Adderall Study Database
Visual Abstract
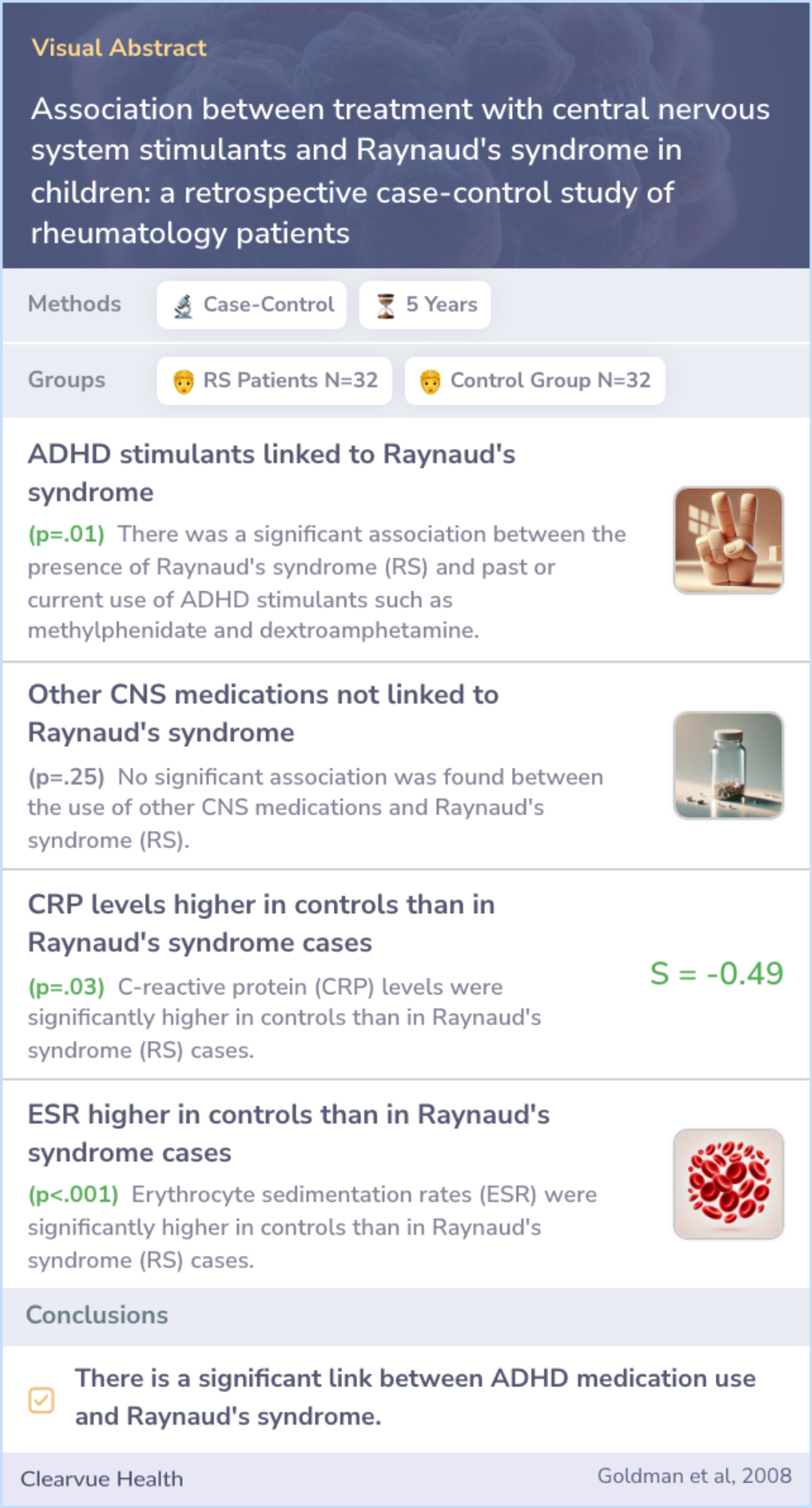
Association between treatment with central nervous system stimulants and Raynaud's syndrome in children: a retrospective case-control study of rheumatology patients
CNS Stimulants and Raynaud's Syndrome in Children
October 8, 2024
author
Goldman W, Seltzer R, Reuman P
journal
Arthritis Rheum.
Date Published
2008 Feb
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The research focused on whether ADHD medications are linked to Raynaud's syndrome.
💡
What They Found
The study found a significant association between ADHD medications and the development of Raynaud's syndrome.
📚
What This Means
The findings suggest a potential risk of Raynaud's syndrome with ADHD medications, aligning with current evidence on their adverse effects.
Study Summary
Study Overview
Researchers compared children with Raynaud's syndrome (RS) to those without it to explore possible links with ADHD treatments. They found that children on CNS stimulants had notably heightened RS symptoms, signifying a potential risk. The study urges physicians to be attentive to these complications when treating young patients with ADHD, especially if they show signs of RS, emphasizing a careful approach in medication choices.
Despite the small size of the study, it opens the door for further inquiry into the long-term impacts of stimulant medications on these children's health.
Despite the small size of the study, it opens the door for further inquiry into the long-term impacts of stimulant medications on these children's health.
Abstract: background
To investigate whether central nervous system (CNS) stimulants used for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are associated with the development of Raynaud's syndrome (RS).

Preliminary Evidence of Adverse Effects
"Although this was a small study, our findings provide preliminary evidence of an adverse effect of CNS stimulant medication in patients seen at a rheumatology clinic."
Signs Worsening from CNS Stimulants
"Physicians should be aware that in children with signs and symptoms of RS (cold hands and feet and livedo reticularis), these signs and symptoms may worsen if CNS stimulants are taken."
Need for Vigilance
"Our findings suggest that there may be a need for increased vigilance in monitoring patients with RS who are prescribed CNS stimulants."
Study Summary
Methods
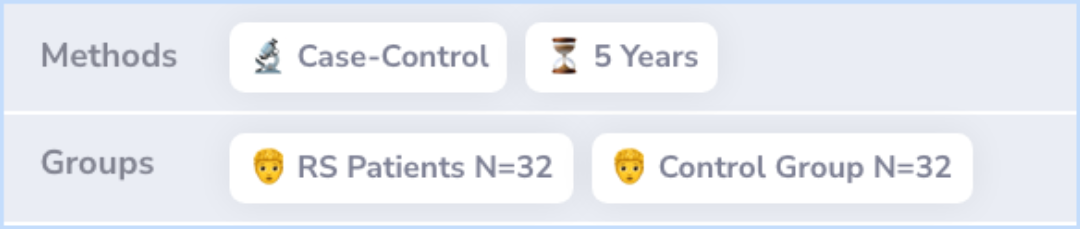
Researchers conducted a case-control study by reviewing pediatric rheumatology records over five years. They studied patients showing signs of Raynaud's syndrome and compared them to age- and gender-matched controls with no such signs.
The goal was to identify any significant relationships between the use of ADHD medications and Raynaud's, and they also compared some lab test differences between both groups.
The goal was to identify any significant relationships between the use of ADHD medications and Raynaud's, and they also compared some lab test differences between both groups.
Abstract: methods
A case-control design was used for this study. All patients seen in a pediatric rheumatology practice during a 5-year period who had signs and symptoms of RS and met diagnostic criteria for RS as determined by pulse volume recording were studied as c...more
Study Summary
Results
The study involved 64 patients, split between those with Raynaud's and those without. A significant connection was found between Raynaud's syndrome and the use of ADHD stimulants like methylphenidate (Ritalin) and dextroamphetamine (Adderall).
Interestingly, other medications didn't show the same link. Additionally, certain lab measurements often used to detect inflammation were lower in Raynaud's patients compared to controls.
Interestingly, other medications didn't show the same link. Additionally, certain lab measurements often used to detect inflammation were lower in Raynaud's patients compared to controls.
Abstract: results
Sixty-four patients were enrolled in the study (32 cases with RS [23 female, 9 male] and 32 control patients). McNemar's test showed a significant association between the presence of RS and past or current use of ADHD stimulants (methylphenidate and ...more

Study Summary
Conclusions
This study suggests a noteworthy association between ADHD stimulant medications and Raynaud's. While the study size was relatively small, it highlights a potential side effect that clinicians should consider when treating patients in rheumatology settings.
These findings emphasize the need for further research to better understand how these medicines influence conditions beyond ADHD.
These findings emphasize the need for further research to better understand how these medicines influence conditions beyond ADHD.
Abstract: conclusions
The results of this study indicate that there is a significant association between development of RS and therapy with CNS stimulants used for the treatment of ADHD. Although this was a small study, these findings provide preliminary evidence of an ad...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
🧠
CNS Stimulant Mechanisms
CNS stimulants like methylphenidate and Adderall boost dopamine and norepinephrine levels, aiding ADHD treatment.
❤️
Adverse Cardiovascular Impact
ADHD medications such as methylphenidate and Adderall may elevate heart rate and cause cardiovascular issues.
📏
Growth Considerations in Children
Long-term use of ADHD stimulants can lead to reduced growth in children, affecting height and weight.
🔄
Potential Neurochemical Changes
Chronic ADHD medication use might alter brain chemistry, with risks of dependency and long-term effects.
👨⚕️
Age and Administration Guidelines
Methylphenidate is FDA-approved for children 6+ for ADHD, with dosage tailored to patient response.
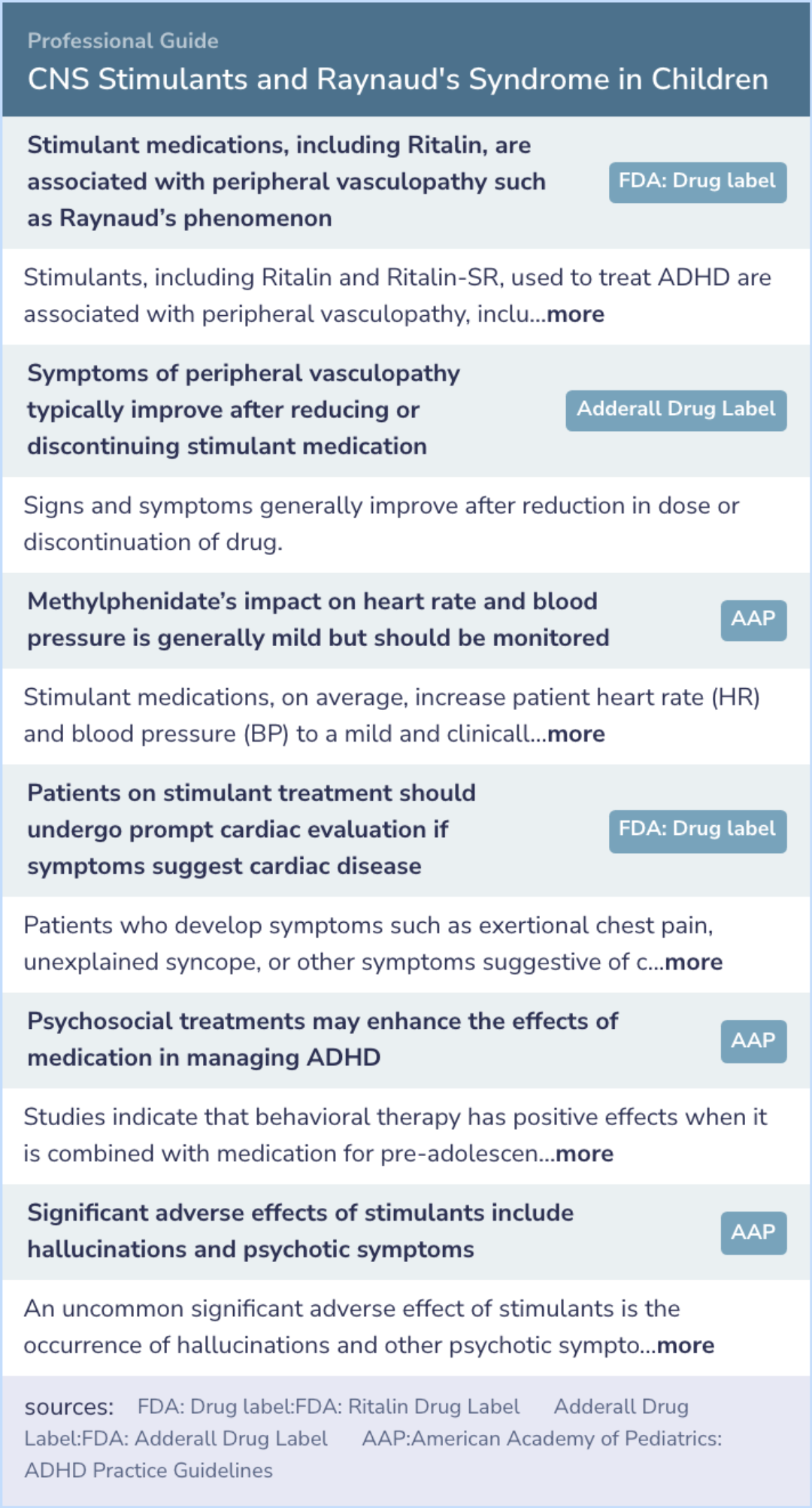
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: CNS Stimulants and Raynaud's Syndrome in Children
In line with the findings linking ADHD stimulants to Raynaud’s syndrome, stimulant medications like Ritalin and Adderall have been associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon.
Notably, symptoms usually improve after reducing or discontinuing stimulant use.
While the impact of stimulants on heart rate and blood pressure is typically mild, clinicians are advised to monitor these vital signs due to potential substantial increases in some individuals.
Notably, symptoms usually improve after reducing or discontinuing stimulant use.
While the impact of stimulants on heart rate and blood pressure is typically mild, clinicians are advised to monitor these vital signs due to potential substantial increases in some individuals.
Evidence Summary
Exploring the Link Between Methylphenidate and Suicide Attempts
This page reviews the potential connection between methylphenidate, a common ADHD treatment, and suicide attempts. It examines research data to explore whether there is a discernible link or pattern.
Methylphenidate is widely prescribed for attention disorders like ADHD, and this analysis focuses on identifying any associated risks related to suicide attempts.
The review is grounded in available data, aiming to highlight potential patterns or relationships in these cases.
Methylphenidate is widely prescribed for attention disorders like ADHD, and this analysis focuses on identifying any associated risks related to suicide attempts.
The review is grounded in available data, aiming to highlight potential patterns or relationships in these cases.
Evidence Summary
MAS-XR and Its Effects on Growth in Children with ADHD
The article delves into the impact of MAS-XR medication on the physical growth of children diagnosed with ADHD. It highlights the long-term effects, specifically focusing on changes in height and weight over time.
These findings are based on data collected from various clinical trials, offering a detailed look at how MAS-XR influences growth patterns in children undergoing treatment for ADHD.
The research emphasizes monitoring these physical changes in patients to understand the broader implications of MAS-XR use.
These findings are based on data collected from various clinical trials, offering a detailed look at how MAS-XR influences growth patterns in children undergoing treatment for ADHD.
The research emphasizes monitoring these physical changes in patients to understand the broader implications of MAS-XR use.
Evidence Summary
Methylphenidate: Enhancing Memory and Focus
Methylphenidate, a popular ADHD medication, does more than just improve focus; it sharpens working memory too. This dual benefit aids learning and productivity in schools and workplaces, making it versatile beyond traditional ADHD treatment.
Research highlights its role in enhancing working memory, thus improving performance in tasks that require sustained attention and concentration. These insights can inform its use strategically in educational and professional settings.
Research highlights its role in enhancing working memory, thus improving performance in tasks that require sustained attention and concentration. These insights can inform its use strategically in educational and professional settings.
Evidence Summary
Long-Term Effects of Methylphenidate on Brain Health
Methylphenidate boosts attention and mental skills but may lead to side effects if used for extended periods. Current research is scrutinizing how this medication affects brain health over time. While often enhancing focus, its long-term usage brings various risks. The ongoing inquiry aims to shed light on its impact on the brain’s overall function and health.