Adderall Study Database
Visual Abstract
Neurocognitive, Autonomic, and Mood Effects of Adderall: A Pilot Study of Healthy College Students
Adderall (Mixed Amphetamine Salts) Has Minimal Cognitive Effects in College Students Without ADHD
September 12, 2024
author
Weyandt LL, White TL, Gudmundsdottir BG, Nitenson AZ, Rathkey ES, De Leon KA, Bjorn SA
journal
Pharmacy
Date Published
2018-06-27
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The research investigated whether Adderall enhances cognitive functioning in college students without ADHD.
💡
What They Found
The study found that Adderall had minimal effects on cognition but significant effects on autonomic responses and emotional states.
📚
What This Means
The findings show that Adderall does not significantly enhance neurocognitive performance in healthy college students, aligning with current evidence that it is mainly effective for individuals with ADHD.
Study Summary
Study Overview
Adderall is used to treat ADHD and is popular among college students for boosting attention and focus.
However, studies show that while Adderall might improve attention, it does not significantly enhance other cognitive abilities such as memory or problem-solving.
In fact, users often report feeling more confident but may face challenges in task completion and social interactions.
Additionally, Adderall causes emotional and physical activation without providing strong cognitive benefits, indicating a disconnect between expectations and reality.
However, studies show that while Adderall might improve attention, it does not significantly enhance other cognitive abilities such as memory or problem-solving.
In fact, users often report feeling more confident but may face challenges in task completion and social interactions.
Additionally, Adderall causes emotional and physical activation without providing strong cognitive benefits, indicating a disconnect between expectations and reality.
Abstract: background
Prescription stimulant medications are considered a safe and long-term effective treatment for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Studies support that stimulants enhance attention, memory, self-regulation and executive function in indiv...more

Dissociation of Effects
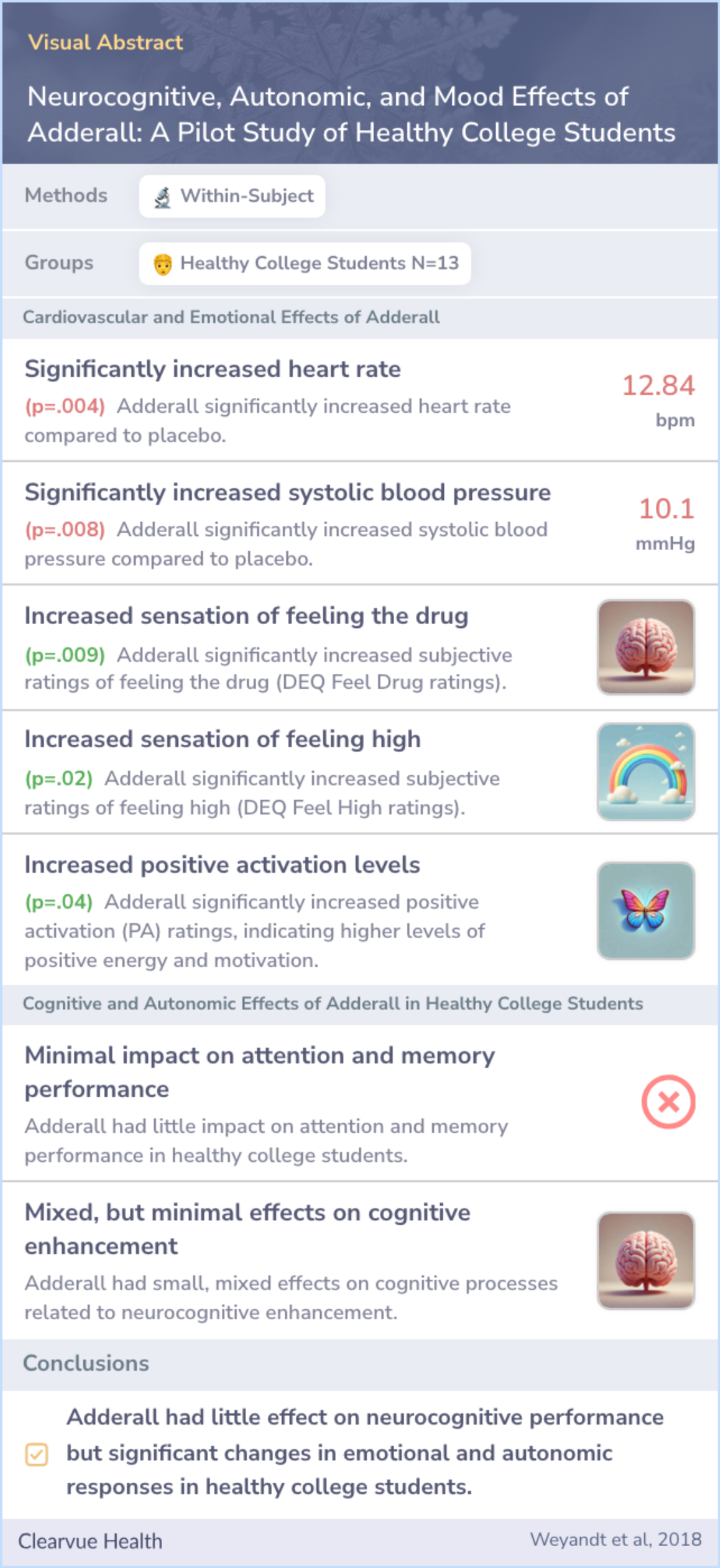
"Overall, the present findings indicate dissociation between the effects of Adderall on activation and neurocognition, and more importantly, contrary to common belief, Adderall had little impact on neurocognitive performance in healthy college students."
Impact on Confidence
"These findings support that Adderall can have neurocognitive effects that are discordant with drug expectancies, and while improving attention skills, may simultaneously degrade students' confidence in their abilities to problem solve, complete tasks, and interact with others."
Emotional Activation
"The present pilot study indicates that a moderate dose of Adderall has small to minimal effects on cognitive processes relevant to academic enhancement, in contrast with its significant, large effects on activated positive emotion, autonomic activity, and subjective drug responses."
Study Summary
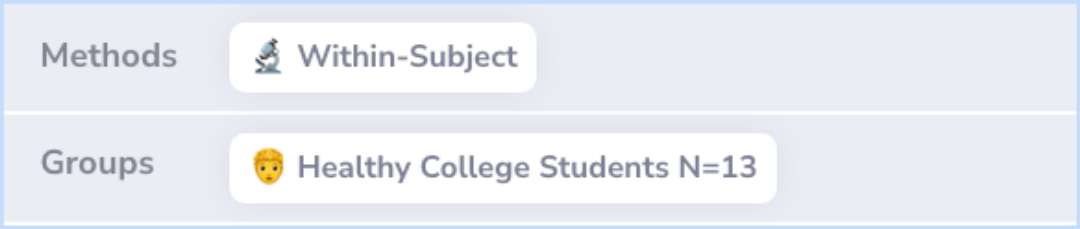
Methods
To explore the effects of Adderall on non-ADHD college students, researchers conducted a detailed study. They used a small group of healthy college students (13 participants) and employed a method where neither the participants nor the researchers knew who received Adderall or a placebo – this is known as a double-blind design. This way, each participant served as their own control, allowing a direct comparison of effects.
The study targeted cognitive and emotional functions, considering how these students felt about their brain performance after taking the drug. This approach included evaluating both mental abilities and feelings towards using the medication.
The study targeted cognitive and emotional functions, considering how these students felt about their brain performance after taking the drug. This approach included evaluating both mental abilities and feelings towards using the medication.
Abstract: methods
We investigated the effects of mixed-salts amphetamine (i.e., Adderall, 30 mg) on cognitive, autonomic and emotional functioning in a pilot sample of healthy college students without ADHD (n = 13), using a double-blind, placebo-controlled, within-sub...more
Study Summary
Results
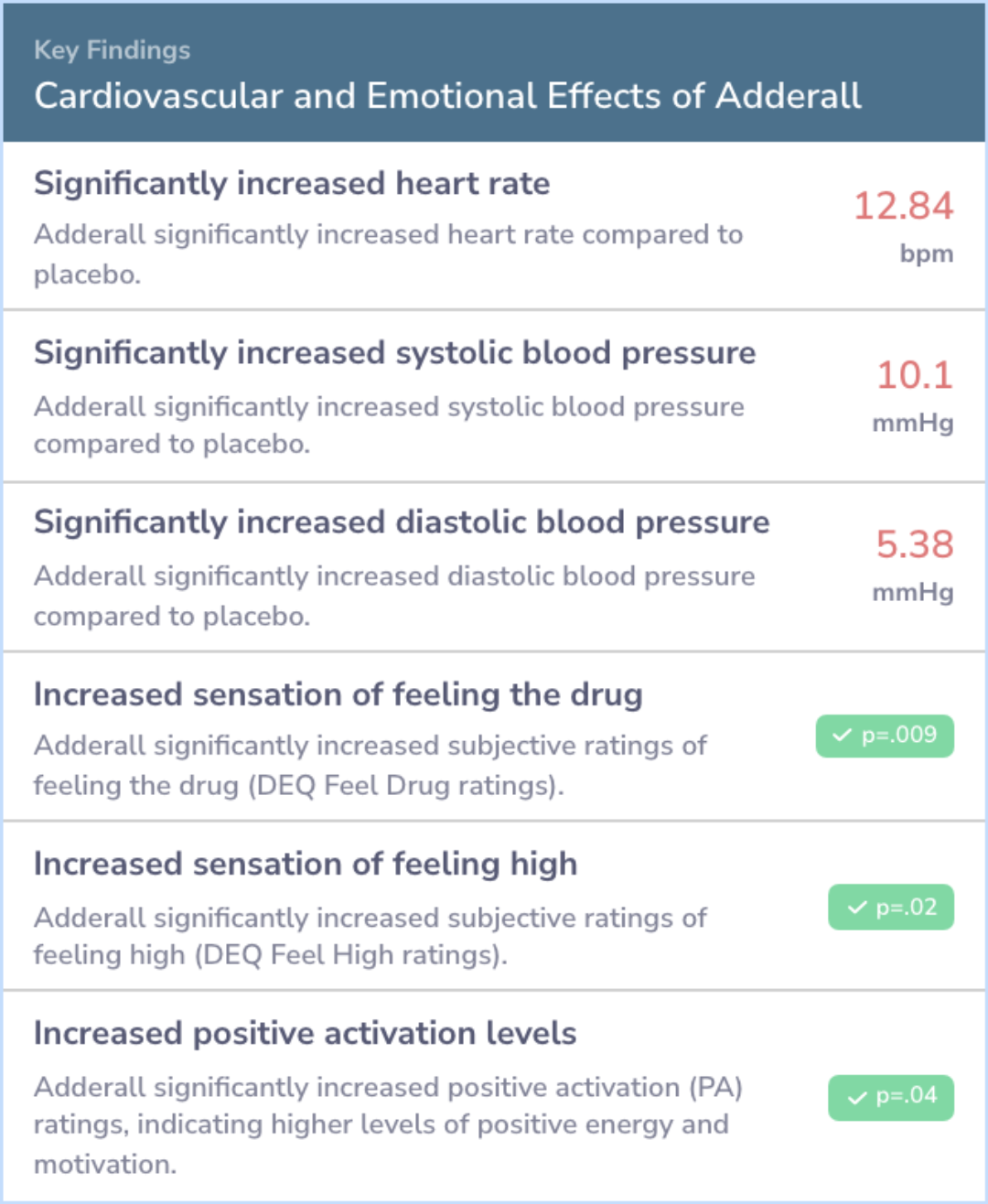
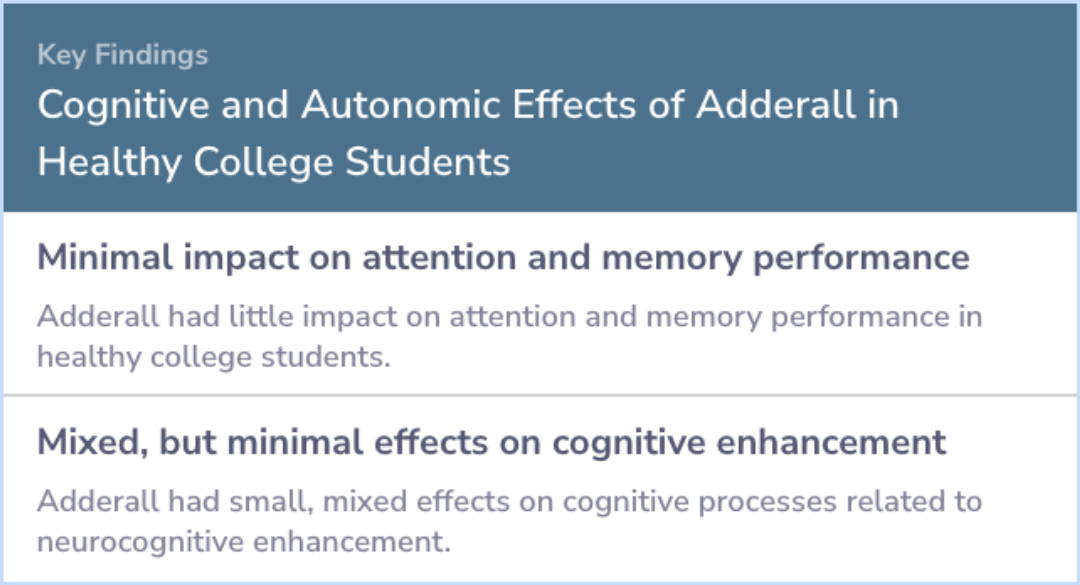
The study found that Adderall had very little impact on improving cognitive abilities, which are the mental skills we use every day. While some small effects on mental processes were observed, the results were largely inconsistent. However, the drug did significantly affect physical responses, like heart rate, as well as how the participants felt and experienced the drug, boosting emotions and alertness.
Importantly, the popular belief that Adderall enhances mental sharpness in college students without ADHD is not supported by this study. Due to the exploratory nature and small size of the study, these outcomes should be viewed with caution.
Importantly, the popular belief that Adderall enhances mental sharpness in college students without ADHD is not supported by this study. Due to the exploratory nature and small size of the study, these outcomes should be viewed with caution.
Abstract: results
Results revealed that Adderall had minimal, but mixed, effects on cognitive processes relevant to neurocognitive enhancement (small effects), and substantial effects on autonomic responses, subjective drug experiences, and positive states of activate...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
The findings suggest that expecting cognitive enhancement from Adderall in healthy students is likely misguided. This study may guide future research and inform educational messaging for college students and adults who use Adderall hoping for a cognitive edge.
Further exploration is needed to better understand the true effects of these stimulants on the non-ADHD population. It’s also critical to communicate accurately about what these drugs can and cannot do, preventing misuse driven by misconceptions about their cognitive benefits.
Further exploration is needed to better understand the true effects of these stimulants on the non-ADHD population. It’s also critical to communicate accurately about what these drugs can and cannot do, preventing misuse driven by misconceptions about their cognitive benefits.
Abstract: conclusions
The results have implications for future studies and the education of healthy college students and adults who commonly use Adderall to enhance neurocognition.

Background Information
Patient Guide
💊
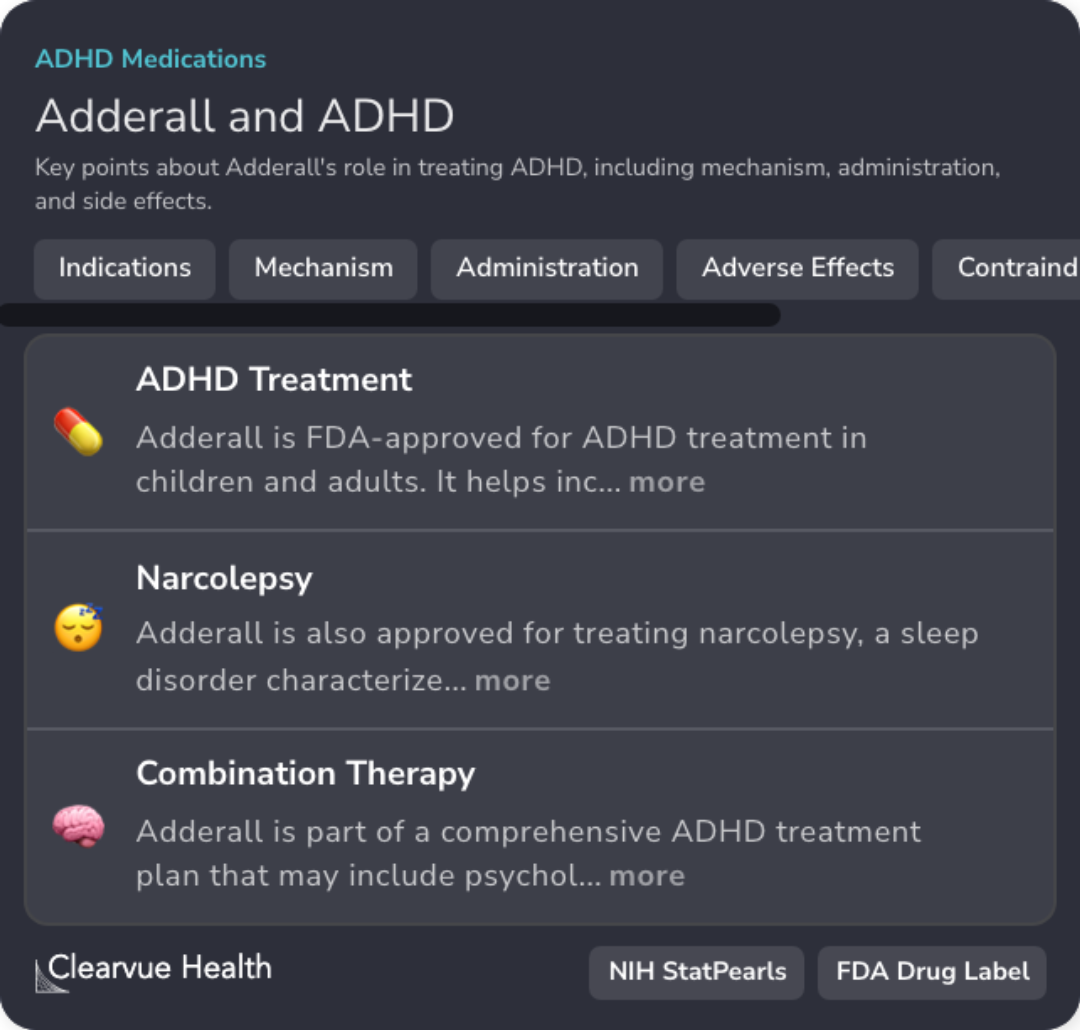
Adderall's Approved Uses
Adderall is FDA-approved for treating ADHD and narcolepsy, impacting attention and sleep disorders.
🧬
Neurotransmitter Dynamics
Adderall boosts dopamine and norepinephrine by blocking their reuptake, enhancing focus and energy.
❤️
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Chronic Adderall use may alter brain chemistry and poses risks of cardiovascular events and growth suppression.
🔍
Monitoring for Misuse
Due to high misuse potential, monitoring for abuse and diversion is essential with Adderall use.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Adderall (Mixed Amphetamine Salts) Has Minimal Cognitive Effects in College Students Without ADHD
Amphetamines remain FDA-approved for treating ADHD in both adults and children over six, emphasizing its established efficacy in this demographic.
Clinical effectiveness varies, especially between immediate and extended-release formulations, guiding initial dosage decisions before potentially switching to an extended-release format.
However, the combination of Adderall with certain serotonergic agents is associated with an increased risk of serotonin syndrome, demanding vigilant monitoring.
Additionally, serious cardiovascular events, such as myocardial infarction, further underscore the necessity for thorough cardiac evaluations, particularly in patients with pre-existing cardiac abnormalities.
Moreover, long-term stimulant use in children raises concerns about growth velocity and potential reductions in adult height, warranting careful consideration.
The efficacy of Adderall over extended periods calls for periodic reassessment to ensure its continued benefit for the individual's treatment plan.
Clinical effectiveness varies, especially between immediate and extended-release formulations, guiding initial dosage decisions before potentially switching to an extended-release format.
However, the combination of Adderall with certain serotonergic agents is associated with an increased risk of serotonin syndrome, demanding vigilant monitoring.
Additionally, serious cardiovascular events, such as myocardial infarction, further underscore the necessity for thorough cardiac evaluations, particularly in patients with pre-existing cardiac abnormalities.
Moreover, long-term stimulant use in children raises concerns about growth velocity and potential reductions in adult height, warranting careful consideration.
The efficacy of Adderall over extended periods calls for periodic reassessment to ensure its continued benefit for the individual's treatment plan.
Evidence Summary
Unpacking ADHD: Diverse Impacts Beyond Behavior
ADHD is recognized as a diverse disorder. This study reveals how children with ADHD face challenges across different areas, such as emotion regulation and executive functions, but not necessarily in recognizing disgust or delay aversion. These findings underscore ADHD's complex nature.
Investigating these areas provides insights beyond cognitive deficits, highlighting how emotional processing may also distinguish children with ADHD from their peers.
Investigating these areas provides insights beyond cognitive deficits, highlighting how emotional processing may also distinguish children with ADHD from their peers.
Evidence Summary
ADHD and Social Challenges in Youth
Children with ADHD face notable challenges in social settings, often predicting issues like peer rejection and inadequate social skills. This study tracked children aged 6 to 10, finding that those with ADHD displayed persistent social problems over two years. Their ability to use emotional cues effectively in decision-making was linked to these difficulties. Both inattention and impulsivity contributed to these social hurdles.
Similar to college students misusing stimulants for non-existing ADHD, these findings illustrate a nuanced picture of challenges faced by those diagnosed in their formative years.
Similar to college students misusing stimulants for non-existing ADHD, these findings illustrate a nuanced picture of challenges faced by those diagnosed in their formative years.