Ritalin Paper Database
Visual Abstract
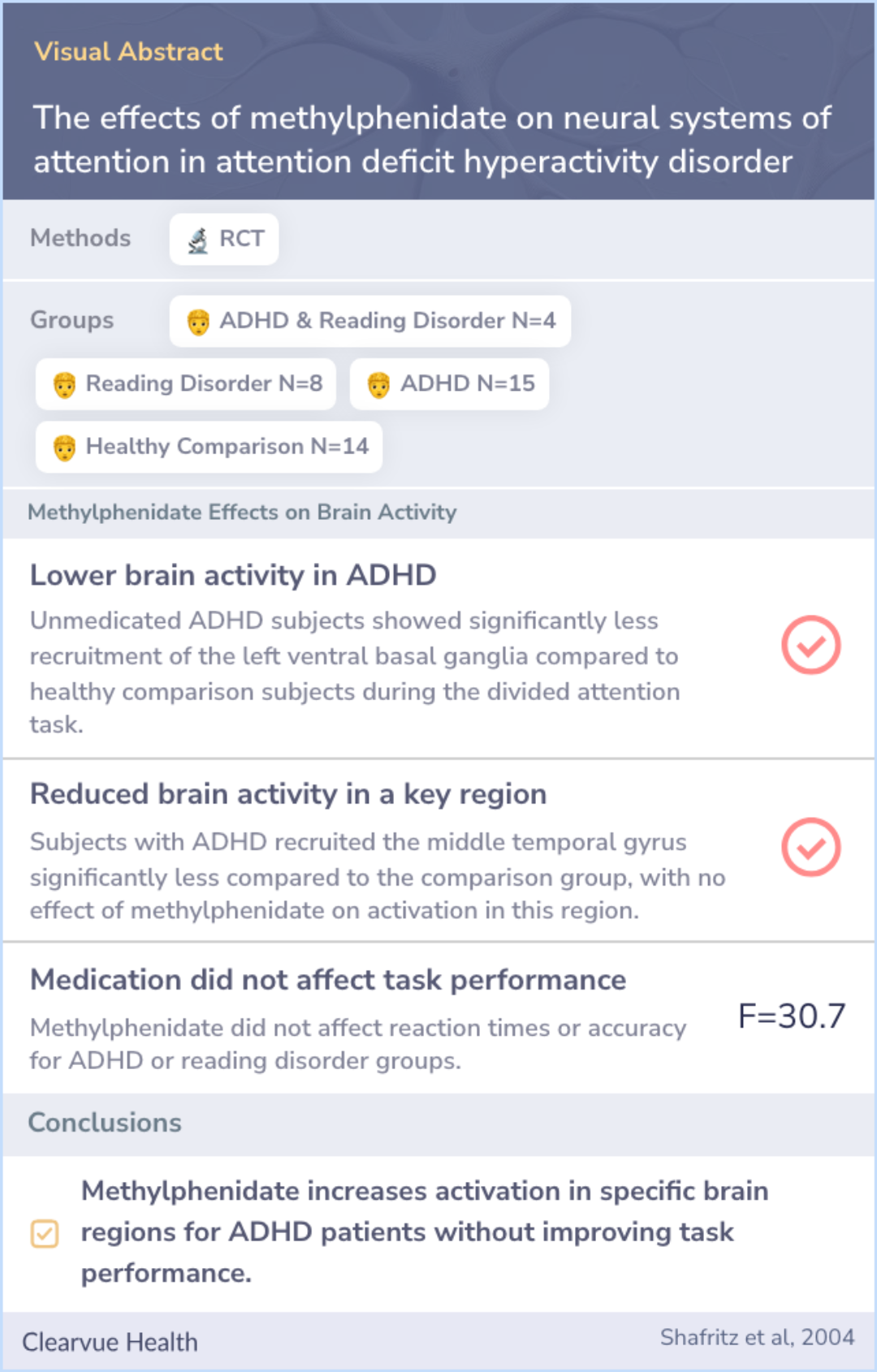
The effects of methylphenidate on neural systems of attention in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Effects of methylphenidate on neural attention in ADHD
October 18, 2024
author
Shafritz KM, Marchione KE, Gore JC, Shaywitz SE, Shaywitz BA
journal
Am J Psychiatry
Date Published
2004 Nov
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The main research question was how methylphenidate affects brain activity related to selective and divided attention in adolescents with ADHD and reading disorders.
💡
What They Found
The study found that methylphenidate increased activation in the left ventral basal ganglia but did not affect task performance. ADHD subjects also showed less activation in the middle temporal gyrus without direct effects from the drug.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that methylphenidate may help normalize brain activity in attention-related areas for adolescents with ADHD, but it doesn't necessarily improve their task performance. This aligns with current evidence on the brain effects of methylphenidate.
Study Summary
Study Overview
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) affects many adolescents during their school years and beyond. This study explored how ADHD influences attention and self-control, focusing on specific brain areas, particularly the frontal regions, that may not function optimally in individuals with the disorder.
The study also investigated how methylphenidate affects brain activity linked to attention. Using advanced imaging, researchers aimed to uncover how the medication alters information processing related to impulse control and decision-making. These insights could clarify why some students respond well to treatment while others do not, advancing our understanding of ADHD beyond impulsivity alone.
The study also investigated how methylphenidate affects brain activity linked to attention. Using advanced imaging, researchers aimed to uncover how the medication alters information processing related to impulse control and decision-making. These insights could clarify why some students respond well to treatment while others do not, advancing our understanding of ADHD beyond impulsivity alone.
Abstract: background
Recent studies have suggested that attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is associated with abnormalities in basal ganglia and prefrontal cortical functioning. However, these studies have primarily relied upon cognitive tasks that reflect i...more
Impacts of Medication
"Our results indicate that adolescents with either ADHD or reading disorder show quite similar neural activation patterns to healthy comparison subjects during the performance of selective and divided attention tasks."
Brain Function and ADHD
"These findings serve to reinforce the role of these cortical and subcortical structures in the processing of attention-related information and the generation of behavioral responses."
Study Summary
Methods
This study utilized functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to assess brain activity in 15 adolescents with ADHD, 8 with a reading disorder, and 4 with both, aged 12 to 18. Participants underwent two sessions: one with methylphenidate and another with a placebo.For comparison, 14 healthy adolescents aged 12 to 20 who did not take medication were included. This setup allowed researchers to observe the effects of the medication on brain activity during attention-demanding tasks.
Abstract: methods
The authors used functional magnetic resonance imaging to investigate the neural correlates of selective and divided attention in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pharmacological challenge with methylphenidate in 15 adolescents with ADH...more

Study Summary
Results
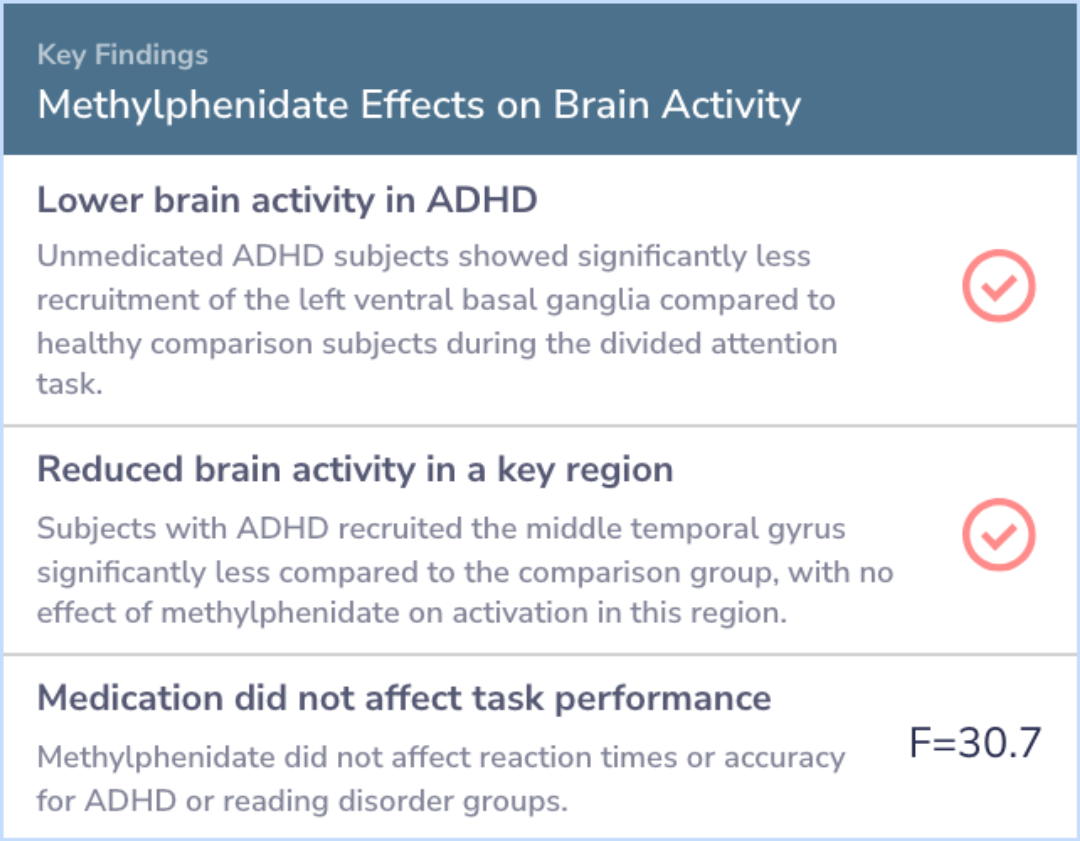
In tasks requiring divided attention, unmedicated subjects with ADHD or a reading disorder exhibited less activity in the left ventral basal ganglia compared to healthy controls. However, administering methylphenidate increased activity in this brain region, though it did not enhance task performance.Additionally, individuals with ADHD showed significantly reduced activation in the middle temporal gyrus compared to comparison subjects, but methylphenidate did not directly change activity in this area.
Abstract: results
During the divided attention task, unmedicated subjects with ADHD or reading disorder recruited the left ventral basal ganglia significantly less than the healthy comparison subjects. Methylphenidate led to an increase in activation in this region bu...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
The study revealed that ADHD is associated with irregular processing in brain networks related to attention, particularly within the striatal circuits. Methylphenidate appears to help normalize activity in these areas.While the findings suggest that medication can modify brain activity, they also indicate that it may not necessarily enhance performance on attention tasks, highlighting the complexity of ADHD and the need for further research on medication efficacy.
Abstract: conclusions
These results suggest that ADHD is associated with abnormal processing in attentional networks, with specific dysfunction in striatal circuitry. Methylphenidate may act to normalize activity within this network.
Background Information
Patient Guide
👨⚕️
Methylphenidate Overview
A central nervous system stimulant used primarily to treat ADHD and narcolepsy.
🧠
Mechanism of Action
Methylphenidate blocks the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine, increasing their concentration in the synaptic cleft.
🔬
Neuroprotection Potential
May provide neuroprotection in conditions like Parkinson's disease by regulating dopamine levels.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Effects of methylphenidate on neural attention in ADHD
The study's findings emphasize the importance of current professional guidelines regarding ADHD treatment. Methylphenidate remains the first-line treatment for preschool children, as data on nonstimulant medications is limited. Behavioral interventions should be the first approach, with methylphenidate considered if these are ineffective.Clinicians must assess adolescents for substance use and consider comorbid conditions. Monitoring vital signs is necessary as stimulant medications can raise heart rate and blood pressure. Combining behavioral therapy with medication can yield positive outcomes, underscoring the importance of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Evidence Summary
Atomoxetine vs. Methylphenidate: Understanding Treatment Options for ADHD
The article compares two medications, Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate, used to treat ADHD.
It discusses the effectiveness, side effects, and patient response to each medication.
The article provides information to help readers understand the differences and make informed choices.
It discusses the effectiveness, side effects, and patient response to each medication.
The article provides information to help readers understand the differences and make informed choices.
Evidence Summary
Methylphenidate's Role in Improving Cognitive Functions
Methylphenidate, commonly prescribed for ADHD, improves attention, focus, and cognitive function.
Research backs these claims, showing enhancements in mental performance.
This medication acts on neural pathways to aid those with ADHD, supporting better cognitive outcomes and attention spans.
Research backs these claims, showing enhancements in mental performance.
This medication acts on neural pathways to aid those with ADHD, supporting better cognitive outcomes and attention spans.
Evidence Summary
Improving Task Management in ADHD
Individuals with ADHD find complex tasks challenging due to difficulties with response inhibition and sustained attention.
Research shows that organizational strategies and structured support can significantly improve their ability to manage these tasks and perform better academically.
- People with ADHD often struggle with tasks that require a lot of thinking, impacting their performance in school and other areas of life.
- Individuals with ADHD have difficulty stopping inappropriate actions, leading to challenges in completing tasks that need sustained attention.
- Good organizational skills can help students with ADHD improve their academic performance and manage complex tasks more effectively.
Research shows that organizational strategies and structured support can significantly improve their ability to manage these tasks and perform better academically.
- People with ADHD often struggle with tasks that require a lot of thinking, impacting their performance in school and other areas of life.
- Individuals with ADHD have difficulty stopping inappropriate actions, leading to challenges in completing tasks that need sustained attention.
- Good organizational skills can help students with ADHD improve their academic performance and manage complex tasks more effectively.