Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
Depression and generalized anxiety disorder: cumulative and sequential comorbidity in a birth cohort followed prospectively to age 32 years
Comorbidity of Depression and Generalized Anxiety Disorder
November 25, 2024
author
Moffitt TE, Harrington H, Caspi A, Kim-Cohen J, Goldberg D, Gregory AM, Poulton R
journal
Arch Gen Psychiatry
Date Published
2007 Jun
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original

Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers aimed to understand the sequential and cumulative comorbidity between generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and major depressive disorder (MDD).
💡
What They Found
The study found that generalized anxiety does not always precede depression, as the conditions are reciprocally related more than previously thought.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that the relationship between GAD and MDD is strong and symmetrical, and the disorders could be categorized together as distress disorders.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This research explored the relationship between generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and major depressive disorder (MDD), aiming to reshape how we think about these conditions. It highlighted a more complex interaction than previously thought, suggesting these disorders could be seen together.
The findings reveal that GAD and MDD often influence each other, indicating the need for updated diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches that address their combined effects.
The findings reveal that GAD and MDD often influence each other, indicating the need for updated diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches that address their combined effects.
Abstract: background
To revisit the sequential and cumulative comorbidity between GAD and MDD using data from a prospective longitudinal cohort.

Bidirectional Relationship
"Our findings challenge the traditional view that generalized anxiety disorder typically precedes and eventually leads to major depressive disorder, as the data show that the reverse sequence occurs almost as frequently, suggesting a bidirectional relationship between these disorders."
Symmetrical Development
"This study provides evidence that GAD and MDD have a more symmetrical developmental relationship than previously recognized, which could influence how these disorders are categorized in diagnostic classifications."
Treatment Strategies
"These findings advocate for a reconsideration of diagnostic criteria and treatment strategies for GAD and MDD, as the overlapping and recurrent nature of these disorders may benefit from a unified treatment approach."
Study Summary
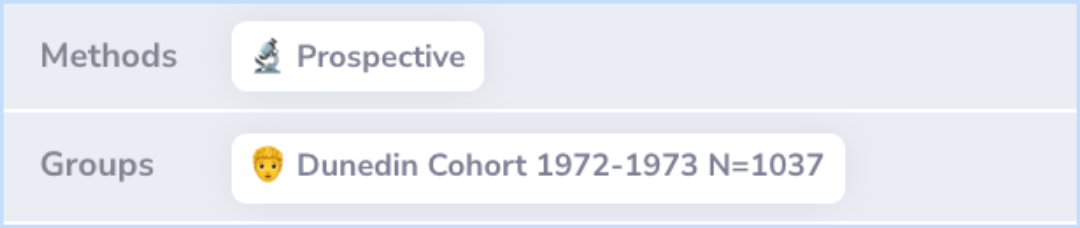
Methods
Researchers conducted a long-term study in New Zealand, using a group of people born in 1972-1973. This cohort included 1,037 members and was tracked from age 11 to 32.
The study used a 'life history calendar' to record the use of mental health services and conducted health assessments at seven different ages to diagnose anxiety and depression over time.
The study used a 'life history calendar' to record the use of mental health services and conducted health assessments at seven different ages to diagnose anxiety and depression over time.
Abstract: methods
Prospective longitudinal cohort study. New Zealand. The representative 1972-1973 Dunedin birth cohort of 1037 members was followed up to age 32 years with 96% retention. Research diagnoses of anxiety and depression were made at ages 11, 13, 15, 18, 2...more
Study Summary
Results
The study found that anxiety started before or at the same time as depression in 37% of cases. Conversely, depression started before or at the same time as anxiety in 32% of cases. Most people with anxiety had a history of depression, but less than half the people with depression had anxiety.
In adulthood, 12% had both disorders. Among these, mental health services and medication use were common, illustrating the substantial impact of these comorbid conditions.
In adulthood, 12% had both disorders. Among these, mental health services and medication use were common, illustrating the substantial impact of these comorbid conditions.
Abstract: results
Sequentially, anxiety began before or concurrently in 37% of depression cases, but depression began before or concurrently in 32% of anxiety cases. Cumulatively, 72% of lifetime anxiety cases had a history of depression, but 48% of lifetime depressio...more


Study Summary
Conclusions
This study challenges the common belief that anxiety usually comes before depression and eventually becomes depression. It found that the reverse happens nearly as often.
The findings suggest a strong link between GAD and MDD, indicating these disorders could be part of a single group of distress disorders. This suggests that both disorders should be considered equally in diagnosis, as their connection is more balanced than previously thought.
The findings suggest a strong link between GAD and MDD, indicating these disorders could be part of a single group of distress disorders. This suggests that both disorders should be considered equally in diagnosis, as their connection is more balanced than previously thought.
Abstract: conclusions
Challenging the prevailing notion that generalized anxiety usually precedes depression and eventually develops into depression, these findings show that the reverse pattern occurs almost as often. The GAD-MDD relation is strong, suggesting that the d...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
🔗
Shared Comorbidities in Disorders
GAD and MDD often coexist, making treatment approaches multifaceted and interconnected.
🧬
Genetic and Biological Roots
Both GAD and MDD have genetic factors and involve changes in neurotransmitter systems.
♻️
Chronic Nature and Recurrence
GAD and MDD are long-term, with relapse being common, highlighting the need for ongoing management.
🔍
Diagnostic Challenges
Diagnosing GAD and MDD involves careful assessment due to overlapping symptoms and comorbidities.
📅
Age and Progression
While the onset of MDD commonly occurs around age 40, cases are rising in younger populations.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Comorbidity of Depression and Generalized Anxiety Disorder
In line with the findings, individuals experiencing both anxiety and depression report greater functional impairment and a lower quality of life compared to those with a single disorder.
The co-occurrence of these conditions often results in a more chronic course than individual disorders.
Furthermore, genetic influences, such as shared heritability with neuroticism, may predispose individuals to this comorbidity, underscoring the need for tailored treatment approaches.
Age of onset varies, often aligning with the primary disorder, further complicating treatment outcomes in comorbid cases.
The co-occurrence of these conditions often results in a more chronic course than individual disorders.
Furthermore, genetic influences, such as shared heritability with neuroticism, may predispose individuals to this comorbidity, underscoring the need for tailored treatment approaches.
Age of onset varies, often aligning with the primary disorder, further complicating treatment outcomes in comorbid cases.
Evidence Summary
The Link Between Anxiety and Heart Disease
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is commonly found in people with coronary heart disease, highlighting a significant link between anxiety and heart health. Many with heart disease experience anxiety symptoms that align with GAD, indicating a frequent overlap of these conditions.
Exploring this connection sheds light on how mental and physical health intersect, specifically how heart disease may impact, or be impacted by, anxiety disorders like GAD.
Exploring this connection sheds light on how mental and physical health intersect, specifically how heart disease may impact, or be impacted by, anxiety disorders like GAD.
Evidence Summary
The Role of Emotional Regulation in Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders often go hand in hand with difficulties in managing emotions. These emotional struggles can intensify symptoms, adding to the overall distress felt by those with anxiety.
Problems with emotional regulation are not just side effects but deeply intertwined with the experience of anxiety. Addressing these challenges has the potential to bring relief and improve quality of life for those affected.
Problems with emotional regulation are not just side effects but deeply intertwined with the experience of anxiety. Addressing these challenges has the potential to bring relief and improve quality of life for those affected.
Evidence Summary
How Mindfulness-Based Therapy Eases Anxiety
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) combines meditation with therapeutic techniques to help those with Generalized Anxiety Disorder manage stress and anxiety. By emphasizing mindfulness and being present, MBCT encourages a focused awareness that can reduce anxious thoughts.
Participants learn practical skills, like breathing exercises, to better handle their symptoms, offering tools that help bring calm and control in moments of anxiety.
Participants learn practical skills, like breathing exercises, to better handle their symptoms, offering tools that help bring calm and control in moments of anxiety.



