Ritalin Paper Database
Visual Abstract
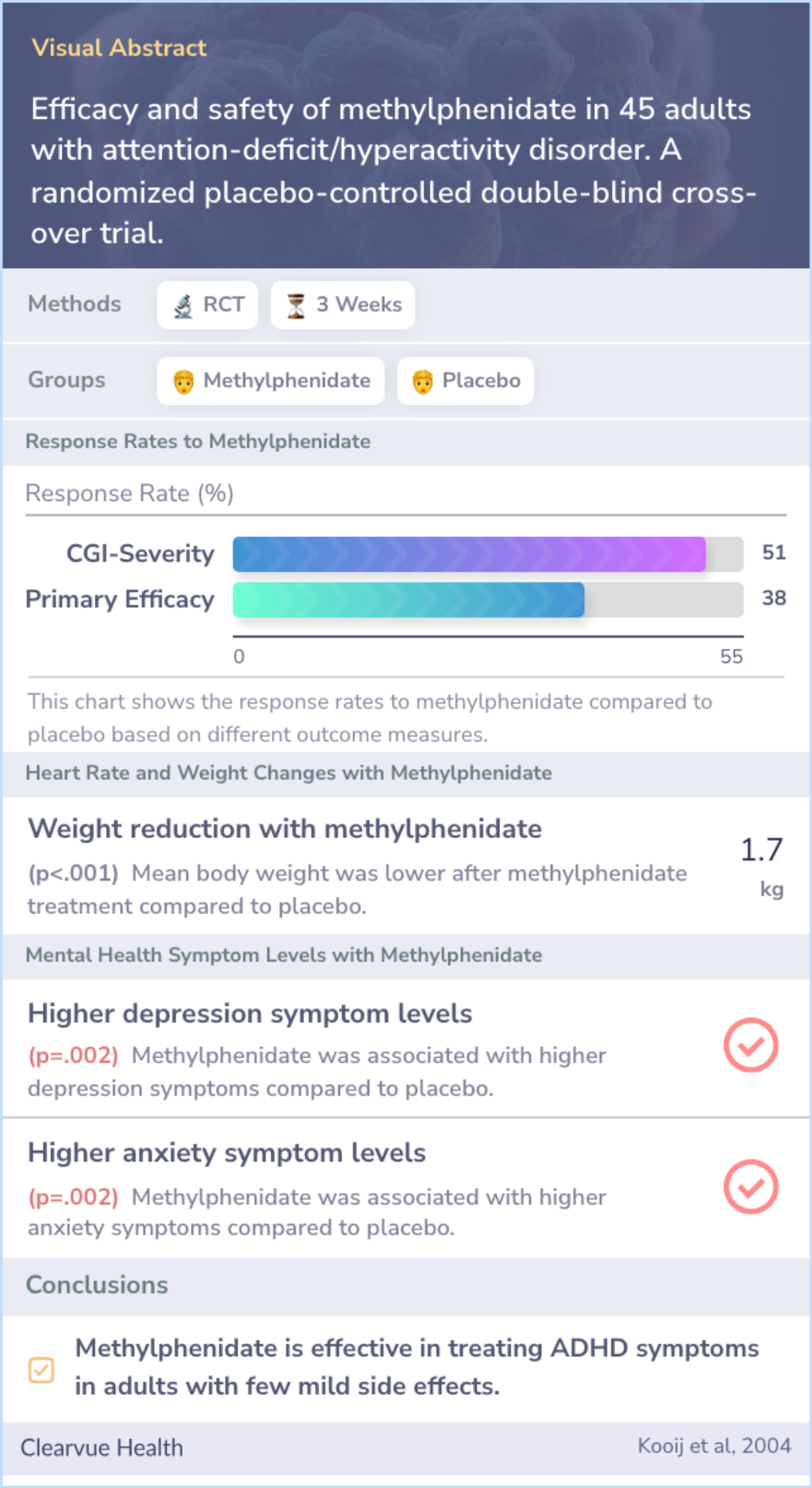
Efficacy and safety of methylphenidate in 45 adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. A randomized placebo-controlled double-blind cross-over trial.
Methylphenidate (Ritalin) Effectively Reduces ADHD Symptoms in Adults
October 18, 2024
author
Kooij JJ, Burger H, Boonstra AM, Van der Linden PD, Kalma LE, Buitelaar JK
journal
Psychol Med
Date Published
2004 Aug
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
They studied the effectiveness and safety of methylphenidate (Ritalin) in adults with ADHD.
💡
What They Found
They found that methylphenidate (Ritalin) was effective in treating ADHD symptoms in adults, with response rates between 38% and 51%, and side effects were few and mild.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that methylphenidate (Ritalin) is a viable short-term treatment for adult ADHD, aligning with existing evidence that supports its use in children and adolescents.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to explore how effective methylphenidate, commonly known as Ritalin, is for adults with ADHD. Researchers wanted to understand its impact on symptoms and any potential side effects.
The findings revealed that Ritalin could help manage ADHD symptoms in adults, showing promise as a treatment option. The mild side effects reported suggest that it might be a safe choice for those looking to improve their focus and daily functioning.
The findings revealed that Ritalin could help manage ADHD symptoms in adults, showing promise as a treatment option. The mild side effects reported suggest that it might be a safe choice for those looking to improve their focus and daily functioning.
Abstract: background
Data on the efficacy and safety of methylphenidate in adults with attention deficit/ hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are lacking in Europe. This study was undertaken to report on the efficacy and safety of methylphenidate in an adult out-patient popula...more

Study Aim
"This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of methylphenidate in adults with ADHD."
Symptom Management
"These findings support the notion that methylphenidate can help adults with ADHD manage their symptoms."
Treatment Potential
"Methylphenidate represents a viable treatment option for adults seeking help with ADHD."
Study Summary
Methods
In a double-blind, randomized crossover trial, 45 adults diagnosed with ADHD from childhood were treated with either methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) or a placebo.
The participants started with a low dose, which was gradually increased over three weeks. The study design ensured neither participants nor researchers knew who was receiving the actual medication until the trial was over.
The participants started with a low dose, which was gradually increased over three weeks. The study design ensured neither participants nor researchers knew who was receiving the actual medication until the trial was over.
Abstract: methods
A double-blind randomized cross-over trial comparing methylphenidate and placebo in 45 adults with ADHD with childhood onset was performed in a dose-titration design. Methylphenidate was titrated from 0.5 mg/kg per day in week 1 up to 1.0 mg/kg per d...more
Study Summary
Results
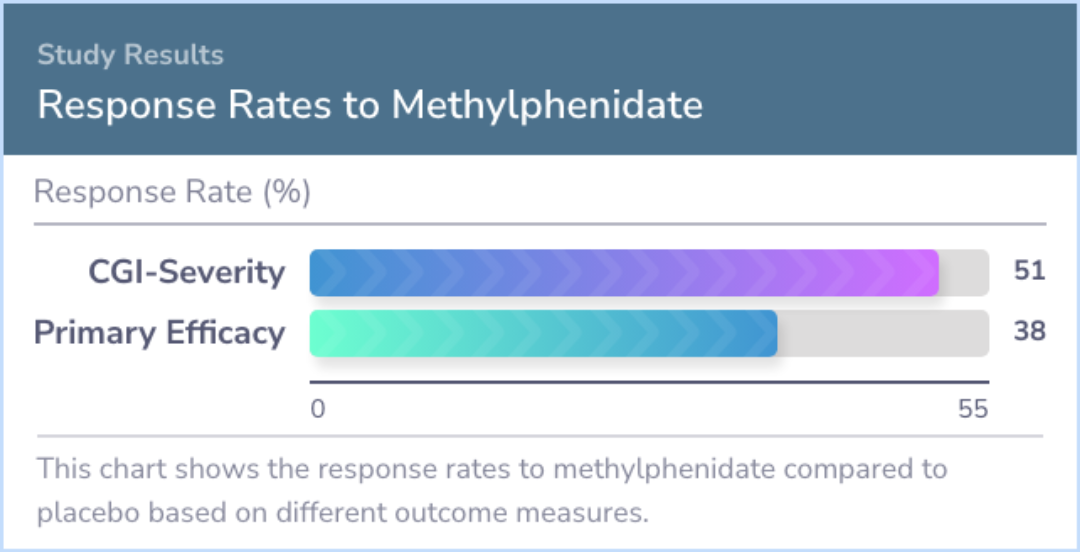
The response to methylphenidate varied, with about 38% to 51% of participants experiencing significant improvement. By comparison, only 7% to 18% responded to the placebo.
While both groups reported side effects, those associated with methylphenidate were mild and generally not much higher than the placebo group, suggesting the medication is relatively well-tolerated in the short term.
While both groups reported side effects, those associated with methylphenidate were mild and generally not much higher than the placebo group, suggesting the medication is relatively well-tolerated in the short term.
Abstract: results
Response rates using methylphenidate varied between 38 and 51%, and using placebo between 7 and 18% (p<0.05), depending on outcome measure used. Although the overall percentage of subjects having any side effect on both methylphenidate and placebo wa...more


Study Summary
Conclusions
Methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) was found to be both effective and safe for short-term use in adults with ADHD. The study concluded that more research is needed to assess long-term effects.
Future studies should also consider how factors like gender, co-existing conditions, and socio-economic status may influence treatment outcomes in adult ADHD patients.
Future studies should also consider how factors like gender, co-existing conditions, and socio-economic status may influence treatment outcomes in adult ADHD patients.
Abstract: conclusions
Methylphenidate proves to be an effective and well tolerated treatment for symptoms of ADHD in adults in the short term. Future research should study the long-term response and clarify the impact of gender, co-morbidity, socio-economic status and IQ ...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
👨⚕️
Primary Usage
Methylphenidate is FDA-approved for treating ADHD in children and adults.
🧠
Mechanism of Action
Methylphenidate blocks the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine, increasing their synaptic concentration.
❤️
Cardiovascular Risks
Methylphenidate can exacerbate symptoms like palpitations and is not recommended for patients with serious heart conditions.
🧠
Psychiatric Concerns
Methylphenidate may aggravate symptoms of psychosis or bipolar disorder and cause new or worsened aggressive behavior.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Methylphenidate (Ritalin) Effectively Reduces ADHD Symptoms in Adults
In line with the abstract, adults with ADHD often experience significant impairment, as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder frequently persists from childhood into adulthood.
Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate, generally provide effective symptomatic relief and improve daily functioning in adults with ADHD.
Meta-analyses reveal greater effect sizes for stimulants in short-term trials for adult ADHD, underscoring their efficacy compared to nonstimulant medications.
Combining stimulant medication with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) enhances treatment outcomes more effectively than using either approach alone.
Before starting stimulants, clinicians must review the patient's cardiovascular history to ensure safety during treatment.
Stimulants are well tolerated when administered as directed, with common side effects including dry mouth, insomnia, and diminished appetite.
Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate, generally provide effective symptomatic relief and improve daily functioning in adults with ADHD.
Meta-analyses reveal greater effect sizes for stimulants in short-term trials for adult ADHD, underscoring their efficacy compared to nonstimulant medications.
Combining stimulant medication with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) enhances treatment outcomes more effectively than using either approach alone.
Before starting stimulants, clinicians must review the patient's cardiovascular history to ensure safety during treatment.
Stimulants are well tolerated when administered as directed, with common side effects including dry mouth, insomnia, and diminished appetite.
Evidence Summary
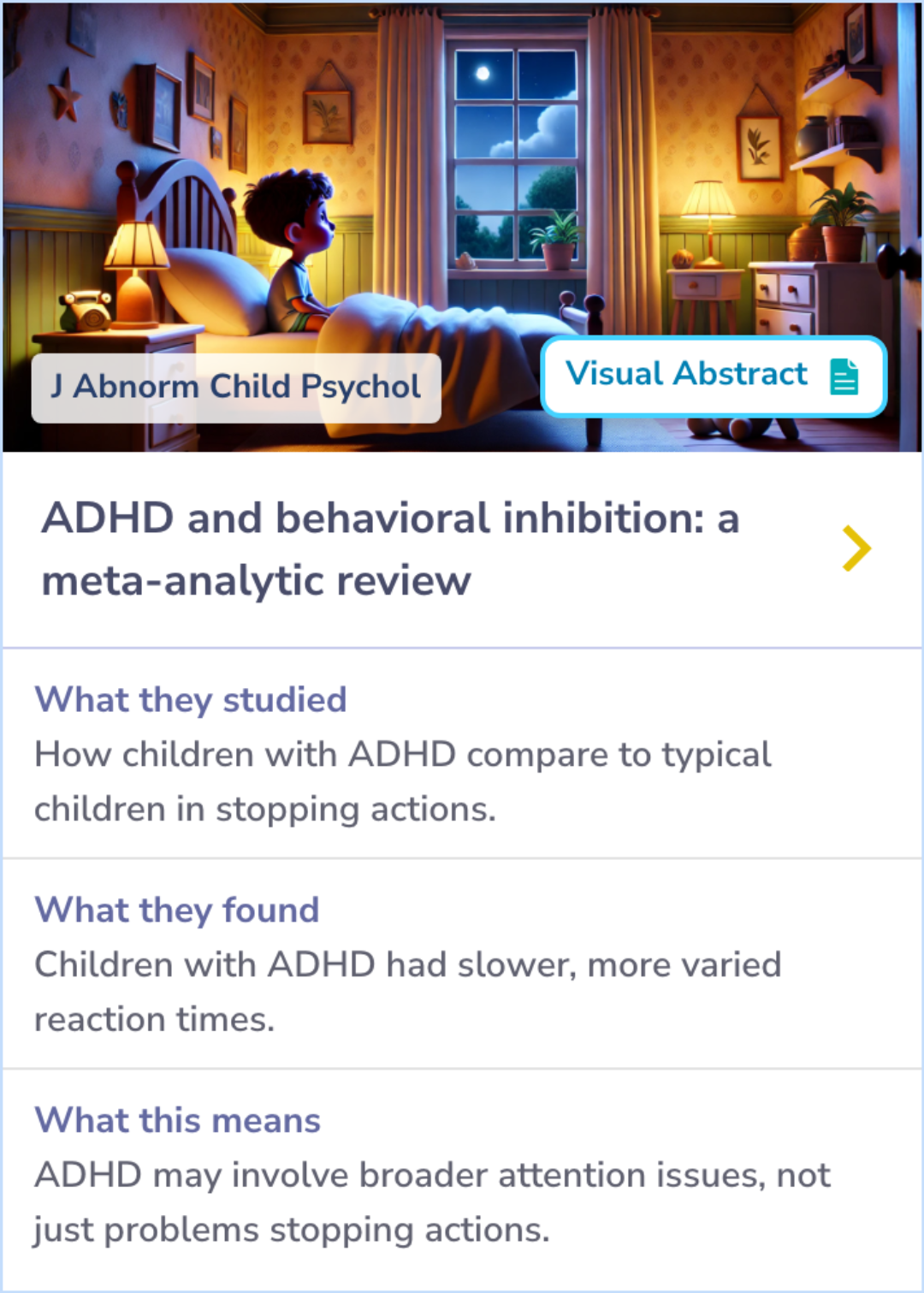
Attention Differences in Children with ADHD
Building upon attention issues explored, research compared children with ADHD to typically developing children in stopping actions.
Using the stop-signal paradigm, the study found that children with ADHD exhibited slower and more varied reaction times.
This suggests ADHD involves broader attention issues beyond just difficulty in stopping actions.
Using the stop-signal paradigm, the study found that children with ADHD exhibited slower and more varied reaction times.
This suggests ADHD involves broader attention issues beyond just difficulty in stopping actions.
Evidence Summary
Task Completion Challenges in ADHD
Individuals with ADHD encounter significant internal distractions.
Research shows they struggle more in distracting environments and take longer to complete tasks.
These challenges affect various activities, highlighting strategies needed to manage attention and minimize distractions.
Research shows they struggle more in distracting environments and take longer to complete tasks.
These challenges affect various activities, highlighting strategies needed to manage attention and minimize distractions.
Evidence Summary
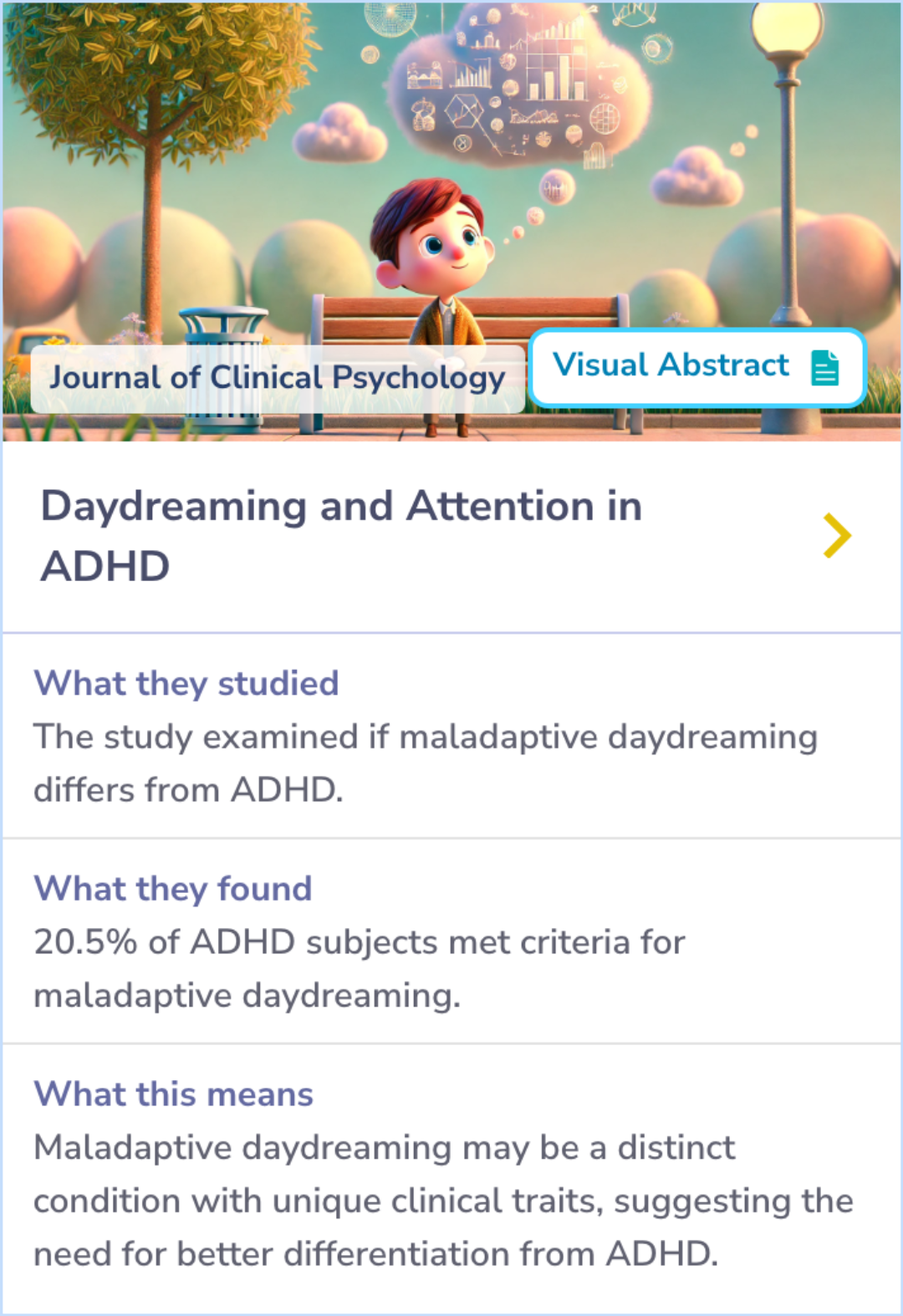
Exploring Maladaptive Daydreaming in Adults with ADHD
Building upon the treatment findings of ADHD symptoms, researchers also explored a similar condition, maladaptive daydreaming, (MD) in adults.
Interestingly, only 20.5% of participants with ADHD met the criteria for MD.
This highlights that MD might be a separate condition with distinct characteristics, warranting clearer differentiation from ADHD.
Interestingly, only 20.5% of participants with ADHD met the criteria for MD.
This highlights that MD might be a separate condition with distinct characteristics, warranting clearer differentiation from ADHD.