Strattera Paper Database
Visual Abstract
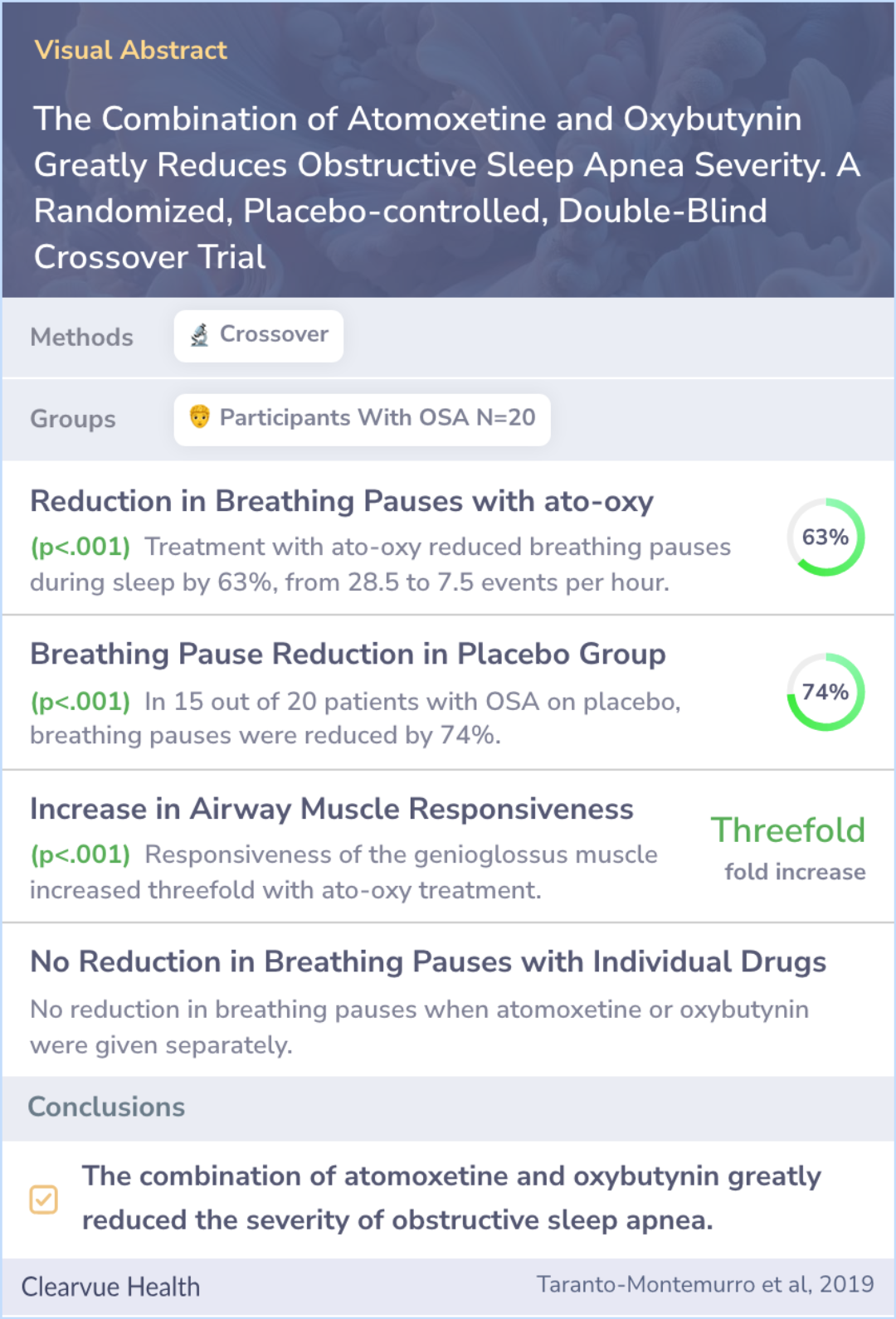
The Combination of Atomoxetine and Oxybutynin Greatly Reduces Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity. A Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Crossover Trial
Combination of Atomoxetine and Oxybutynin Reduces OSA Severity
September 14, 2024
author
Taranto-Montemurro L, Messineo L, Sands SA, Azarbarzin A, Marques M, Edwards BA, Eckert DJ, White DP, Wellman A
journal
Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Date Published
2019-05-15
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study aimed to assess the effect of combining a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (atomoxetine) and an antimuscarinic (oxybutynin) on the severity of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and genioglossus muscle responsiveness.
💡
What They Found
The combination of atomoxetine and oxybutynin significantly reduced the severity of obstructive sleep apnea and increased genioglossus muscle responsiveness.
📚
What This Means
These findings show the combined use of atomoxetine and oxybutynin may offer a new pharmacological treatment approach for obstructive sleep apnea, aligning with the focus on addressing norepinephrine pathways seen in current evidence about atomoxetine's mechanism.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to explore a new way to treat obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) by using a combination of two medications. Researchers hoped that these drugs would increase muscle activity in the airway and improve the quality of sleep for patients.
The findings suggest that combining these two medications might work together to tackle different aspects of OSA, paving the way for new therapeutic approaches to help patients breathe better during sleep.
The findings suggest that combining these two medications might work together to tackle different aspects of OSA, paving the way for new therapeutic approaches to help patients breathe better during sleep.
Abstract: background
We aimed to determine the effects of the combination of a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (atomoxetine) and an antimuscarinic (oxybutynin) on OSA severity (apnea-hypopnea index [AHI]; primary outcome) and genioglossus responsiveness (secondary outc...more

Combination of Drugs
"This study shows that the combination of atomoxetine and oxybutynin administered before bedtime can acutely reduce or abolish OSA in patients with a wide range of severity."
New Therapeutic Possibilities
"These findings open new possibilities for the pharmacologic treatment of OSA."
Synergistic Effects
"One possibility is that the two drugs combined may have synergistic effects on upper airway dilator muscles: aside from preventing genioglossus REM-related atonia, the antimuscarinic scopolamine significantly increased genioglossus respiratory-related activity during NREM sleep in animal models."
Study Summary
Methods
In a trial with 20 participants, researchers tested the effects of a mix of atomoxetine (Strattera) and oxybutynin (Ditropan) against a placebo. This trial was double-blind and participants were randomly assigned.
They were tested over one night using various sleep parameters, including AHI and genioglossus responsiveness, measured through polysomnography. In some cases, Atomoxetine and oxybutynin were tested alone on a subset of patients for comparison.
They were tested over one night using various sleep parameters, including AHI and genioglossus responsiveness, measured through polysomnography. In some cases, Atomoxetine and oxybutynin were tested alone on a subset of patients for comparison.
Abstract: methods
A total of 20 people completed a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover trial comparing 1 night of 80 mg atomoxetine plus 5 mg oxybutynin (ato-oxy) to placebo administered before sleep. The AHI and genioglossus muscle responsiveness ...more

Study Summary
Results
The study involved participants around 53 years old with a higher body mass index. When given both drugs, the severity of their sleep apnea dropped by 63%. Among patients on placebo with significant OSA, 74% experienced reduced symptoms.
The responsive behavior of their tongue muscle also increased significantly. However, neither drug alone produced the same improvements, highlighting the importance of their combined use.
The responsive behavior of their tongue muscle also increased significantly. However, neither drug alone produced the same improvements, highlighting the importance of their combined use.
Abstract: results
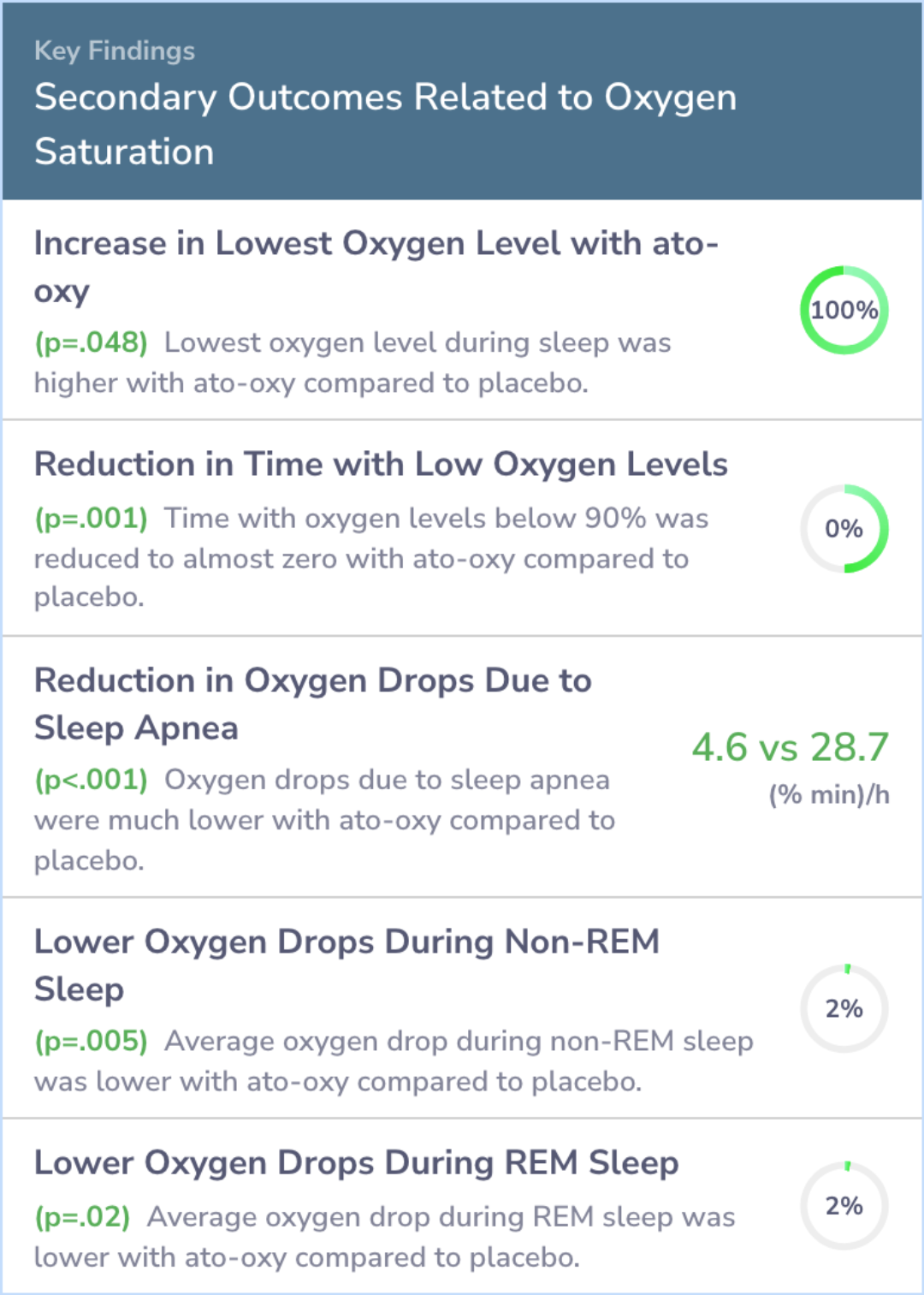
The participants' median (interquartile range) age was 53 (46-58) years and body mass index was 34.8 (30.0-40.2) kg/m2. ato-oxy lowered AHI by 63% (34-86%), from 28.5 (10.9-51.6) events/h to 7.5 (2.4-18.6) events/h (P < 0.001). Of the 15/20 patients ...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
Combining atomoxetine (Strattera) and oxybutynin (Ditropan) before sleep significantly eased OSA symptoms. This study suggests the potential for medications to manage OSA, a disorder mostly dealt with through mechanical aids.
These promising results could pave the way for developing more drug-based treatments, giving patients new management options for OSA. The trial details are registered for public access.
These promising results could pave the way for developing more drug-based treatments, giving patients new management options for OSA. The trial details are registered for public access.
Abstract: conclusions
A combination of noradrenergic and antimuscarinic agents administered orally before bedtime on 1 night greatly reduced OSA severity. These findings open new possibilities for the pharmacologic treatment of OSA. Clinical trial registered with www.clin...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
⚙️
Atomoxetine's Noradrenergic Action
Atomoxetine is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, vital in modulating airway tone.
🧬
Pharmacological Details of Atomoxetine
Well-absorbed with high protein binding, metabolized by CYP2D6, impacting drug efficacy.
⚠️
Adverse Effects and Risks Associated with Atomoxetine
Includes headache, nausea, and serious risks like cardiovascular events; monitoring is essential.
🔄
Off-label Uses of Atomoxetine
Used for conditions beyond ADHD, indicating its broader potential pharmacological applications.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Combination of Atomoxetine and Oxybutynin Reduces OSA Severity
The combination of atomoxetine and oxybutynin significantly reduced obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) severity, reflecting its effect on upper airway patency.
In this context, atomoxetine's role as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor is particularly relevant.
However, its use requires careful consideration due to potential cardiovascular and psychiatric side effects, liver injury, and contraindications with other medications.
In this context, atomoxetine's role as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor is particularly relevant.
However, its use requires careful consideration due to potential cardiovascular and psychiatric side effects, liver injury, and contraindications with other medications.
Evidence Summary
Atomoxetine: Heart and Blood Vessel Risks
Atomoxetine, a common treatment for ADHD, may also affect heart health. This overview highlights the potential cardiovascular risks associated with the drug, shedding light on possible heart and blood vessel issues linked to its use.
Focusing on the relationship between atomoxetine and cardiovascular health, this content provides insights into the heart-related side effects of the medication, with particular attention to its broader impact beyond ADHD treatment.
Focusing on the relationship between atomoxetine and cardiovascular health, this content provides insights into the heart-related side effects of the medication, with particular attention to its broader impact beyond ADHD treatment.
Evidence Summary
Patterns and Effects of Methylphenidate Misuse
The reviewed studies expose patterns and motivations behind the misuse of methylphenidate, a medication for ADHD. These findings highlight recurring reasons why people misuse this drug, revealing concerning trends in improper usage.
The research also uncovers potential negative outcomes from misuse, stressing the need for better management strategies for those prescribed methylphenidate, commonly known as Ritalin or Concerta.
The research also uncovers potential negative outcomes from misuse, stressing the need for better management strategies for those prescribed methylphenidate, commonly known as Ritalin or Concerta.
Evidence Summary
Ritalin and Future Substance Misuse: Investigations Unveiled
Exploring a potential link, four studies review if Ritalin prescriptions lead to a higher risk of substance misuse over time. Researchers aim to uncover whether individuals who use Ritalin are more likely to struggle with substance abuse in the future.
These investigations provide insights into the long-term risks associated with Ritalin. By examining existing prescriptions, the studies delve into the possibility of increased substance misuse later in life.
These investigations provide insights into the long-term risks associated with Ritalin. By examining existing prescriptions, the studies delve into the possibility of increased substance misuse later in life.



