Ritalin Paper Database
Visual Abstract
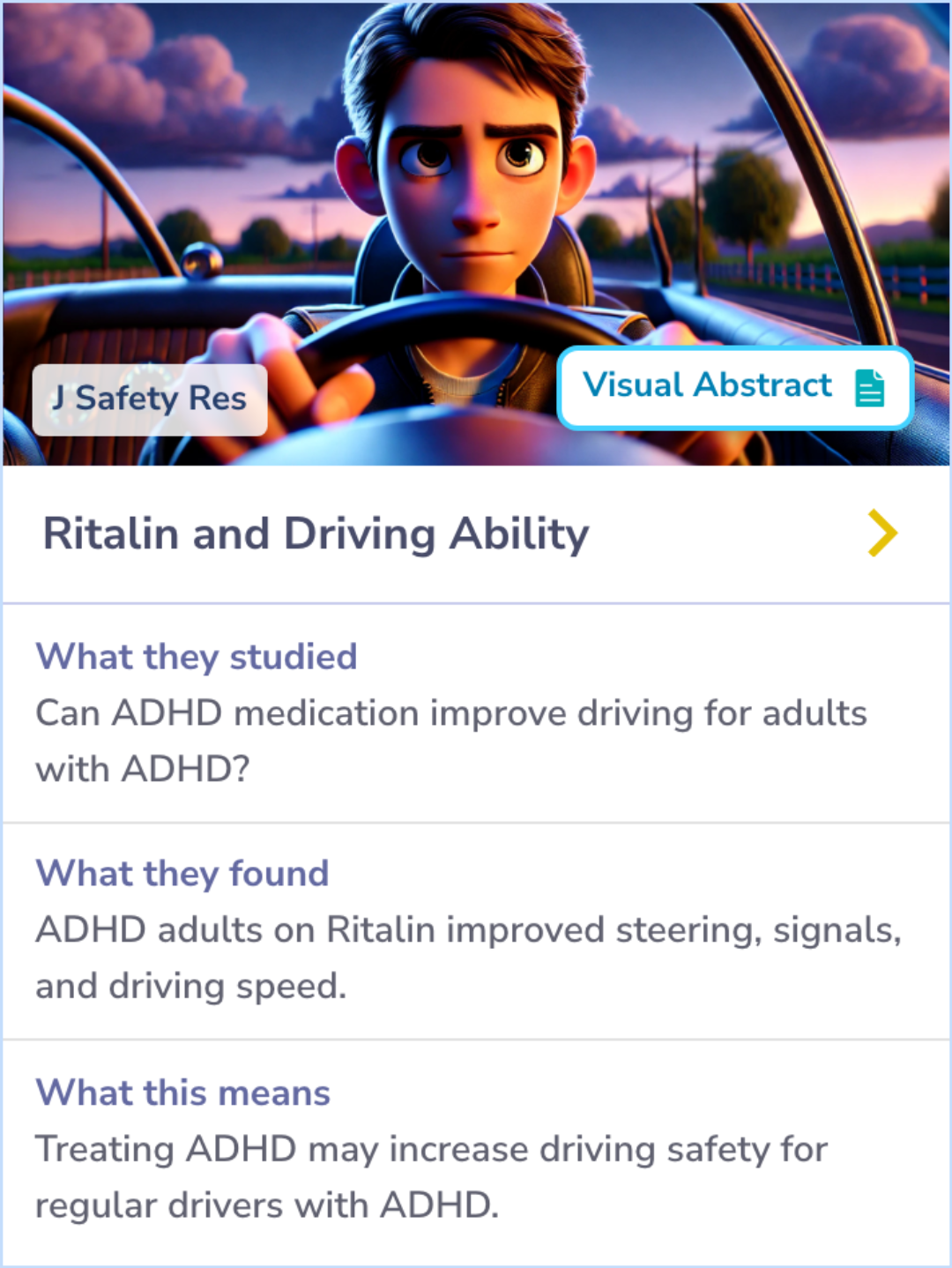
Once-a-day Concerta methylphenidate versus three-times-daily methylphenidate in laboratory and natural settings
Concerta vs. thrice-daily MPH
August 27, 2024
author
Pelham WE, Gnagy EM, Burrows-Maclean L, Williams A, Fabiano GA, Morrisey SM, Chronis AM, Forehand GL, Nguyen CA, Hoffman MT, Lock TM, Fielbelkorn K, Coles EK, Panahon CJ, Steiner RL, Meichenbaum DL, Onyango AN, Morse GD
journal
Pediatrics
Date Published
2001 Jun
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
They studied the effectiveness and duration of action of extended-release Concerta compared to immediate-release methylphenidate taken three times a day in children with ADHD.
💡
What They Found
They found that both Concerta and immediate-release methylphenidate were effective in improving children's behavior, with Concerta lasting at least 12 hours and being preferred by more parents.
📚
What This Means
These findings indicate that Concerta is effective for daily and evening behavior improvement in children with ADHD, similar to current evidence supporting methylphenidate's use for ADHD treatment.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to evaluate how well Concerta, a long-acting form of methylphenidate, works throughout the day in children with ADHD. Researchers wanted to see if it could provide consistent benefits from morning until evening, especially compared to immediate-release versions of the medication. The study involved controlled settings where children were observed in classroom and play environments to measure the effectiveness of the medication over time.
The results revealed that Concerta successfully maintained its effects for up to 12 hours, covering both daytime and evening behavior. This long-lasting effect makes it a strong option for children who need extended medication coverage. Additionally, the findings suggest that using a single daily dose of Concerta might be more convenient and preferred by parents, especially when other non-medication approaches aren't enough to manage symptoms.
The results revealed that Concerta successfully maintained its effects for up to 12 hours, covering both daytime and evening behavior. This long-lasting effect makes it a strong option for children who need extended medication coverage. Additionally, the findings suggest that using a single daily dose of Concerta might be more convenient and preferred by parents, especially when other non-medication approaches aren't enough to manage symptoms.
Abstract: background
Methylphenidate (MPH), the most commonly prescribed drug for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), has a short half-life, which necessitates multiple daily doses. The need for multiple doses produces problems with medication administration...more

Concerta's Long-Lasting Effects
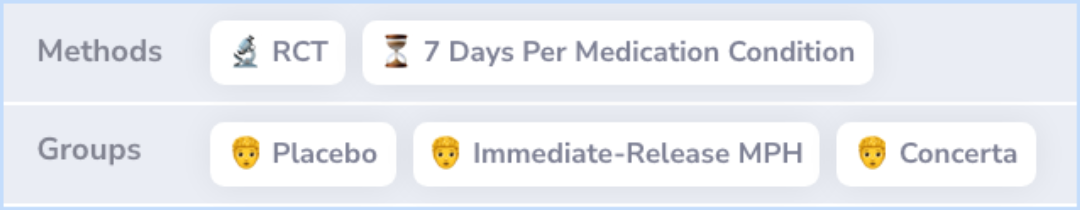
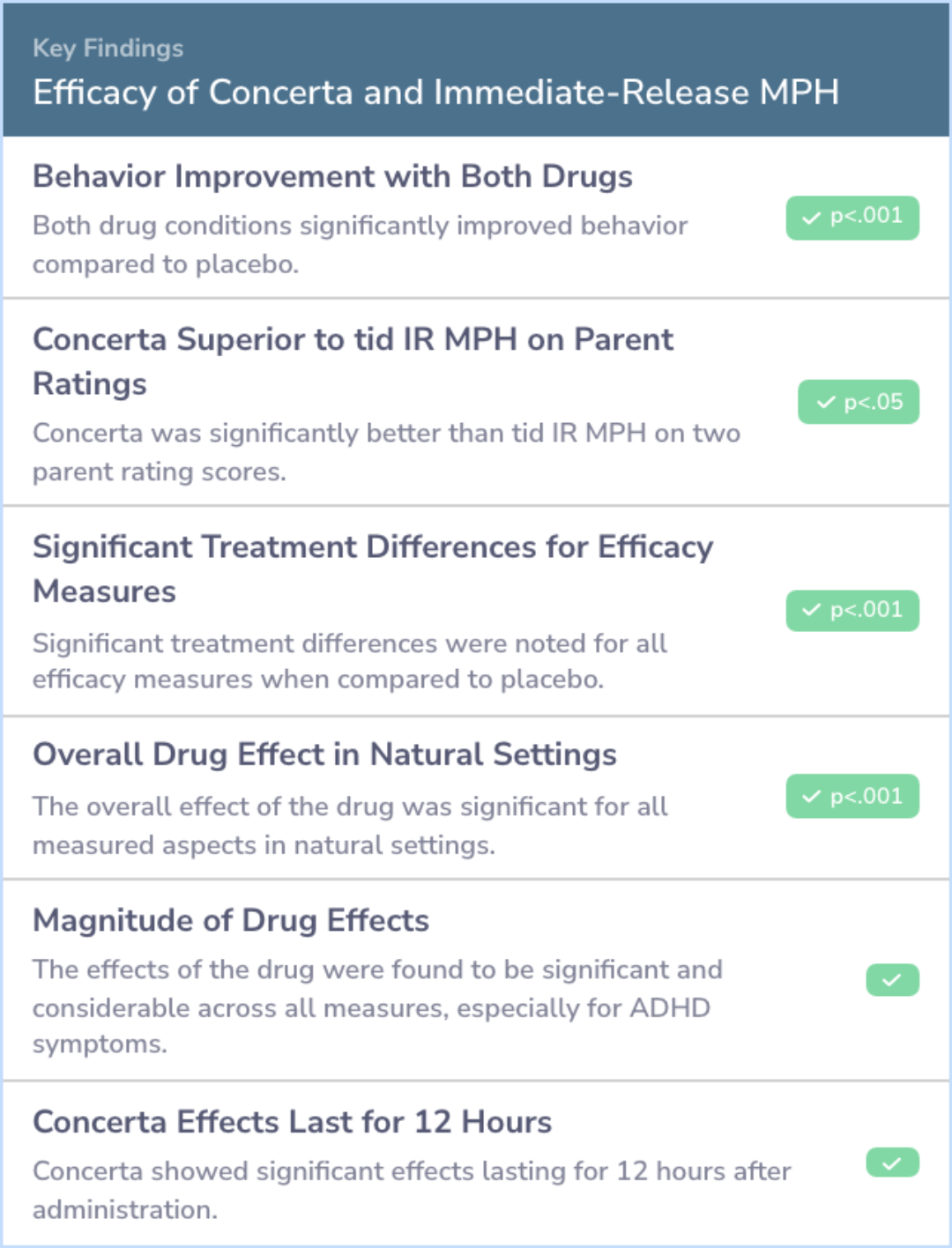
"The fact that Concerta had significant effects through 12 hours after administration in the laboratory setting and on measures of evening behavior in the natural setting indicates that the span of action of Concerta is sufficiently long and comparable to tid IR MPH."
Parent Preference for Once-Daily Dosing
"This investigation clearly supports the efficacy of the Concerta long-acting formulation of MPH for parents who desire to have medication benefits for their child throughout the day and early evening."
Concerta as a Preferred Option
"For those who do need a full 12 hours of medication coverage, based on the results of this study, Concerta would seem to be the choice."
Study Summary
Methods
The study included 68 children aged 6-12 with ADHD, comparing placebo, immediate-release (IR) MPH three times daily, and Concerta once daily. The study used a within-subject, double-blind design. Three dosing levels were tested: 5 mg IR MPH tid (three times daily)/18 mg Concerta qd (once daily), 10 mg IR MPH tid/36 mg Concerta qd, and 15 mg IR MPH tid/54 mg Concerta qd. Each regimen lasted 7 days. A daily report card (DRC) tracked individualized behavior goals, completed by teachers and reinforced by parents. Classroom and social behaviors were measured in a lab setting on Saturdays. Parents and teachers provided ratings of behavior and treatment effectiveness. Reports of adverse effects were also collected.
Abstract: methods
Sixty-eight children with ADHD, 6 to 12 years old, participated in a within-subject, double-blind comparison of placebo, immediate-release (IR) MPH 3 times a day (tid), and Concerta, a once-daily MPH formulation. Three dosing levels of medication wer...more
Study Summary
Results
Results indicated that both medication conditions differed significantly from placebo and showed no significant differences from each other. Both Concerta and IR MPH improved school behavior and lasted through the evening. Concerta showed equivalent effects to tid MPH in lab settings, lasting at least 12 hours. Although side effects were similar, parents showed a preference for Concerta over tid MPH and placebo. Both medications enhanced productivity and accuracy in academic tasks, reduced disruptive behavior, and improved rule following and social interactions in structured and unstructured settings. Medications prevented behavior deterioration over the day, with the DRC proving useful in both lab and natural settings.
Abstract: results
On virtually all measures in all settings, both drug conditions were significantly different from placebo, and the 2 drugs were not different from each other. In children's regular school settings, both medications improved behavior as measured by te...more
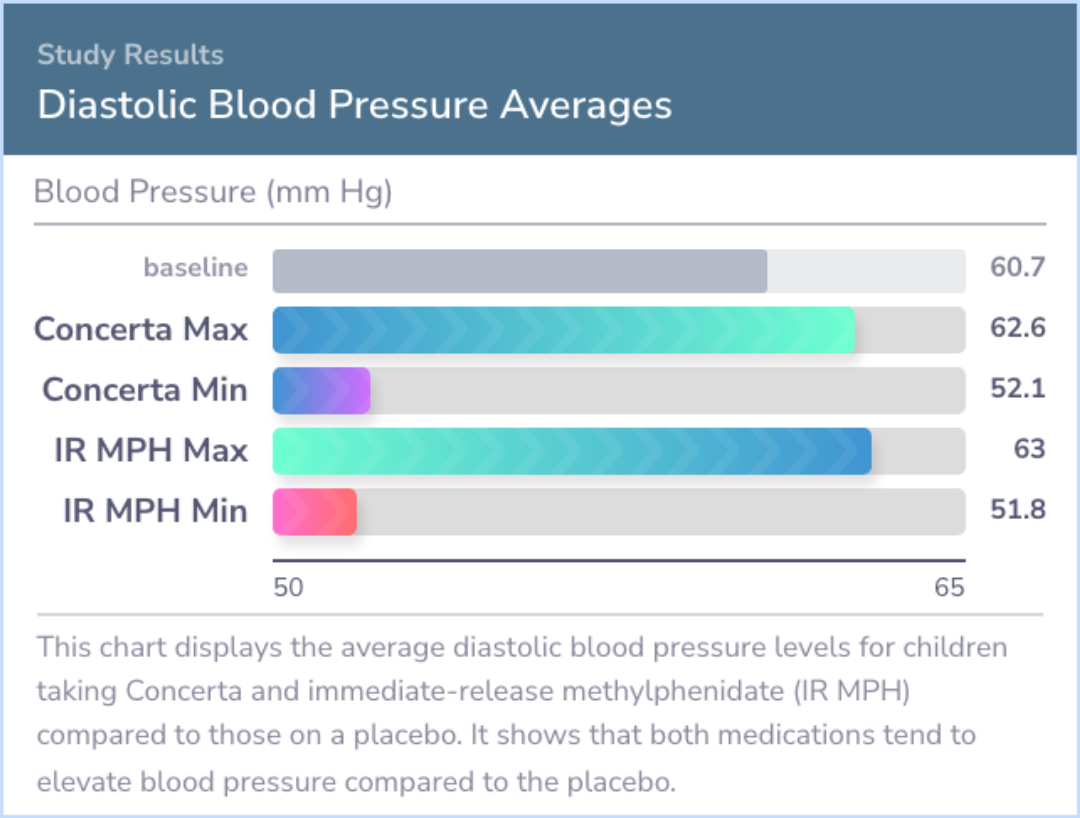
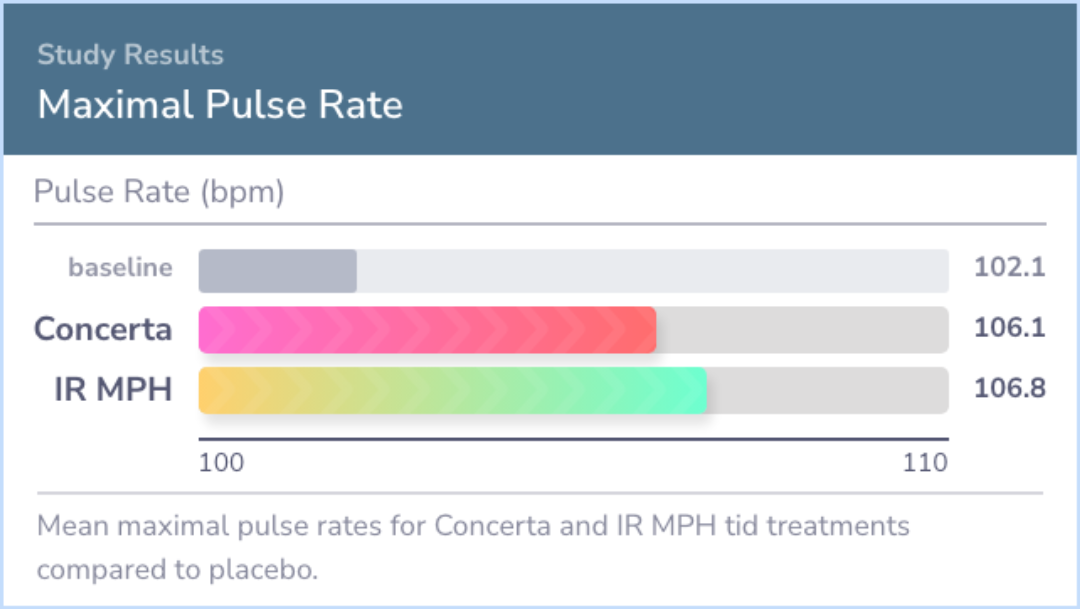
Study Summary
Conclusions
The study strongly supports the use of Concerta, a long-acting MPH formulation, for providing all-day behavioral benefits for children with ADHD, extending into the early evening. This once-daily medication can help parents manage their child's ADHD symptoms effectively throughout the day without the challenges of multiple dosing.
Abstract: conclusions
This investigation clearly supports the efficacy of the Concerta long-acting formulation of MPH for parents who desire to have medication benefits for their child throughout the day and early evening. (ABSTRACT TRUNCATED)
Background Information
Patient Guide
🧠
Mechanism of Action
Methylphenidate blocks norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake, increasing their synaptic concentration.
💊
Formulation Types
Available in immediate-release, extended-release, and sustained-release formulations for different needs.
🧒
Age Limit for Use
Children must be six years or older to be prescribed methylphenidate for ADHD.
❤️
Cardiovascular Risks
May exacerbate symptoms like palpitations and is not recommended for those with serious heart conditions.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Concerta vs. thrice-daily MPH
The study's findings underscore the efficacy of Concerta in managing ADHD symptoms, which aligns with the noted significant impact of stimulant medications on ADHD symptoms.
Methylphenidate (MPH) remains the recommended first-line pharmacologic treatment for preschool children, particularly due to the lack of sufficient studies on nonstimulants.
Combining behavioral therapy with medication has shown positive effects on pre-adolescent children, reinforcing the study’s backdrop of behavioral interventions.
Clinicians should monitor heart rate and blood pressure in patients on stimulants, as some individuals may experience notable increases.
Effective treatment also involves continuous communication between pediatricians, teachers, and school personnel.
When behavioral interventions alone are insufficient, methylphenidate may be considered to alleviate moderate-to-severe disturbances in young children’s functioning.
Methylphenidate (MPH) remains the recommended first-line pharmacologic treatment for preschool children, particularly due to the lack of sufficient studies on nonstimulants.
Combining behavioral therapy with medication has shown positive effects on pre-adolescent children, reinforcing the study’s backdrop of behavioral interventions.
Clinicians should monitor heart rate and blood pressure in patients on stimulants, as some individuals may experience notable increases.
Effective treatment also involves continuous communication between pediatricians, teachers, and school personnel.
When behavioral interventions alone are insufficient, methylphenidate may be considered to alleviate moderate-to-severe disturbances in young children’s functioning.
Evidence Summary
Concerta vs. Thrice-Daily MPH: A Behavioral Comparison
Concerta delivers a long-lasting effect as a once-daily medication, unlike the short-acting benefits of thrice-daily MPH.
This comparison highlights that both options show significant differences from placebo, while their effects on behavior are remarkably similar.
In daily settings, both medications improve children's behavior and classroom productivity.
Parents reported a preference for Concerta, noting its once-a-day dosage convenience and sustained effectiveness through evening hours.
This comparison highlights that both options show significant differences from placebo, while their effects on behavior are remarkably similar.
In daily settings, both medications improve children's behavior and classroom productivity.
Parents reported a preference for Concerta, noting its once-a-day dosage convenience and sustained effectiveness through evening hours.
Evidence Summary
Impact of ADHD Medication on Driving
Studying vehicular issues in adults with ADHD reveals significant driving risks. They used a virtual reality simulator and evaluated two doses of methylphenidate against a placebo. High doses improved impulsiveness and steering, while low doses aided turn signal use. Simulator experience possibly masked some effects.
Evidence Summary
Understanding Atomoxetine vs. Methylphenidate
This discussion contrasts two ADHD medications: Atomoxetine and Methylphenidate.
Each drug has unique characteristics, effectiveness, and side effects that impact patient experiences.
Understanding these elements can aid in discerning how each medication works and how they respond differently to various patients.
By highlighting these differences, individuals can become more informed about their treatment options.
Each drug has unique characteristics, effectiveness, and side effects that impact patient experiences.
Understanding these elements can aid in discerning how each medication works and how they respond differently to various patients.
By highlighting these differences, individuals can become more informed about their treatment options.