Adderall Study Database
Visual Abstract
Comparative efficacy and tolerability of medications for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children, adolescents, and adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Efficacy and tolerability of ADHD medications: a systematic review
October 18, 2024
author
Cortese S, Adamo N, Del Giovane C, Mohr-Jensen C, Hayes AJ, Carucci S, Atkinson LZ, Tessari L, Banaschewski T, Coghill D, Hollis C, Simonoff E, Zuddas A, Barbui C, Purgato M, Steinhausen HC, Shokraneh F, Xia J, Cipriani A
journal
Lancet Psychiatry
Date Published
2018 Sep
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
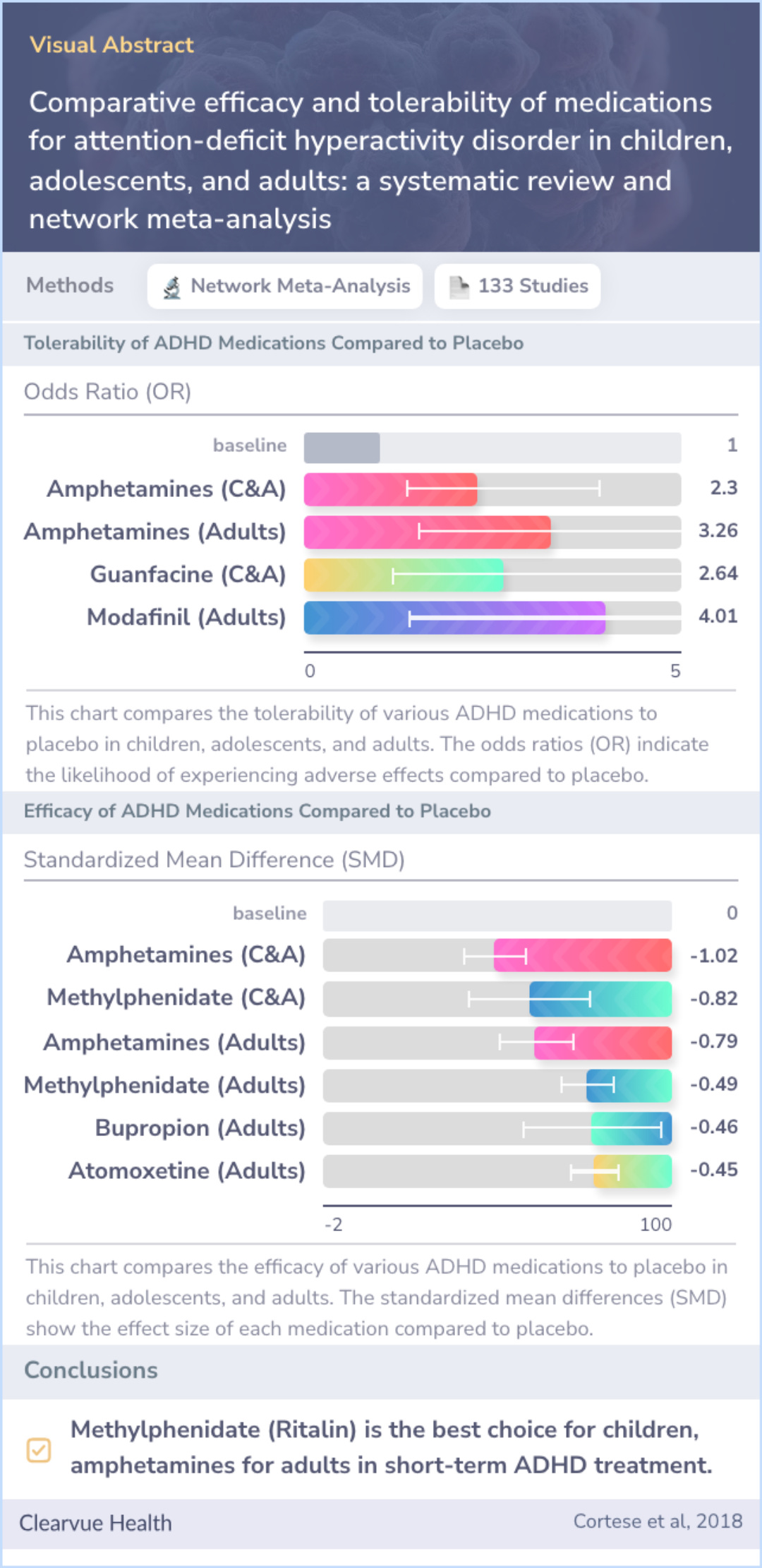
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and tolerability of different ADHD medications in children, adolescents, and adults.
💡
What They Found
The study found that methylphenidate (Ritalin) was effective for children and adolescents, while amphetamines were more suitable for adults.
📚
What This Means
These findings indicate that methylphenidate (Ritalin) aligns with current guidelines as a preferred choice for children and adolescents, while amphetamines should be considered for adults, supporting the current evidence.
Study Summary
Study Overview
Medications for ADHD have been found to be more effective than placebo for short-term treatment, especially in children and adolescents. Methylphenidate is recommended as a first choice for younger patients, while amphetamines are preferred for adults.
Amphetamines have shown both high effectiveness and good tolerability among adults. In children, methylphenidate is better accepted than amphetamines and is as tolerable as placebo. Additionally, monitoring weight and blood pressure is important when using medications like atomoxetine, as they can cause changes.
Amphetamines have shown both high effectiveness and good tolerability among adults. In children, methylphenidate is better accepted than amphetamines and is as tolerable as placebo. Additionally, monitoring weight and blood pressure is important when using medications like atomoxetine, as they can cause changes.
Abstract: background
We aimed to estimate the comparative efficacy and tolerability of oral medications for ADHD in children, adolescents, and adults.

First-Choice Medications
"Our findings represent the most comprehensive available evidence base to inform patients, families, clinicians, guideline developers, and policymakers on the choice of ADHD medications across age groups."
Broad Support for ADHD Treatments
"Taking into account both efficacy and safety, evidence from this meta-analysis supports methylphenidate in children and adolescents, and amphetamines in adults, as preferred first-choice medications for the short-term treatment of ADHD."
Need for Longer Studies
"The paucity of trials with randomised outcomes beyond 12 weeks highlights the need to fund studies to assess long-term effects of these drugs."
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers explored numerous scientific studies, specifically double-blind randomized controlled trials. This means studies where both the participants and the researchers didn't know who was receiving which specific treatment, making the results more reliable. These trials examined the effects of various ADHD drugs like amphetamines (including Adderall and Vyvanse), atomoxetine (Strattera), and methylphenidate (Ritalin), among others, compared to a placebo—a harmless pill.
The study used both direct comparisons and more complex statistical methods like network meta-analysis to combine results across different studies. Study risks were assessed systematically using established tools and methods to ensure confidence in the findings. To guarantee the accuracy of the gathered data, authors reached out to study authors and drug makers for further information. Eventually, these careful evaluations would inform medical and public recommendations for ADHD medications.
The study used both direct comparisons and more complex statistical methods like network meta-analysis to combine results across different studies. Study risks were assessed systematically using established tools and methods to ensure confidence in the findings. To guarantee the accuracy of the gathered data, authors reached out to study authors and drug makers for further information. Eventually, these careful evaluations would inform medical and public recommendations for ADHD medications.
Abstract: methods
We did a literature search for published and unpublished double-blind randomised controlled trials comparing amphetamines (including lisdexamfetamine), atomoxetine, bupropion, clonidine, guanfacine, methylphenidate, and modafinil with each other or p...more

Study Summary
Results
The study included 133 trials, with the majority focused on children and adolescents. The outcomes showed that, over about 12 weeks, most medications were more effective than a placebo in reducing ADHD symptoms in both young people and adults. For instance, ADHD symptoms in children improved notably with amphetamines and methylphenidate according to clinicians' assessments. However, teachers only noted improvements with methylphenidate and modafinil. Among adults, amphetamines, atomoxetine, and methylphenidate appeared more effective than a placebo.
Regarding side effects, amphetamines seemed to have more side effects than placebo in both age groups, whereas certain other medications showed tolerability issues only in adults. Notably, head-to-head comparisons favored amphetamines over other drugs like atomoxetine and methylphenidate for effectiveness, particularly in adult patients.
Regarding side effects, amphetamines seemed to have more side effects than placebo in both age groups, whereas certain other medications showed tolerability issues only in adults. Notably, head-to-head comparisons favored amphetamines over other drugs like atomoxetine and methylphenidate for effectiveness, particularly in adult patients.
Abstract: results
133 double-blind randomised controlled trials (81 in children and adolescents, 51 in adults, and one in both) were included. The analysis of efficacy closest to 12 weeks was based on 10 068 children and adolescents and 8131 adults; the analysis of to...more
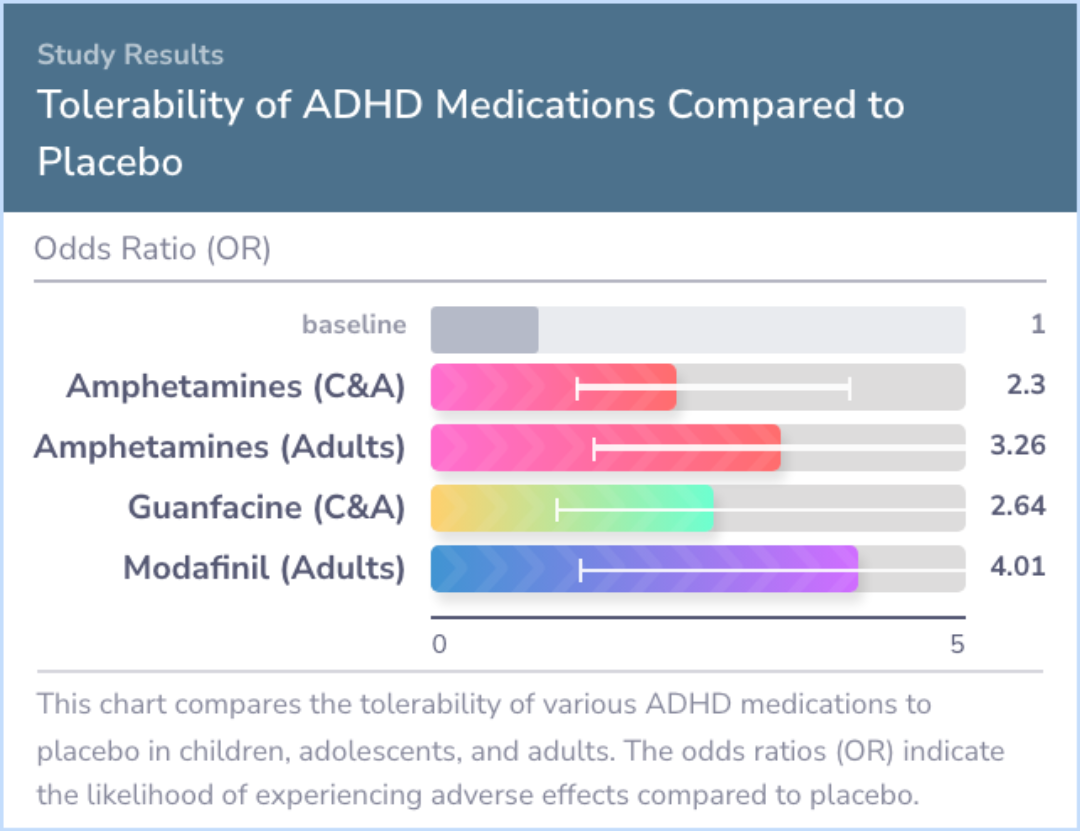
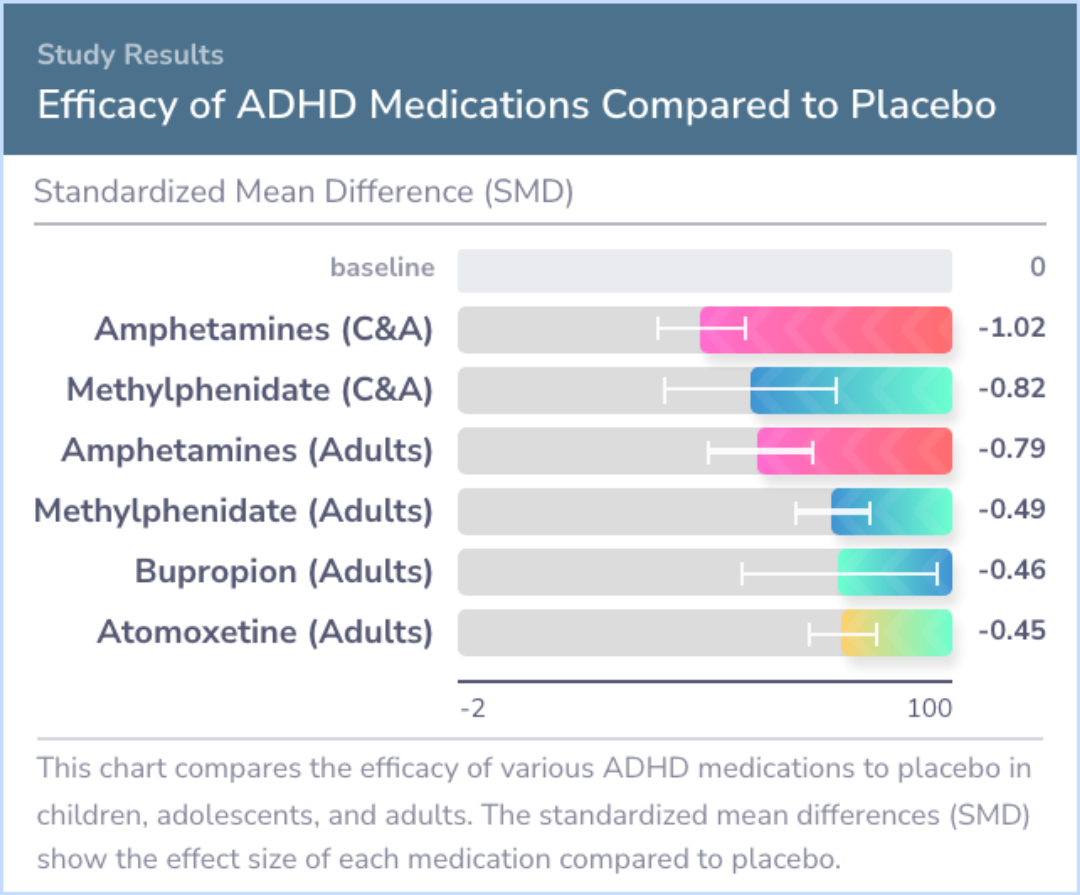
Study Summary
Conclusions
This study shines a light on the most exhaustive evidence surrounding ADHD medication efficacy and safety across varying age groups. It suggests that, for short-term treatment, methylphenidate might be the best initial choice for children and adolescents, while amphetamines could be more suitable for adults.
These insights aim to help guide the choice of ADHD medications used by families, healthcare professionals, and policymakers.
These insights aim to help guide the choice of ADHD medications used by families, healthcare professionals, and policymakers.
Abstract: conclusions
Our findings represent the most comprehensive available evidence base to inform patients, families, clinicians, guideline developers, and policymakers on the choice of ADHD medications across age groups. Taking into account both efficacy and safety, ...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
💊
Adderall for ADHD Across Age Groups
Adderall is FDA-approved for treating ADHD in both children and adults, aligning with the study's focus on medication efficacy across different age groups.
🧬
Adderall's Central Nervous System Impact
Adderall's effectiveness stems from its ability to stimulate the CNS by increasing dopamine and norepinephrine levels, relevant to efficacy comparisons in the study.
⚠️
Adverse Effects and Tolerability
Potential adverse effects like cardiovascular risks and growth suppression in children highlight the need for tolerability assessments, as covered in the study.
🧠
Long-Term Implications of Adderall
Chronic use of Adderall may lead to neurochemical changes, emphasizing the study's call for further research on long-term effects of ADHD medications.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Efficacy and tolerability of ADHD medications: a systematic review
Consistent with findings that emphasize the short-term efficacy of methylphenidate for children and amphetamines for adults, guidelines underscore specific treatment approaches tailored to age and unique patient profiles.
In preschool-aged children, behavioral interventions are advised as the first line of treatment, while methylphenidate is suggested if these methods do not yield significant results.
Before commencing medication therapy in adolescents, clinicians should evaluate for any substance use issues, given the potential for adverse effects such as hallucinations or psychotic symptoms of stimulants.
In preschool-aged children, behavioral interventions are advised as the first line of treatment, while methylphenidate is suggested if these methods do not yield significant results.
Before commencing medication therapy in adolescents, clinicians should evaluate for any substance use issues, given the potential for adverse effects such as hallucinations or psychotic symptoms of stimulants.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate for ADHD Treatment
Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate are two widely used medications for ADHD. Each has its own profile in terms of effectiveness, side effects, and how patients respond to treatment. This comparison highlights the key differences to help readers make more informed choices about their treatment options.
Effectiveness varies between these medications, as do the side effects. This contrast provides a clearer view of what to expect from each option.
Effectiveness varies between these medications, as do the side effects. This contrast provides a clearer view of what to expect from each option.
Evidence Summary
Adderall XR vs. Strattera: Attention, Behavior, and Side Effects in Children
The comparison highlights how Adderall XR and Strattera, two common ADHD medications, differ in their effects on school-aged children. It examines both drugs' effectiveness in improving attention and behavior, providing insight into how each medication performs in real-world settings.
The comparison also delves into the side effects children experience with each medication, offering a clear picture of what families might expect when choosing between these options.
The comparison also delves into the side effects children experience with each medication, offering a clear picture of what families might expect when choosing between these options.
Evidence Summary
Boosting Focus and Academic Success with Stimulant Therapy
Stimulant therapy, particularly for adolescents with ADHD, boosts focus and attention, leading to better academic performance and social interactions. This widely prescribed treatment remains a trusted option under medical supervision, ensuring both safety and efficacy for young individuals. These benefits underscore its role in helping teenagers manage their symptoms effectively.
Physician-supervised use of stimulant medications continues to be a key approach in improving outcomes for teens with ADHD.
Physician-supervised use of stimulant medications continues to be a key approach in improving outcomes for teens with ADHD.



