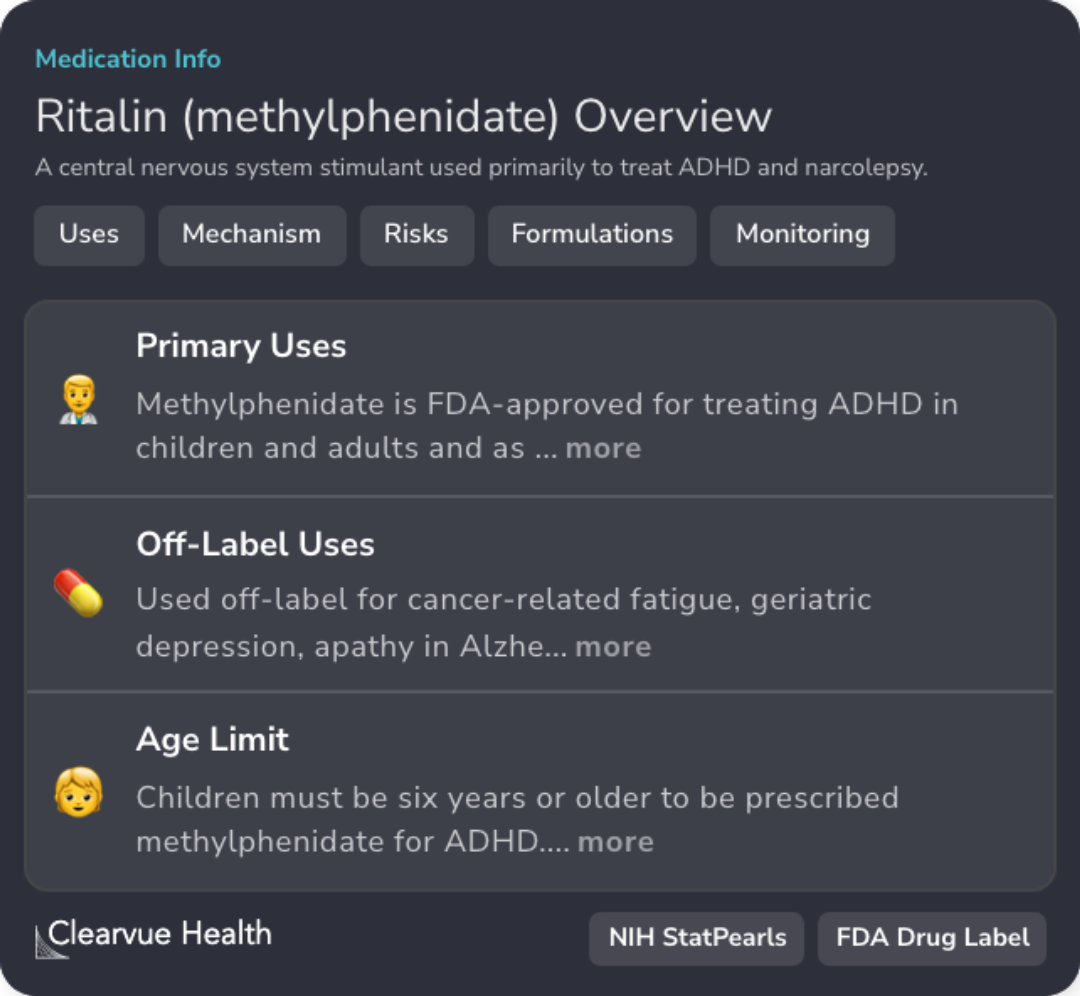
FDA-Approved Uses
Methylphenidate is FDA-approved for treating ADHD in both children and adults.
🧠
Mechanism of Action
Methylphenidate blocks the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine, increasing their concentration in the synaptic cleft.
📏
Optimized Dosage
High doses of methylphenidate yield larger effect sizes in treating adult ADHD.
👀
Monitoring for Side Effects
Regular monitoring for side effects such as cardiovascular issues and psychiatric reactions is required.
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers conducted a thorough search of scientific literature to find studies that were double-blind and placebo-controlled, meaning neither the participants nor the researchers knew who was receiving the medication or a placebo. They specifically looked at studies involving adults with ADHD treated with methylphenidate (Ritalin). Using meta-analysis, they combined data from these studies to calculate the overall effect of the medication and checked for any bias in the publication of the results. Additionally, they analyzed how different study designs might influence the medication's effectiveness.
Abstract: methods
A literature search identified double-blind placebo-controlled MPH treatment studies of ADHD adults. Meta-analysis estimated the pooled effect size for MPH treatment and tested for publication bias. Meta-analysis regression assessed the influence of ...more
Study Summary
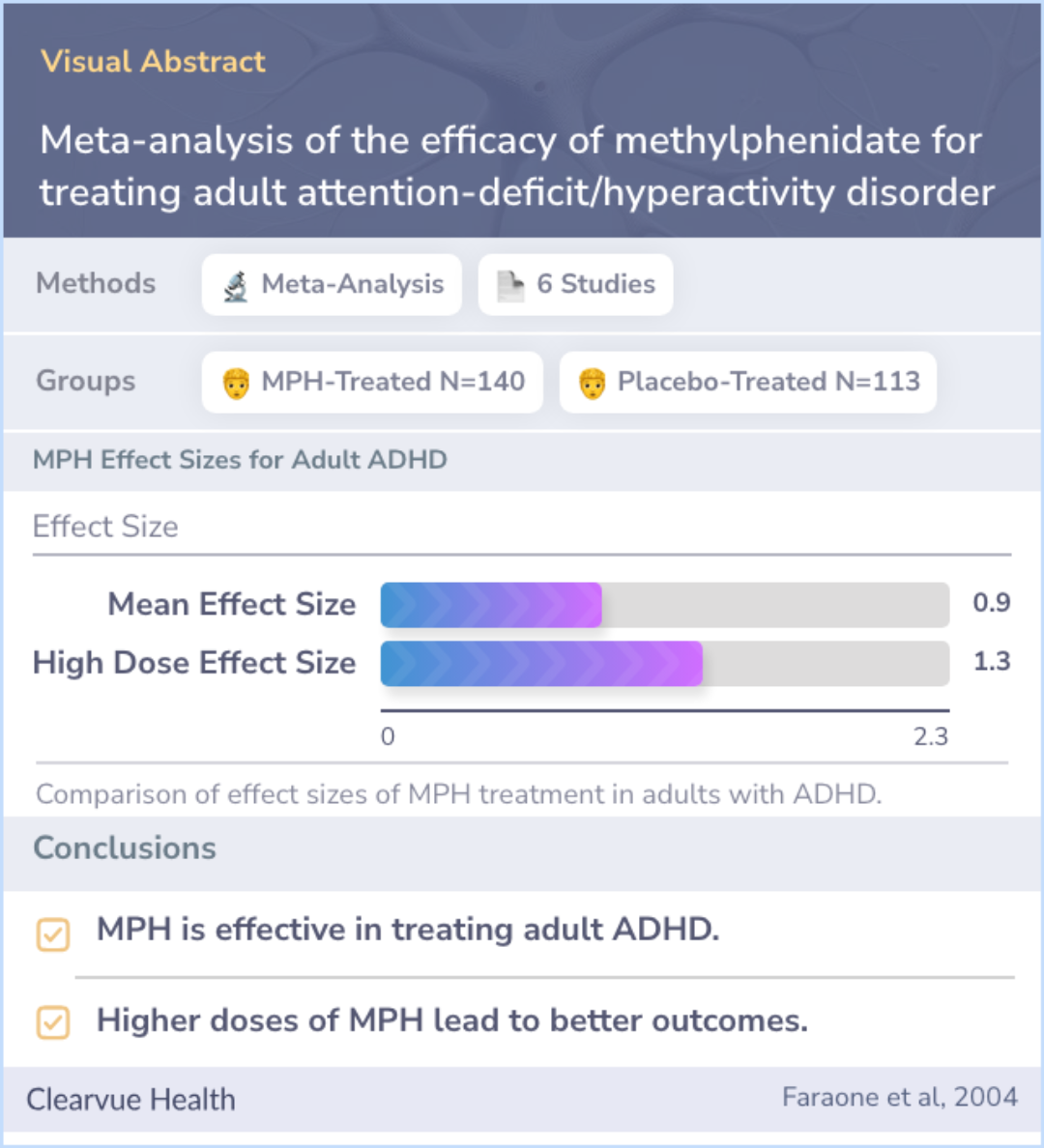
Results
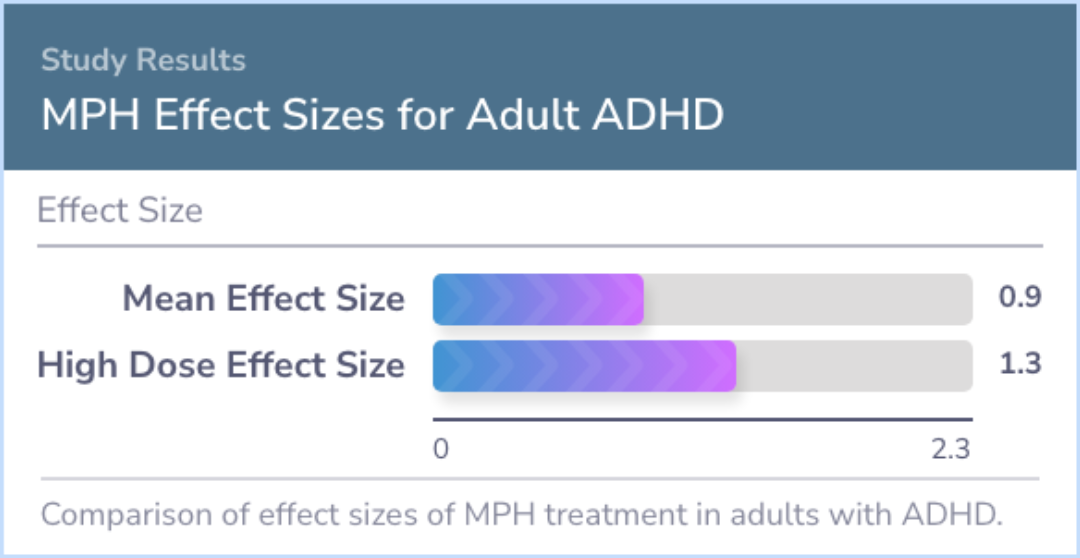
The analysis included six studies that met the criteria, involving a total of 140 adults treated with methylphenidate (Ritalin) and 113 adults given a placebo. The overall effect size, which measures the medication's impact, was found to be 0.9, indicating a significant positive effect. No publication bias was detected, meaning the results are reliable. Larger effects were seen in studies where doctors rated outcomes and higher doses of the medication were used. When the treatment was optimized to higher doses, the effect size increased to 1.3, showing even greater efficacy.
Abstract: results
The mean effect size of 0.9 was statistically significant and there was no evidence of publication bias. Larger MPH effect sizes were associated with physician ratings of outcome and use of higher doses. When treatment is optimized to high doses, the...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
The findings strongly support that methylphenidate (Ritalin) is effective in treating adult ADHD. The level of effectiveness seen in adults is similar to what has been observed in children and adolescents. This consistency provides reassurance to healthcare providers that diagnosing and treating ADHD in adults is valid and that the medication can be beneficial for this age group.
Abstract: conclusions
We found strong support for the assertion that MPH is efficacious for treating adult ADHD. Because the degree of efficacy of MPH in treating ADHD adults is similar to what has been reported from meta-analyses of the child and adolescent literature, o...more

Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Efficacy of Methylphenidate for Adult ADHD
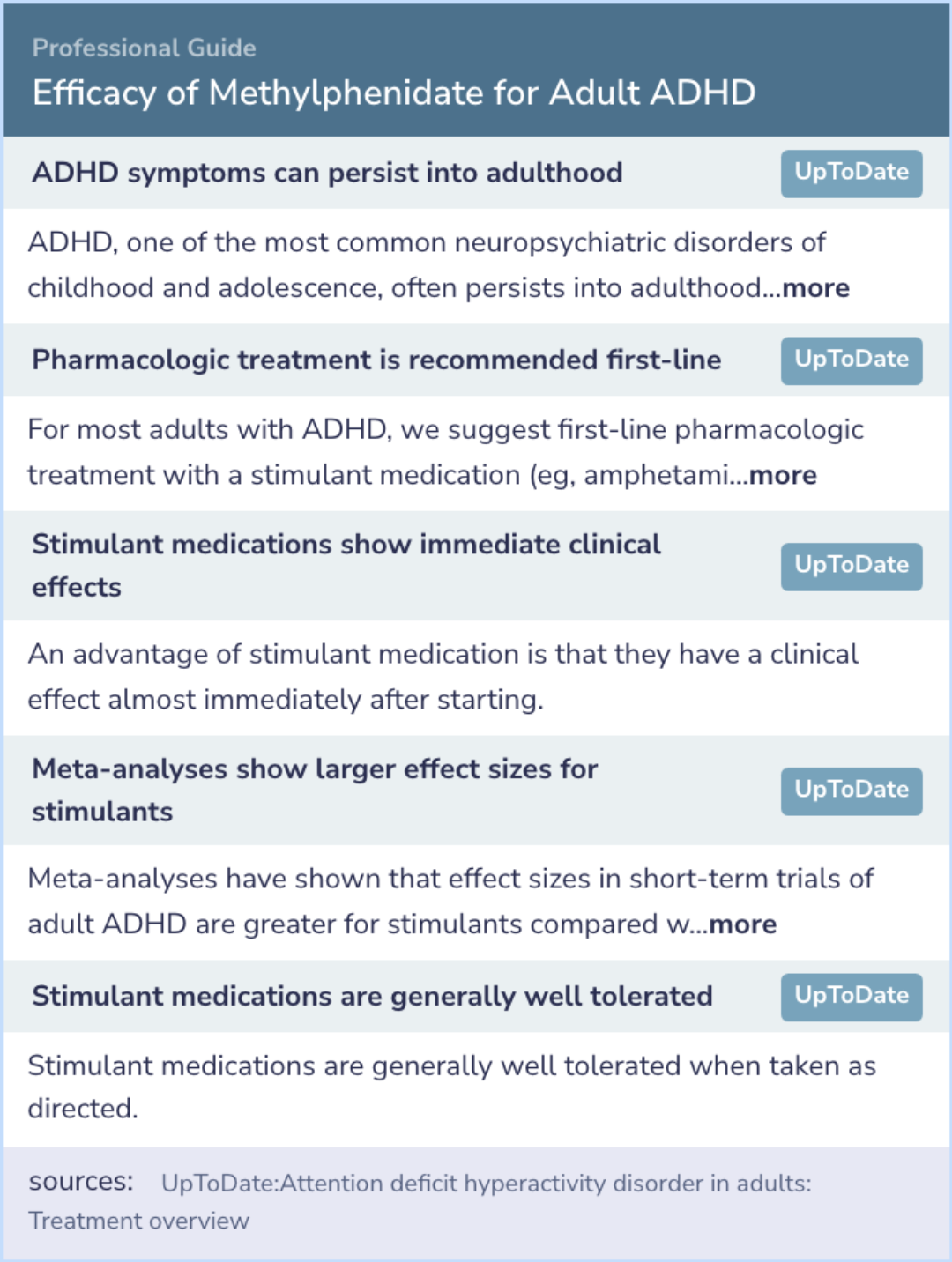
The findings suggest that ADHD symptoms often persist into adulthood.
For most adults with ADHD, first-line pharmacologic treatment with stimulant medications such as methylphenidate is recommended due to their immediate clinical effects.
Meta-analyses show that stimulants have greater effect sizes in short-term trials of adult ADHD compared to nonstimulant medications.
Consistent with the abstract, larger effect sizes for methylphenidate were observed with higher doses and physician ratings.
The mean effect size of 0.9 was statistically significant, and stimulant medications are generally well tolerated when taken as directed.
For most adults with ADHD, first-line pharmacologic treatment with stimulant medications such as methylphenidate is recommended due to their immediate clinical effects.
Meta-analyses show that stimulants have greater effect sizes in short-term trials of adult ADHD compared to nonstimulant medications.
Consistent with the abstract, larger effect sizes for methylphenidate were observed with higher doses and physician ratings.
The mean effect size of 0.9 was statistically significant, and stimulant medications are generally well tolerated when taken as directed.
Evidence Summary
Challenges of Combined Type ADHD in Adults
The combined type of ADHD, which includes inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity, is most common in adults.
It often includes more severe symptoms and is associated with greater challenges like educational difficulties and co-occurring mental health issues, such as major depression and antisocial behavior.
Adults with the combined type of ADHD tend to have more severe symptoms and face greater challenges like educational difficulties and mental health issues.
The combined type of ADHD in adults is often linked with other psychiatric conditions, such as major depression and antisocial disorder.
It often includes more severe symptoms and is associated with greater challenges like educational difficulties and co-occurring mental health issues, such as major depression and antisocial behavior.
Adults with the combined type of ADHD tend to have more severe symptoms and face greater challenges like educational difficulties and mental health issues.
The combined type of ADHD in adults is often linked with other psychiatric conditions, such as major depression and antisocial disorder.
Evidence Summary
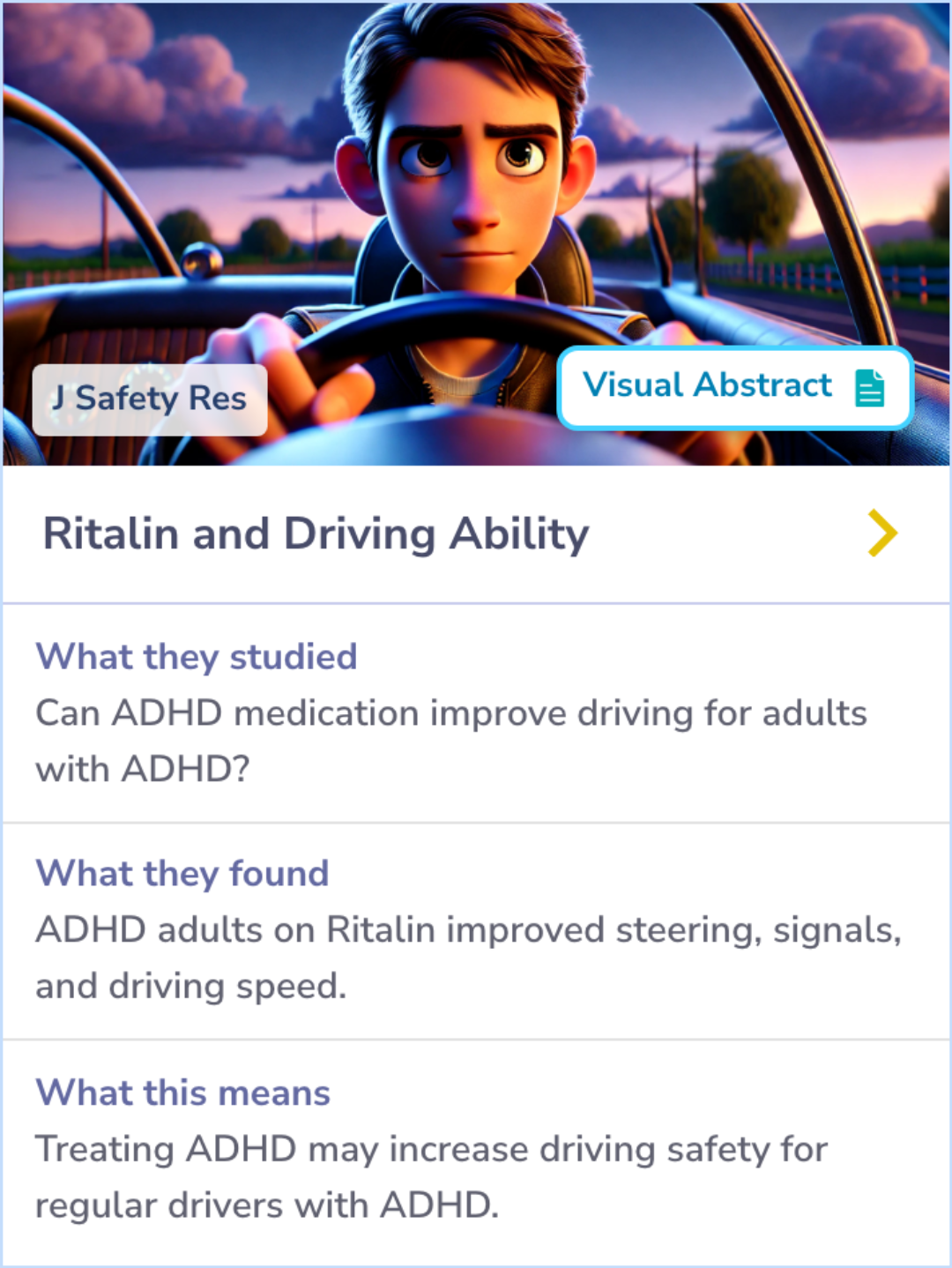
Methylphenidate's Impact on Driving Performance in Adults with ADHD
Building upon the positive outcomes of methylphenidate mentioned in the paper, this study looked into its impact on driving performance in adults with ADHD using a virtual reality driving simulator.
Methylphenidate, at both low and high doses, showed improvements in driving-related behaviors such as impulsiveness, steering variability, driving speed, and turn signal use.
The study used a double-blind, placebo-controlled design and found significant benefits for the high dose in specific driving metrics.
Methylphenidate, at both low and high doses, showed improvements in driving-related behaviors such as impulsiveness, steering variability, driving speed, and turn signal use.
The study used a double-blind, placebo-controlled design and found significant benefits for the high dose in specific driving metrics.