Adderall
Evidence Based Answers
Can Adderall Negatively Impact Cognition?
Long-term Adderall use may lead to cognitive risks like dopamine disruption, potential brain damage in animal studies, and behavioral side effects like anxiety or dizziness.
Published: October 24, 2024
Click to explore a section:
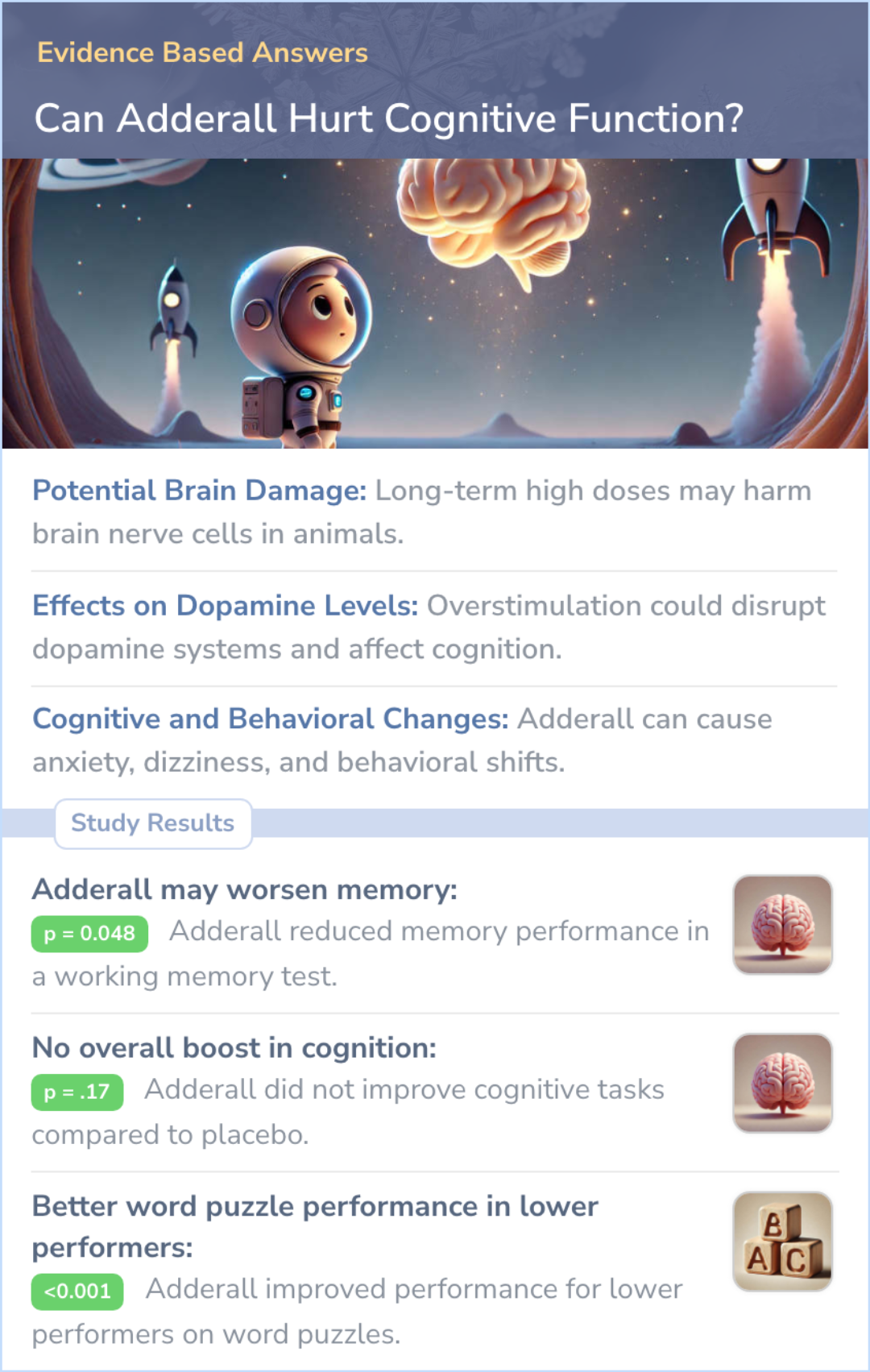
Long-term Adderall use may harm dopamine balance, cause behavioral issues, and carry brain damage risks.
Studies Summary
🔍
Adderall's Mixed Effects on Creativity and Cognition
A study examining Adderall's influence on creativity found that it could enhance creative performance for those with lower baseline abilities, but it might impair those naturally more creative.
📚
Adderall's Minimal Cognitive Impact in College Students
Research on healthy college students without ADHD suggests Adderall has minimal cognitive effects but does influence emotional states and autonomic responses, indicating it may not significantly enhance cognition.
🧠
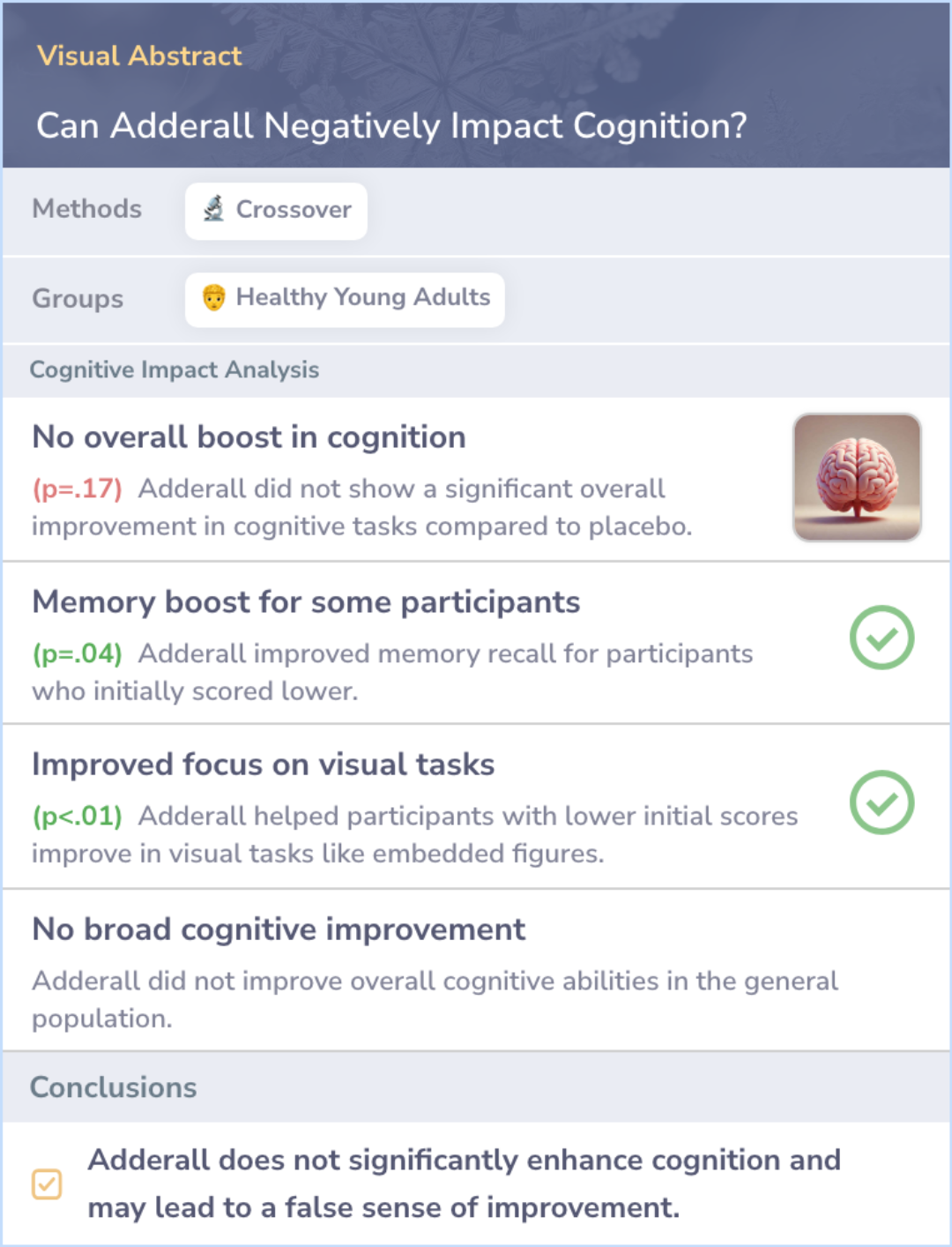
No Significant Cognitive Enhancement with Adderall
A placebo-controlled trial showed Adderall did not significantly enhance cognition in healthy young adults, though some low-ability individuals perceived minor benefits, leading to false perceptions of improvement.
Highly Cited Studies
Long term Effects of Methylphenidate in Adults
Peer Reviewed Study 1
Adderall's Mixed Effects on Creativity and Cognition
Peer Reviewed Study 2
Adderall's Minimal Cognitive Impact in Healthy College Students
Peer Reviewed Study 3
Adderall's Effect on Cognition: Limited Enhancement and Illusory Perceptions
Background: Potential Long-Term Neurotoxicity
Prolonged use of Adderall, especially in high doses, has raised concerns about potential damage to the central nervous system. Most studies on neurotoxicity come from animal models using high doses, and it’s unclear if these findings apply to humans using low doses long-term.
These neurotoxic effects may stem from oxidative stress and the accumulation of harmful substances in the brain, potentially damaging dopamine nerve terminals.
These neurotoxic effects may stem from oxidative stress and the accumulation of harmful substances in the brain, potentially damaging dopamine nerve terminals.
“
Source Quotes:
Concerns have been voiced that, in addition to neurobiological adaptations, prolonged exposure to amphetamine could damage components of the central nervous system.,Although the relevance of these data to the consequences of low dose, prescription use of amphetamines in humans is not entirely clear, the potential for similar damage following prolonged low dose exposure merits some consideration.
Background: Impact on Dopamine and Executive Function
Adderall increases dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain, which are important for attention and executive function. While this can improve focus in those with ADHD, there is concern that long-term use could alter these systems, potentially affecting cognitive abilities.
Overstimulation of brain regions that rely on dopamine might lead to negative cognitive effects if the balance is disrupted.
Overstimulation of brain regions that rely on dopamine might lead to negative cognitive effects if the balance is disrupted.
“
Source Quotes:
The primary pharmacologic effect of both amphetamine and methylphenidate is to increase central dopamine and norepinephrine activity, which impacts executive and attentional function.,Increased catecholamine availability in striatal and cortical regions, as evidenced in preclinical and human studies, affects corticostriatal systems that subserve behaviors related to cognition and executive function.
Background: Behavioral and Cognitive Side Effects
Adderall may cause various behavioral and cognitive side effects. Some individuals might experience changes in behavior, such as increased aggression or anxiety, and cognitive issues like dizziness or impaired coordination. These symptoms could interfere with daily activities, particularly with long-term use.
Monitoring these symptoms and reporting any concerning changes to healthcare providers is advised.
Monitoring these symptoms and reporting any concerning changes to healthcare providers is advised.
“
Source Quotes:
Some side effects can be serious. If you experience any of the following symptoms or those listed in the IMPORTANT WARNING section, call your doctor immediately or get emergency medical treatment: slow or difficult speech, dizziness, weakness or numbness of an arm or leg, seizures, motor or verbal tics, teeth grinding, depression, believing things that are not true, feeling unusually suspicious of others, hallucinating (seeing things or hearing voices that do not exist).
Background: Considerations for Long-Term Use
While Adderall effectively manages ADHD symptoms, there are concerns about its long-term impact on cognition. Some studies suggest that prolonged exposure could impair certain cognitive functions, though the evidence remains inconclusive.
Patients and healthcare providers should weigh the benefits of symptom control against the potential risks to cognition, especially with long-term use.
Patients and healthcare providers should weigh the benefits of symptom control against the potential risks to cognition, especially with long-term use.
“
Source Quotes:
Chronic exposure to amphetamine, particularly methamphetamine, at recreational doses has shown to destroy dopaminergic terminals in the striatum through a variety of mechanisms, including oxidative stress and excitotoxicity.
Peer Reviewed Study
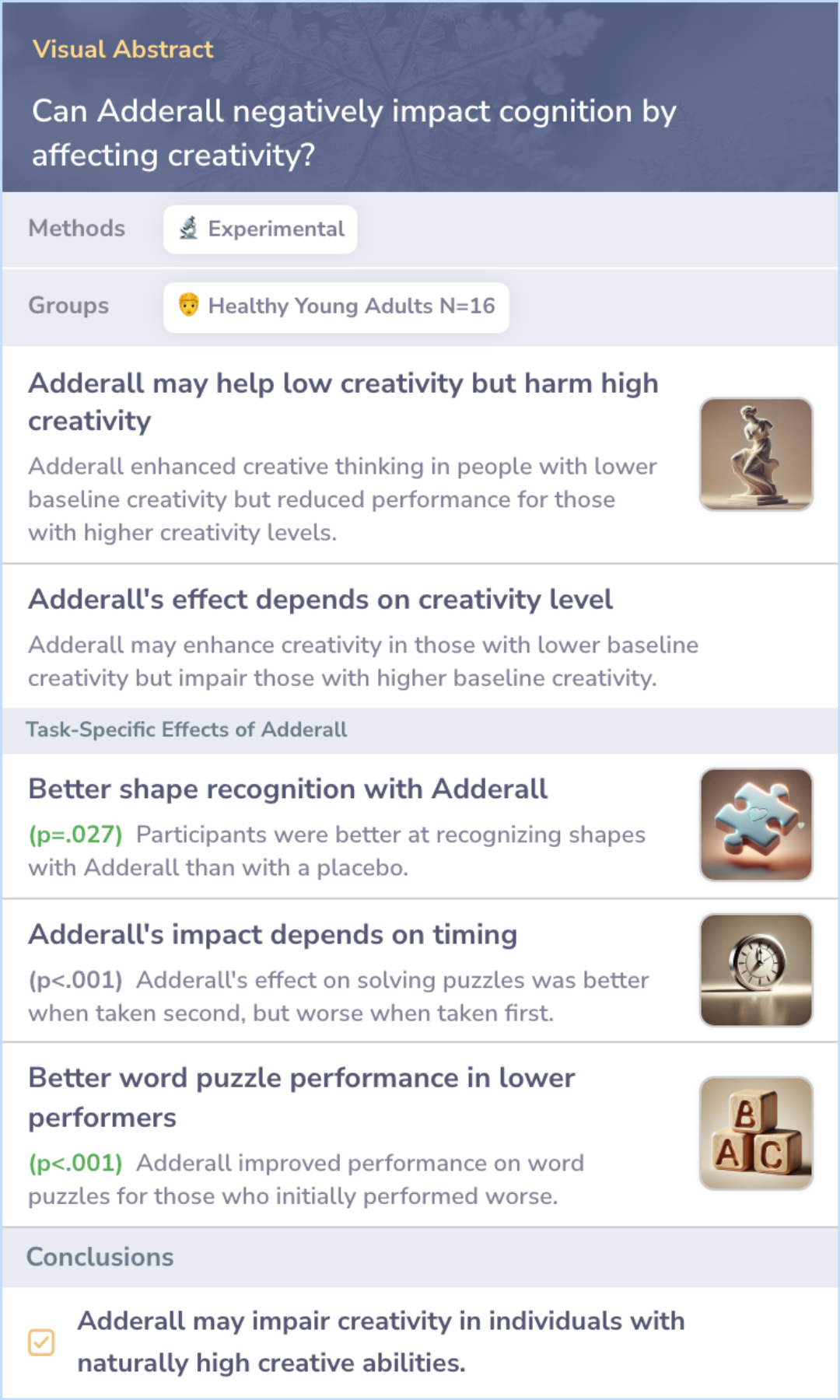
Study: Adderall's Mixed Effects on Creativity and Cognition
This study looked at how Adderall, a drug used to improve attention, might influence creativity in healthy young adults. In a controlled test, 16 participants took Adderall or a placebo and were evaluated on tasks requiring different types of creative thinking. Adderall enhanced performance for some, but also impaired it for others, particularly on tasks that involved focusing on a single correct solution.
The findings suggest that while Adderall might improve creative performance for those with lower baseline abilities, it could potentially harm those who are naturally more creative.
The findings suggest that while Adderall might improve creative performance for those with lower baseline abilities, it could potentially harm those who are naturally more creative.
author
Farah MJ, Haimm C, Sankoorikal G, Smith ME, Chatterjee A
journal
Psychopharmacology
Date Published
2009-01
Peer Reviewed Study
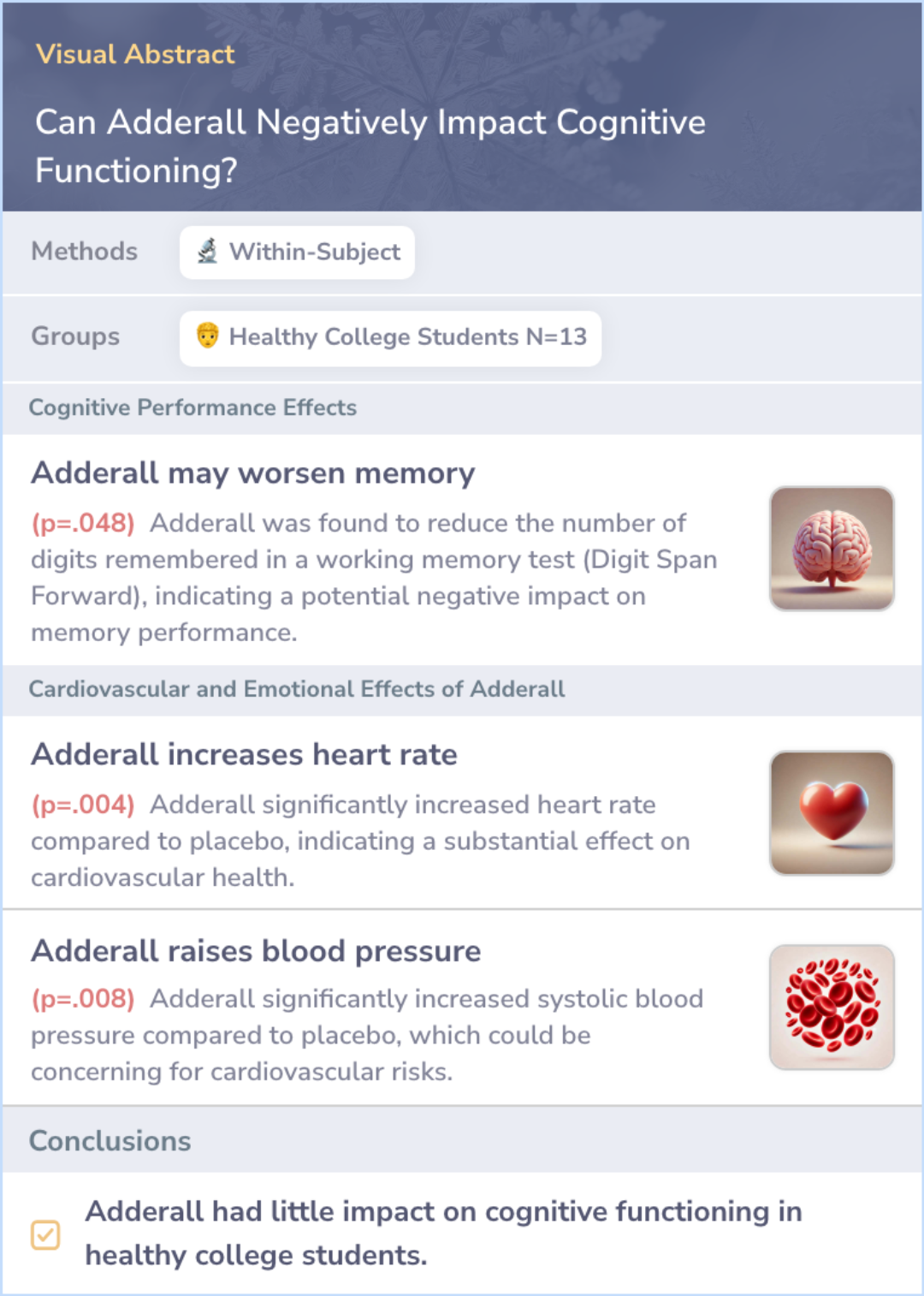
Study: Adderall's Minimal Cognitive Impact in Healthy College Students
Research indicates that Adderall, commonly misused by college students to enhance cognition, has minimal and mixed effects on cognitive abilities.
In a study of healthy college students without ADHD, Adderall showed small cognitive effects but had large impacts on autonomic responses and emotional states.
These findings suggest that, contrary to popular belief, Adderall may not significantly enhance cognitive performance in individuals without ADHD.
In a study of healthy college students without ADHD, Adderall showed small cognitive effects but had large impacts on autonomic responses and emotional states.
These findings suggest that, contrary to popular belief, Adderall may not significantly enhance cognitive performance in individuals without ADHD.
author
Weyandt LL, White TL, Gudmundsdottir BG, Nitenson AZ, Rathkey ES, De Leon KA, Bjorn SA
journal
Pharmacy
Date Published
2018-06-27
Peer Reviewed Study
Study: Adderall's Effect on Cognition: Limited Enhancement and Illusory Perceptions
This study examined whether Adderall, a common psychostimulant, enhances cognitive abilities in healthy young adults. Participants underwent a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial across 13 measures, including memory, creativity, and intelligence.
Results showed no significant cognitive enhancement for most participants, though some low-ability individuals saw minor benefits. Despite this, many participants believed their cognition was enhanced by Adderall.
This suggests that Adderall may not significantly improve cognition in healthy individuals but can create a false perception of cognitive improvement.
Results showed no significant cognitive enhancement for most participants, though some low-ability individuals saw minor benefits. Despite this, many participants believed their cognition was enhanced by Adderall.
This suggests that Adderall may not significantly improve cognition in healthy individuals but can create a false perception of cognitive improvement.
author
Ilieva I, Boland J, Farah MJ
journal
Neuropharmacology
Date Published
2013 Jan
Key Takeaways
Conclusions
Research shows that Adderall's effects on cognition are complex and varied. While some studies report minor improvements in certain cognitive tasks for those with lower baseline abilities, these benefits appear limited and often come with significant risks. In fact, many healthy individuals may experience little to no cognitive enhancement, and the drug's impact might even be detrimental, particularly for those who naturally excel in creativity.
Long-term use poses additional concerns, especially regarding potential neurotoxicity and the overstimulation of dopamine systems, which could negatively affect executive functions. While Adderall can be effective for managing ADHD symptoms, its cognitive benefits for healthy users remain uncertain, and prolonged use may carry significant risks.
Long-term use poses additional concerns, especially regarding potential neurotoxicity and the overstimulation of dopamine systems, which could negatively affect executive functions. While Adderall can be effective for managing ADHD symptoms, its cognitive benefits for healthy users remain uncertain, and prolonged use may carry significant risks.

Evidence Summary
Exploring Long-Term Brain Health Concerns with Adderall
Adderall is widely used for ADHD treatment, but there's growing concern about its long-term effects on the brain. The text highlights the ongoing debate around whether extended use might pose risks to brain health.
While the benefits of Adderall in managing ADHD symptoms are clear, understanding its potential long-term impact remains a critical area of study. Research continues to explore these risks, focusing on how long-term use could affect brain health over time.
While the benefits of Adderall in managing ADHD symptoms are clear, understanding its potential long-term impact remains a critical area of study. Research continues to explore these risks, focusing on how long-term use could affect brain health over time.
Evidence Summary
Adderall and Creativity: Exploring Potential Effects
Adderall is commonly prescribed for attention disorders, but its effect on creativity is a topic of growing interest. A preliminary study explores whether this medication influences how people think creatively. The article delves into the potential impact on innovation, raising questions about whether Adderall might change the way individuals approach creative tasks.
The findings highlight the need to consider how Adderall could affect creativity alongside its intended benefits for attention disorders.
The findings highlight the need to consider how Adderall could affect creativity alongside its intended benefits for attention disorders.
Evidence Summary
Methylphenidate's Influence on Brain Glucose Use
Methylphenidate influences the brain by altering how it uses glucose, which plays a role in attention and behavior. Researchers explore these changes to see how the drug affects cognitive functions.
The study highlights how methylphenidate impacts brain activity during tasks by modifying glucose consumption, offering insights into its effects on attention and behavior.
The study highlights how methylphenidate impacts brain activity during tasks by modifying glucose consumption, offering insights into its effects on attention and behavior.