Trending ADHD Papers
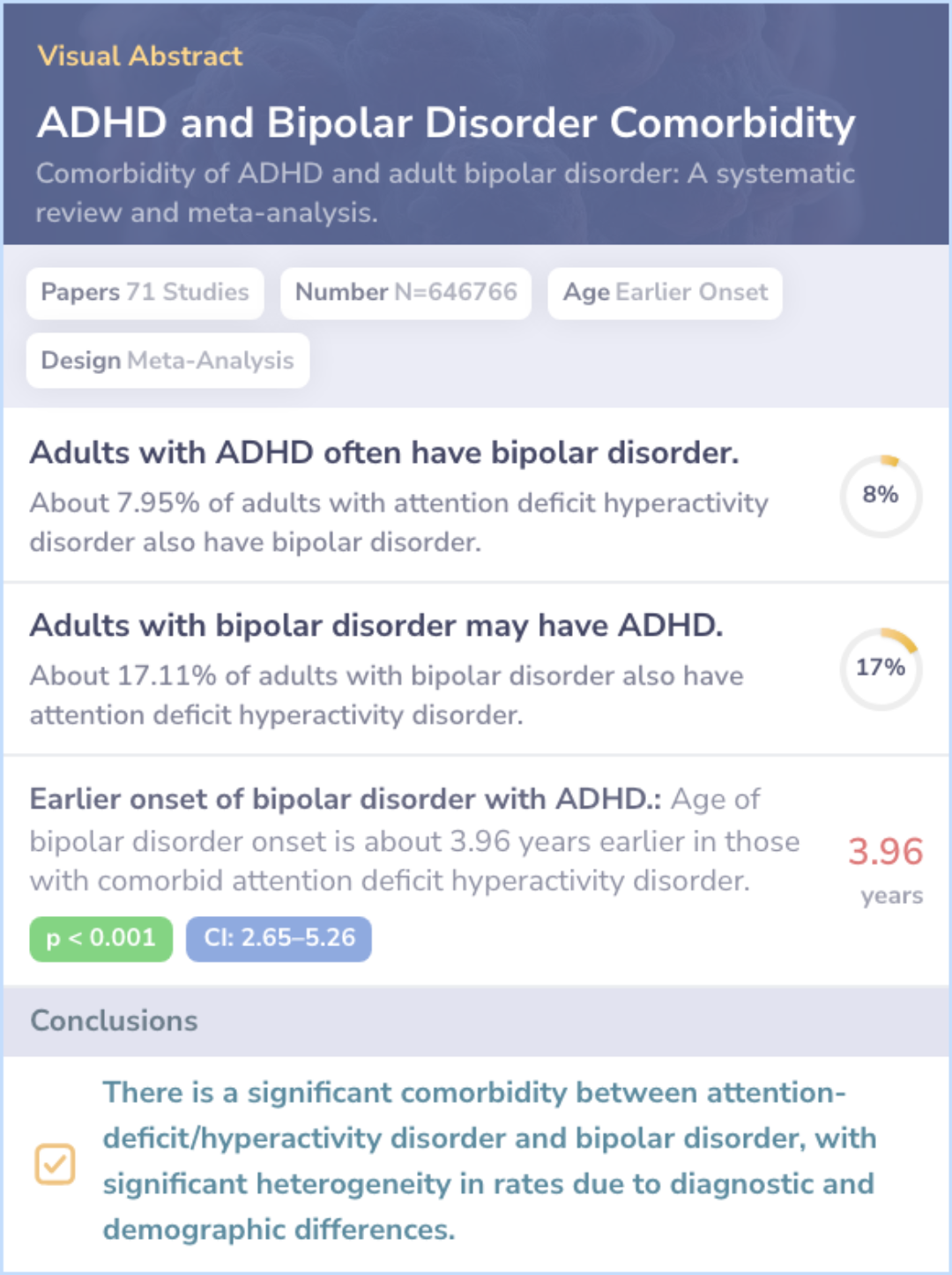
Visual Abstract
Comorbidity of ADHD and adult bipolar disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Comorbidity of ADHD and bipolar disorder
December 9, 2024
author
Schiweck C, Arteaga-Henriquez G, Aichholzer M, Edwin Thanarajah S, Vargas-Cáceres S, Matura S, Grimm O, Haavik J, Kittel-Schneider S, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Faraone SV, Reif A
journal
Neurosci Biobehav Rev
Date Published
undefined
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The researchers aimed to quantify the degree of comorbidity between ADHD and Bipolar Disorder in adults.
💡
What They Found
They found that approximately one in thirteen adults with ADHD also has Bipolar Disorder, and about one in six adults with Bipolar Disorder also has ADHD.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that there's a significant overlap between ADHD and Bipolar Disorder, indicating that both clinicians and patients should be attentive to these comorbidity signs for better diagnosis and treatment, unlike previous abstracts that focused individually on each disorder.
Study Overview
Background & Objectives
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and Bipolar Disorder (BD) often occur together, a phenomenon known as comorbidity. This condition can complicate diagnosis and treatment, as the presence of one disorder may disguise the symptoms of another.
The study aimed to quantify the level of overlap between ADHD and BD by examining a wide array of existing scientific literature. Understanding this relationship can help improve diagnosis and care.
Abstract: background
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and Bipolar Disorder (BD) are common mental disorders with a high degree of comorbidi...more
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers conducted a comprehensive search through scientific literature in October 2020. They analyzed 71 different studies, involving 646,766 participants spread across 18 countries to ensure diverse results.
By combining the data from these studies, they performed a meta-analysis, which involves statistically merging results to look for broader patterns and conclusions.
By combining the data from these studies, they performed a meta-analysis, which involves statistically merging results to look for broader patterns and conclusions.
Abstract: methods
To this end we performed a systematic search of the literature in October 2020. In a meta-analysis of 71 studies with 646,766 participa...more
Study Results
Results
The analysis revealed that nearly 1 in 13 adults with ADHD also have BD, while approximately 1 in 6 adults with BD have ADHD. This shows a significant overlap between the disorders.
The study also found that various factors, such as location and diagnosis methods, influenced these rates. Additionally, people with both ADHD and BD tend to experience the onset of BD earlier by nearly four years compared to those without ADHD.
The study also found that various factors, such as location and diagnosis methods, influenced these rates. Additionally, people with both ADHD and BD tend to experience the onset of BD earlier by nearly four years compared to those without ADHD.

Abstract: results
It was found that about one in thirteen adults with ADHD was also diagnosed with BD (7.95 %; 95 % CI: 5.31-11.06), and nearly one in si...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
The study suggests that differences in cultures and methods must be considered when diagnosing these disorders. High comorbidity rates emphasize the need for caution.
Healthcare providers should be aware of the frequent overlap to avoid misdiagnosis and better manage treatment for individuals dealing with both ADHD and BD, providing them with more tailored and effective care.
Healthcare providers should be aware of the frequent overlap to avoid misdiagnosis and better manage treatment for individuals dealing with both ADHD and BD, providing them with more tailored and effective care.
Abstract: conclusions
Cultural and methodological differences deserve attention for evaluating diagnostic criteria and clinicians should be aware of the high comorbidity rates to prevent misdiagnosis and provide optimal care for both disorders.
Clinical Guidelines
Guidelines suggest that stimulant medications, particularly amphetamines, are recommended as first-line treatment for adults with ADHD. Combining stimulant medication with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is more effective than either treatment alone.
Prior to starting stimulant treatments, healthcare providers review cardiovascular history. Additionally, monitoring for serotonin syndrome is advised when combining serotonergic reuptake inhibitors with stimulants.
Prior to starting stimulant treatments, healthcare providers review cardiovascular history. Additionally, monitoring for serotonin syndrome is advised when combining serotonergic reuptake inhibitors with stimulants.
Literature Review
[Walsh] et al, [undefined]
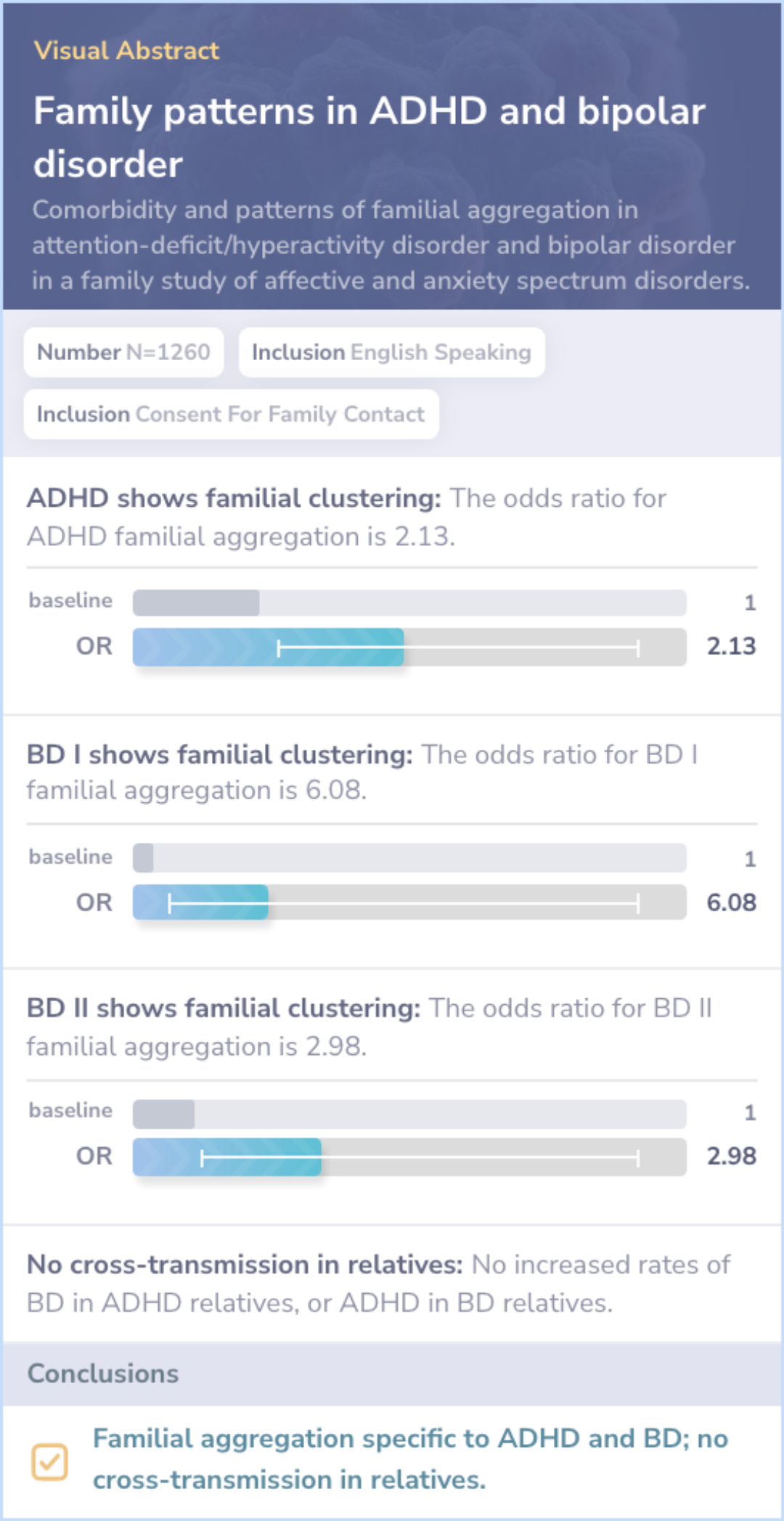
Core Insight:The primary paper highlights a high comorbidity between ADHD and Bipolar Disorder, focusing on contextual factors influencing diagnosis. This paper, however, shows no evidence of shared familial risk, suggesting the high comorbidity could be due to diagnostic artifacts or distinct disorder features.
What It Adds:
Familial Aggregation Specificity: This paper shows specific familial aggregation for ADHD and Bipolar Disorder.
No Cross-Transmission Evidence: The study found no increased cross-transmission in families for ADHD and Bipolar Disorder.
Shared Themes:Both papers suggest complexities in diagnosing ADHD and Bipolar Disorder, noting variances in understanding comorbidity and familial patterns.
Literature Review
[Masi] et al
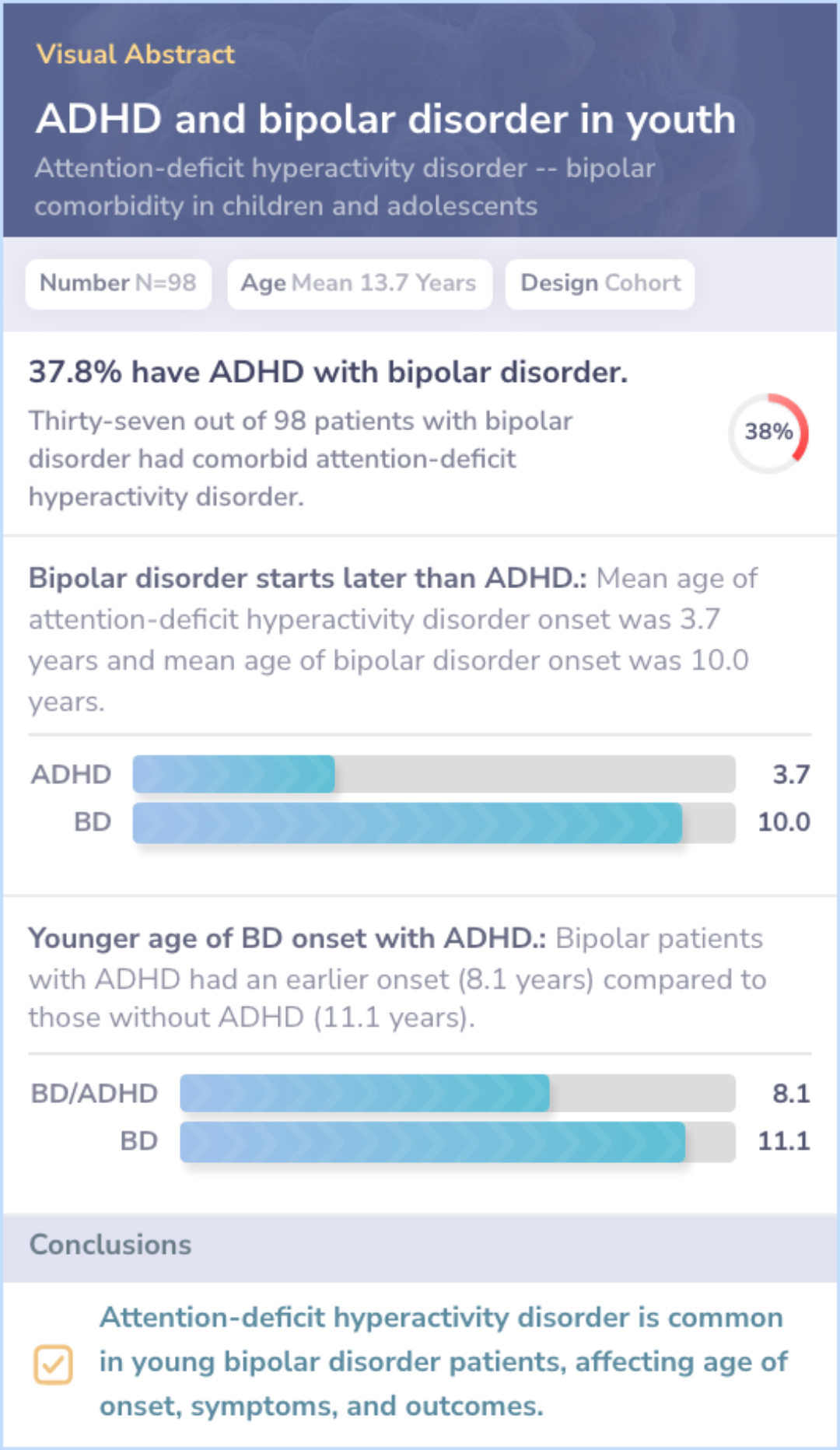
Core Insight:The comparison paper explores comorbidity of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and bipolar disorder in youths, revealing patterns in onset age, mood type, and related disorders.
What It Adds:
Comorbidity Influence: Comorbidity affects mood and associated disorders.
Age of Onset: Comorbid patients experience earlier onset of bipolar disorder.
Literature Review
Nierenberg et al.
Core Insight:Both papers explore ADHD comorbidity in bipolar disorder but differ in focus on children versus adults.
What It Adds:
Focus on Adult ADHD: This paper highlights high ADHD rates in adults with bipolar disorder.
Gender Differences: This paper reports higher ADHD in males than females with bipolar disorder.
Key Differences:This paper finds a 9.5% ADHD rate, lower than the primary paper's 17.11%.
