Adderall Study Database
Visual Abstract
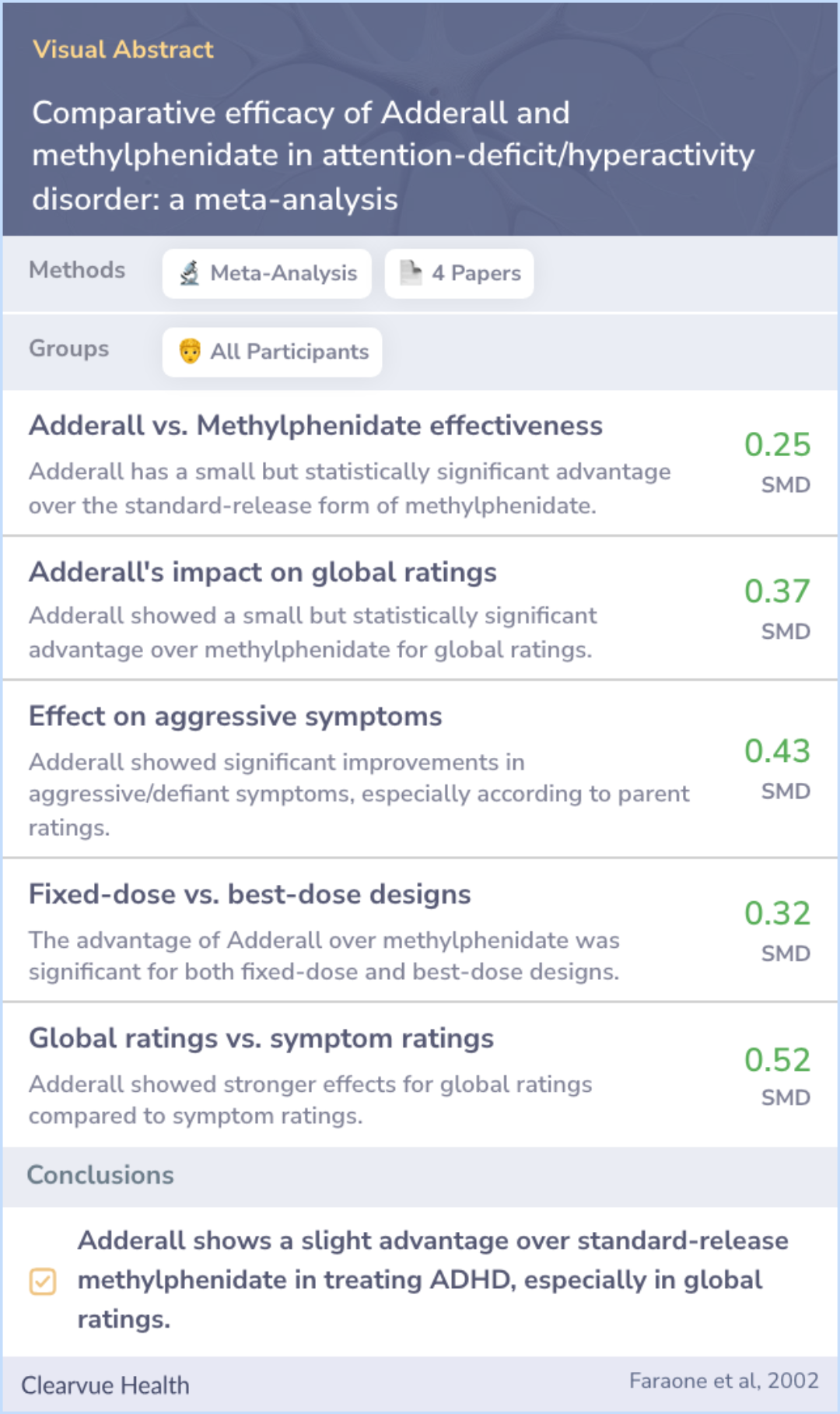
Comparative efficacy of Adderall and methylphenidate in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis
Adderall vs. Methylphenidate (Ritalin) for ADHD – Which Works Better?
October 18, 2024
author
Faraone SV, Biederman J, Roe C
journal
J Clin Psychopharmacol
Date Published
October 2002
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study aimed to compare the efficacy of Adderall and methylphenidate in treating ADHD.
💡
What They Found
The study found that Adderall has a small but statistically significant advantage over standard-release methylphenidate, particularly in global ratings.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that Adderall may offer a slight advantage over methylphenidate, aligning with guidance on ADHD medication where both are approved but indicating possible nuanced differences.
Study Summary
Study Overview
Adderall is officially approved for treating ADHD, enhancing attention and reducing impulsiveness. It is also effective for narcolepsy, which causes excessive daytime drowsiness. Adderall works by stimulating the central nervous system and increasing important chemicals in the brain. Studies show that Adderall might be slightly more effective than another common treatment, MPH. This reflects findings from various trials. Medication, including Adderall, plays a vital role in ADHD treatment plans alongside other therapies. Caution is necessary as there are potential side effects, including impacts on growth and heart health, that require careful monitoring.
Current guidelines emphasize the effectiveness of Adderall in treating ADHD and the need for close monitoring, aligning with findings from the studies.
Current guidelines emphasize the effectiveness of Adderall in treating ADHD and the need for close monitoring, aligning with findings from the studies.
Abstract: background
Because methylphenidate is currently the most widely prescribed medication for attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder, several studies have used it as the active comparator medication for evaluating the efficacy of a newer stimulant, Adderall. The...more

Clarifying Efficacy
"To provide a clearer picture of what conclusions can be drawn from these studies, we performed a meta-analysis."
Nuanced Understanding
"Despite these limitations, our results clarify the varying results from prior studies comparing these two medications."
Measurement Implications
"Our finding of a stronger effect for global ratings over symptom ratings is intriguing and may have implications for measurement of outcome in clinical trials of ADHD."
Study Summary
Methods
Data from four studies were analyzed to compare Adderall with standard-release methylphenidate. The analysis showed that Adderall had a minor but statistically significant edge over methylphenidate. This type of comparison helps to understand whether one medication works better than the other by using specific criteria.
Adderall's advantage was more pronounced in studies that used global assessments, which are overall evaluations, alongside symptom-specific measurements. This distinction derives insights into how these medications perform across different evaluating methods used by researchers.
Adderall's advantage was more pronounced in studies that used global assessments, which are overall evaluations, alongside symptom-specific measurements. This distinction derives insights into how these medications perform across different evaluating methods used by researchers.
Abstract: methods
Data from the four available studies suggest that Adderall has a small but statistically significant advantage over the standard-release form of methylphenidate.
Study Summary
Results
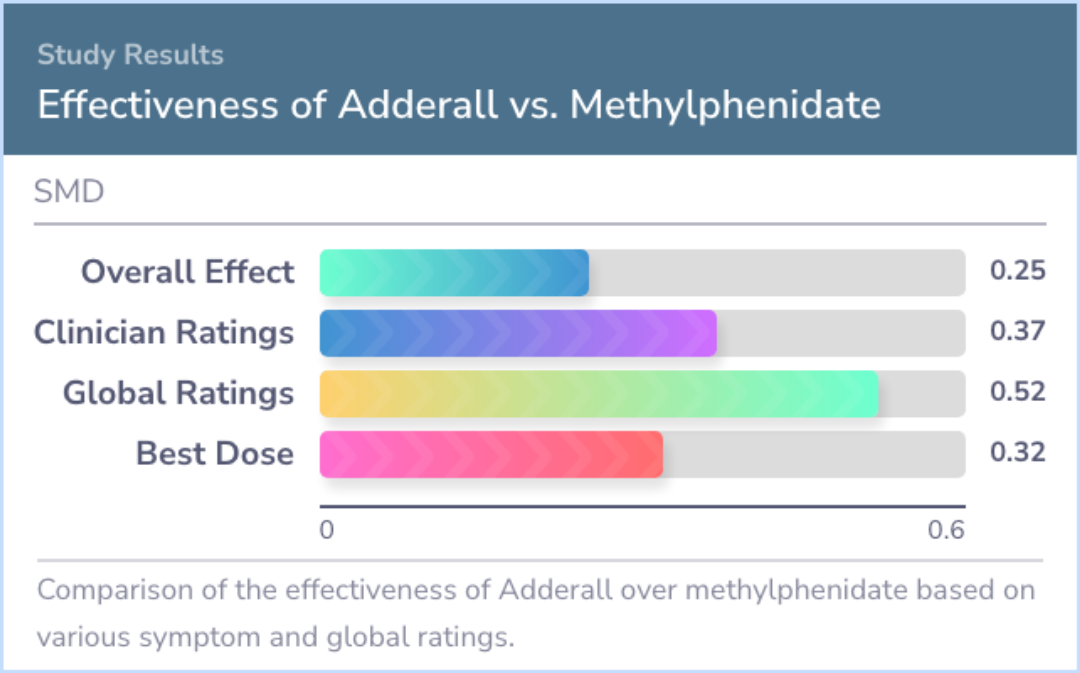
Adderall showed an advantage over methylphenidate for overall symptom improvement and broader evaluations, particularly those made by clinicians and parents. Interestingly, this superiority was not evident in teacher assessments.
The advantage remained noticeable in both fixed and adjustable dosage studies, underscoring Adderall’s consistent performance regardless of the dosing strategy. This suggests that Adderall may often be effective in a wider range of scenarios compared to standard-release methylphenidate.
The advantage remained noticeable in both fixed and adjustable dosage studies, underscoring Adderall’s consistent performance regardless of the dosing strategy. This suggests that Adderall may often be effective in a wider range of scenarios compared to standard-release methylphenidate.
Abstract: results
This advantage was observed for both symptom measures and global ratings but was strongest for global ratings. The effect of Adderall was significant for clinician and parent ratings but not for teacher ratings and was significant for both fixed-dose...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
The study highlights Adderall’s relative benefits over methylphenidate, aiding clinicians in choosing the best treatment for children with ADHD. Such findings streamline clinical decisions, providing actionable insights into the medication's effectiveness.
In summary, understanding these differences can guide physicians in tailoring treatments more effectively, aligning with individual patient needs and responses. This comparative analysis serves as a valuable tool in refining ADHD management strategies.
In summary, understanding these differences can guide physicians in tailoring treatments more effectively, aligning with individual patient needs and responses. This comparative analysis serves as a valuable tool in refining ADHD management strategies.
Abstract: conclusions
The findings contribute to the understanding of the relative efficacy of Adderall versus methylphenidate, which can assist clinicians in making informed treatment decisions for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.

Background Information
Patient Guide
💊
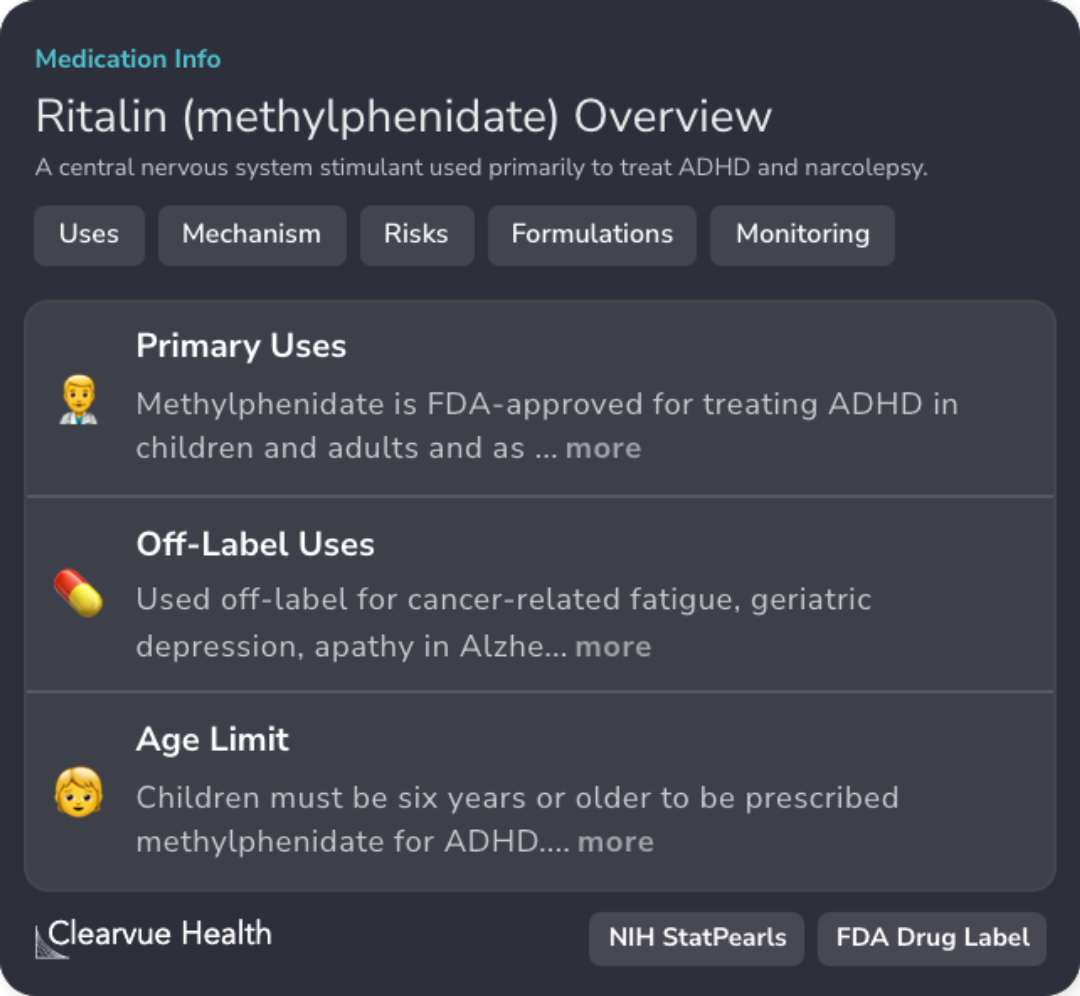
Adderall's Role in ADHD Treatment
FDA-approved for children and adults, Adderall enhances attention and reduces impulsivity in ADHD patients.
🔄
Mechanism of Adderall vs Methylphenidate
Both block norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake, increasing concentration in the synaptic cleft.
📦
Formulation Variability in ADHD Medications
Immediate, extended, and sustained-release forms available for tailored ADHD treatment plans.
🔍
Monitoring Requirements for ADHD Stimulants
Regular evaluations necessary for growth, cardial health, and abuse potential in patients.
⚠️
Adverse Effects and Contraindications
Both drugs may affect growth, cardiovascular health, and induce psychiatric symptoms.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Efficacy of Adderall vs. Methylphenidate in ADHD
In line with the findings that highlight Adderall's superiority over methylphenidate, current professional recommendations underscore the importance of methylphenidate in treating preschool children with moderate-to-severe ADHD symptoms. These guidelines suggest utilizing behavioral interventions first, but considering methylphenidate when those are insufficient. Studies also indicate that longer-acting stimulants, which include forms of methylphenidate, may present lower abuse potential than immediate-release formulations. This extended-release form has shown significant improvements in self-rated ADHD symptoms in meta-analyses. Furthermore, a combination approach integrating stimulant medication with behavioral therapy has proven beneficial for pre-adolescent ADHD management. Experts affirm the substantial short-term efficacy of stimulant medications for adult ADHD, revealing greater effect sizes than nonstimulant drugs.
Evidence Summary
Diverse Factors in ADHD Treatment Impact
Data reveal key differences in the effectiveness of treatments, highlighting varied patient experiences. Different measures capture unique aspects, influencing the interpretation of each medication’s impact.
Specific factors, such as symptom type, dosage, and duration, play roles in how treatments perform. Insights aid medical professionals in tailoring treatments suited to individual needs, ensuring better management of ADHD.
Specific factors, such as symptom type, dosage, and duration, play roles in how treatments perform. Insights aid medical professionals in tailoring treatments suited to individual needs, ensuring better management of ADHD.
Evidence Summary
Boosting School and Social Success with Stimulant Therapy
Stimulant therapy boosts focus and attention in teenagers with ADHD, leading to notable improvements in their school performance and social skills. The treatment, when prescribed and monitored by doctors, remains a trusted choice for addressing ADHD in young people.
This approach offers a safe pathway for managing ADHD symptoms, ensuring effective outcomes through medical supervision and tailored dosing.
This approach offers a safe pathway for managing ADHD symptoms, ensuring effective outcomes through medical supervision and tailored dosing.
Evidence Summary
Enhancing ADHD Treatment with Combined Approaches
Combining methylphenidate with psychosocial treatments proves effective in reducing ADHD symptoms. This dual approach notably enhances attention and behavior in patients compared to using either strategy alone.
Methylphenidate paired with therapy offers a more comprehensive benefit, tackling ADHD symptoms on multiple fronts. This synergy contributes to improved patient outcomes by addressing both biological and behavioral aspects.
Blending medication and therapy yields better results than relying solely on one method.
Methylphenidate paired with therapy offers a more comprehensive benefit, tackling ADHD symptoms on multiple fronts. This synergy contributes to improved patient outcomes by addressing both biological and behavioral aspects.
Blending medication and therapy yields better results than relying solely on one method.



