Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
An effect-size analysis of pharmacologic treatments for generalized anxiety disorder
Effect-size analysis of GAD treatments
November 25, 2024
author
Hidalgo RB, Tupler LA, Davidson JR
journal
J Psychopharmacol
Date Published
2007 Nov
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study analyzed how different medications, such as SSRIs, SNRIs, benzodiazepines, and complementary medicines, affect generalized anxiety disorder.
💡
What They Found
They found that pregabalin showed the highest effectiveness, while complementary medicines had worse outcomes compared to placebo.
📚
What This Means
The findings suggest pregabalin is more effective than other medications for GAD, matching current evidence that prioritizes medications like SSRIs and SNRIs alongside therapy rather than complementary medicines.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to explore the effectiveness of various treatments for Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), especially in children and adolescents. It found that SSRIs show strong responses for treating anxiety in young patients. The implications suggest that treating GAD early could lead to better outcomes, and raises concerns about the effectiveness of some alternative treatments that performed worse than placebo.
The researchers highlighted the need for more studies, especially regarding long-term effects of certain medications, to better understand how to help those suffering from GAD.
The researchers highlighted the need for more studies, especially regarding long-term effects of certain medications, to better understand how to help those suffering from GAD.
Abstract: background
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a prevalent and impairing disorder, associated with extensive psychiatric and medical comorbidity and usually characterized by a chronic course. Different drugs have been investigated in GAD; among them are the f...more

Strong Response to SSRIs
"such a strong response to SSRIs in children and adolescents with GAD may suggest that these compounds were clearly effective in treating childhood/adolescent anxiety in these two studies."
Importance of Early Treatment
"the higher effect size in children and adolescents may suggest that earlier intervention in GAD could lead to better outcomes compared to adults, who have typically been suffering from the disorder for many years before treatment."
Concerns About Alternative Treatments
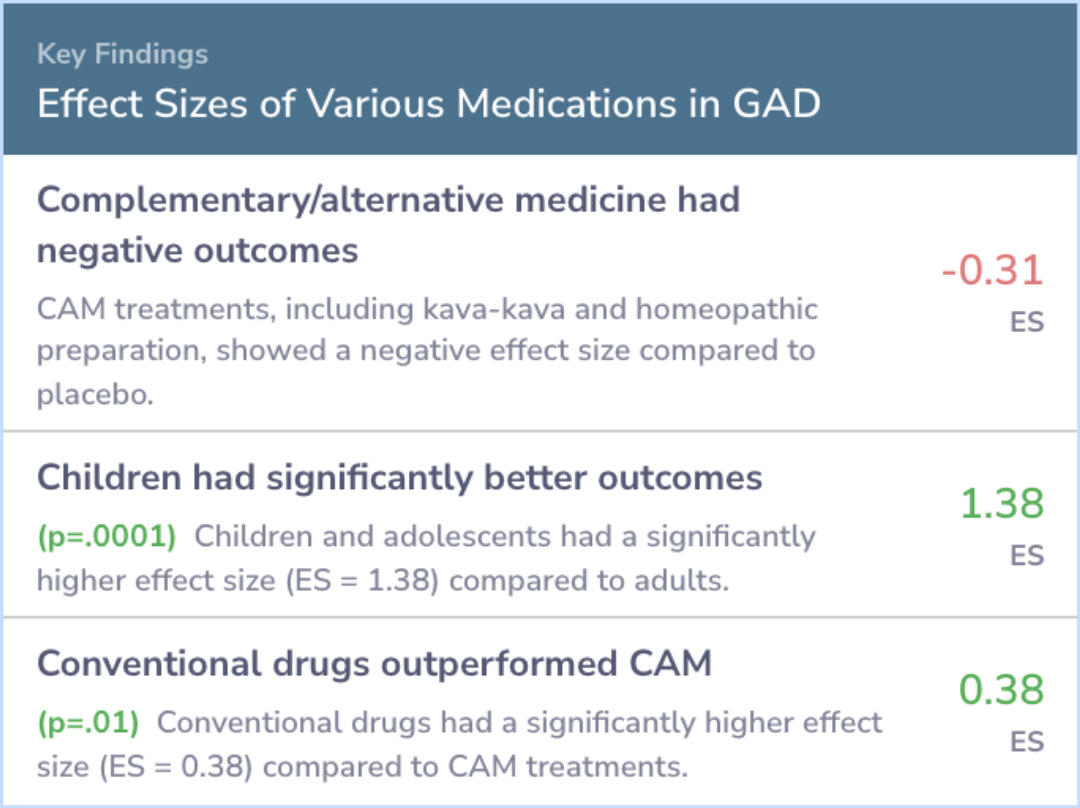
"CAM therapy had a negative mean ES compared with placebo. In other words, patients experiencing GAD taking a sugar pill did better than patients treated with kava-kava or homeopathy."
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers analyzed data from 21 clinical trials comparing medications for GAD with a placebo. These trials used scales like the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) to measure effectiveness. The studies, dating from 1987 to 2003, involved communications with study authors and drug companies.
The data were compiled from the MEDLINE and PsycINFO databases, focusing on guidelines such as DSM-III-R, DSM-IV, or ICD-10 for diagnosing GAD. The primary measure for effectiveness was changes in anxiety scores from the beginning to the end of each trial.
The data were compiled from the MEDLINE and PsycINFO databases, focusing on guidelines such as DSM-III-R, DSM-IV, or ICD-10 for diagnosing GAD. The primary measure for effectiveness was changes in anxiety scores from the beginning to the end of each trial.
Abstract: methods
We conducted an effect size (ES) analysis of 21 double-blind placebo-controlled trials of medications treating DSM-III-R, DSM-IV or ICD-10 GAD using HAM-A change in score from baseline or endpoint score as the main efficacy measure. Literature search...more
Study Summary
Results
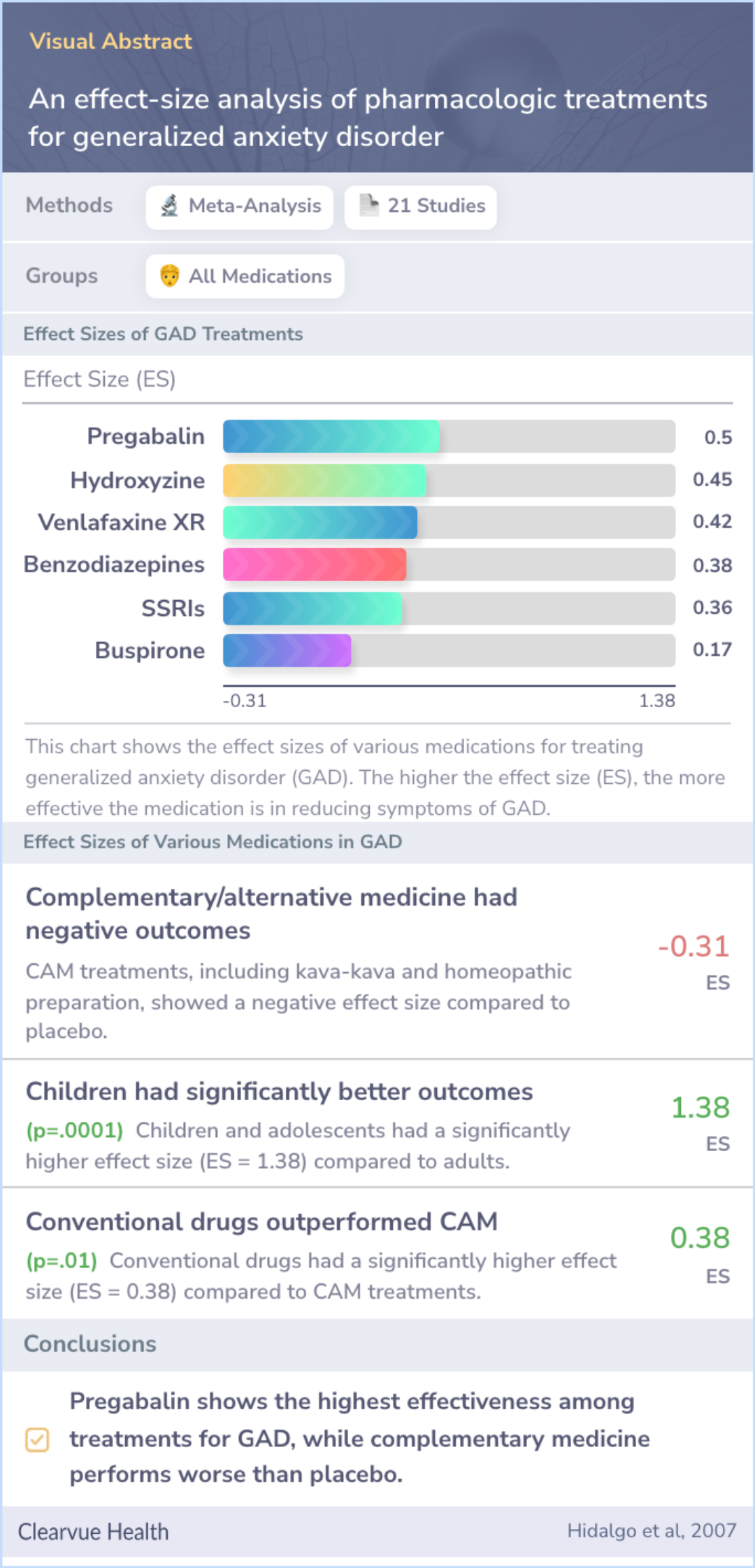
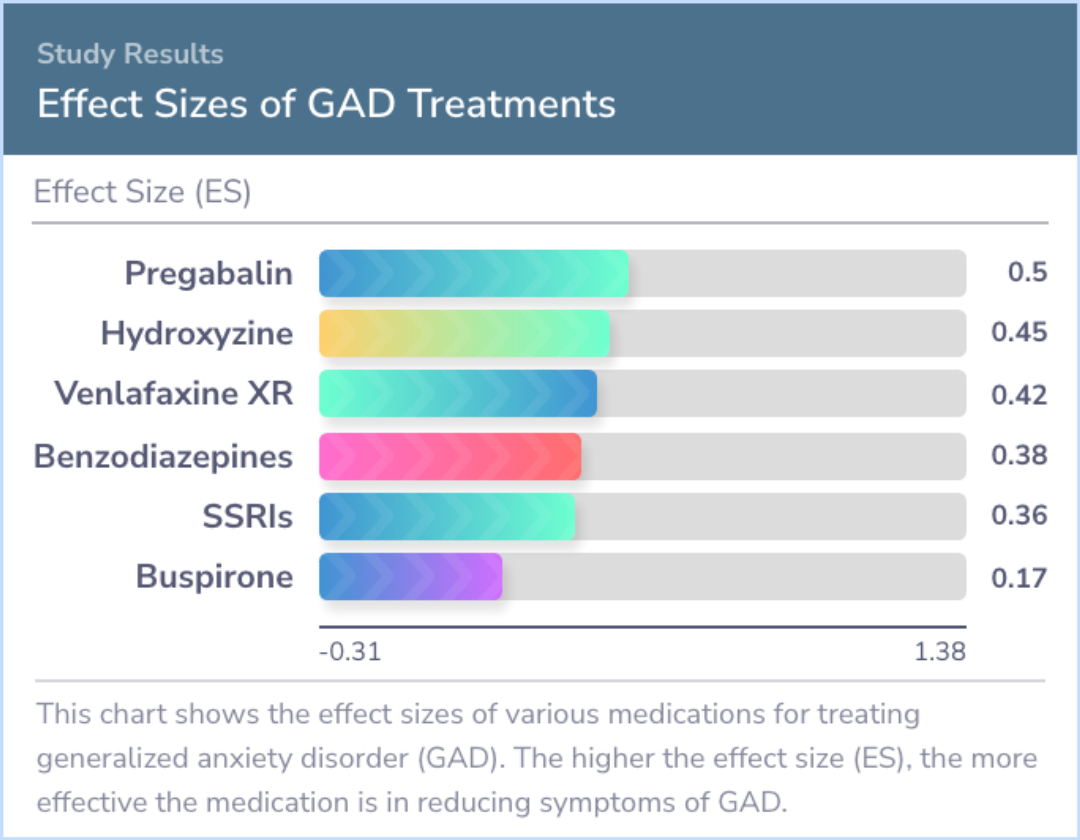
When comparing all medications against placebo, an effect size measure showed a moderate benefit. Pregabalin (Lyrica) scored the highest, followed by antihistamines and SNRIs. Benzodiazepines and SSRIs showed less impact, while alternative treatments like kava had negative effects.
Children and adolescents benefited more from these medications than adults did. Alternative medicine performed worse than placebos. The results did not significantly vary based on study details like location or dosing methods.
Children and adolescents benefited more from these medications than adults did. Alternative medicine performed worse than placebos. The results did not significantly vary based on study details like location or dosing methods.
Abstract: results
comparing all drugs versus placebo, the ES was 0.39. Mean ESs, excluding children, were PGB: 0.50, AH: 0.45, SNRI: 0.42, BZ: 0.38, SSRI: 0.36, AZA: 0.17 and CAM: -0.31. Comparing ES for adults versus children/adolescents (excluding CAM) and conventio...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
The studied medications had varied effectiveness, with some showing moderate benefits and others minimal. Pregabalin emerged as notably effective. Young people responded better to these treatments compared to adults.
Alternative treatments didn't perform well, showing less effectiveness than even placebos. Overall, these findings suggest a variable but generally moderate efficacy for traditional medications over alternative ones for treating generalized anxiety disorder.
Alternative treatments didn't perform well, showing less effectiveness than even placebos. Overall, these findings suggest a variable but generally moderate efficacy for traditional medications over alternative ones for treating generalized anxiety disorder.
Abstract: conclusions
Medications varied in the magnitude of their ES, ranging from moderate to poor. Adolescents and children showed a much greater ES compared with adults. Subjects taking CAM had worse outcomes than placebo.

Background Information
Patient Guide
🧠
Biological Influences in GAD
Genetic predisposition and neurotransmitter imbalances like serotonin and norepinephrine impact GAD.
💊
Pharmacologic Options for GAD
SSRIs, SNRIs, and benzodiazepines are commonly used medications in GAD management.
🔗
GAD's Comorbidities
GAD often coexists with depression, complicating its treatment plan.
⚖️
Challenges in Treatment Compliance
Side effects and cost issues often result in medication compliance struggles.
🔄
Psychiatric and Medical Comorbidity
GAD presents with high levels of psychiatric and medical comorbidity, affecting overall treatment effectiveness.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Effect-size analysis of GAD treatments
In line with the abstract's findings on medication efficacy, SSRIs and SNRIs are recommended as first-line treatments for GAD due to their effectiveness in reducing anxiety symptoms.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) also emerges as a highly effective non-pharmacological treatment option, often provided in structured sessions depending on the individual's needs and severity of symptoms.
Combining pharmacotherapy with CBT might enhance treatment outcomes compared to using either approach alone, although adult-specific data remains indirect.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) also emerges as a highly effective non-pharmacological treatment option, often provided in structured sessions depending on the individual's needs and severity of symptoms.
Combining pharmacotherapy with CBT might enhance treatment outcomes compared to using either approach alone, although adult-specific data remains indirect.
Evidence Summary
Effectiveness and Safety of GAD Medications
The overview highlights different medications used to treat Generalized Anxiety Disorder. It breaks down their effectiveness and safety based on clinical studies, offering an evidence-based perspective on managing GAD. The insights shared are grounded in expert guidelines.
Key details include how these medications perform in clinical settings, with a focus on their ability to manage symptoms and maintain safety profiles over time.
Key details include how these medications perform in clinical settings, with a focus on their ability to manage symptoms and maintain safety profiles over time.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Effectiveness of GAD Treatments
The content highlights how studies have compared different treatments for generalized anxiety disorder, specifically focusing on their ability to reduce anxiety symptoms. Each treatment's effectiveness is measured across multiple studies.
The results emphasize which therapies tend to help the most, with the data showing variability in success between different treatment methods, helping pinpoint which approaches offer the most symptom relief.
The results emphasize which therapies tend to help the most, with the data showing variability in success between different treatment methods, helping pinpoint which approaches offer the most symptom relief.
Evidence Summary
Sertraline for Treating Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Sertraline is a treatment option for generalized anxiety disorder, focusing on reducing anxiety symptoms. The comparison explores how the medication works in easing these symptoms while also examining both its benefits and possible side effects. The goal is to provide a thorough look at its overall effects.
The page highlights sertraline's role in addressing anxiety, offering insight into its therapeutic use and weighing potential outcomes for patients with GAD.
The page highlights sertraline's role in addressing anxiety, offering insight into its therapeutic use and weighing potential outcomes for patients with GAD.