Nutrition: Vegetables
Nutrition Comparisons
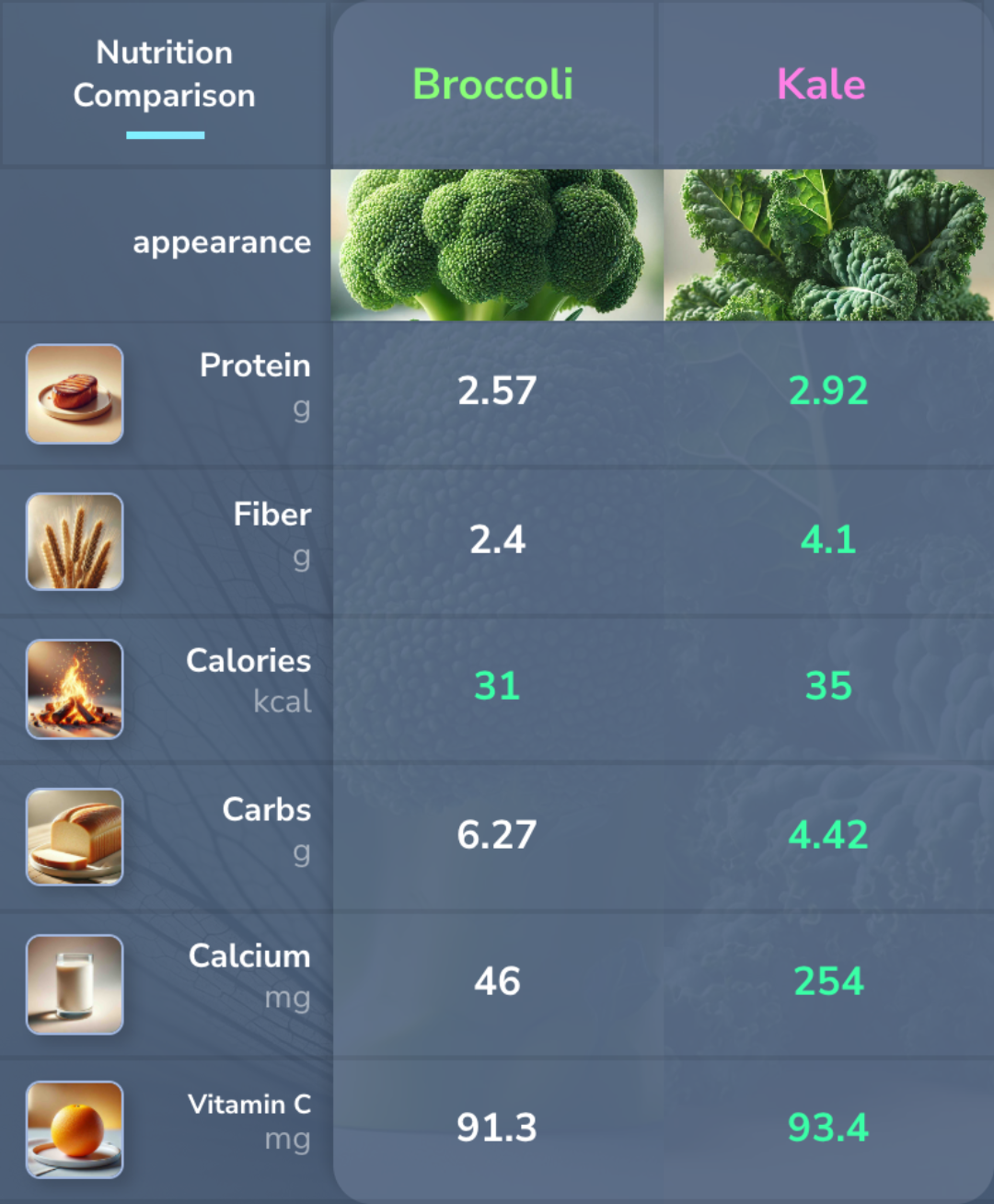
Broccoli vs. Kale
Kale has higher protein, fiber, calcium, potassium, magnesium, and vitamin C, making it a nutrient-rich choice. Broccoli offers slightly more zinc and less sodium, making it a better option for those monitoring sodium intake. Both are low in calories and carbohydrates, making them excellent additions to a healthy diet.
Background:Broccoli

top benefits 👍
🛡️
Cancer Risk Reduction:Broccoli may lower cancer risk.
❤️
Heart Health Support:Broccoli promotes heart health.
🧠
Brain Function Boost:Broccoli enhances brain function.
drawbacks 👎
💨
Gas and Bloating:Broccoli can cause gas.
Background:Kale
top benefits 👍
🦴
Bone Health Boost:Kale is rich in vitamin K, supporting bone strength.
👁️
Eye Protection:Contains lutein and zeaxanthin, promoting eye health.
💪
Antioxidant Power:High in antioxidants, aiding in disease prevention.
drawbacks 👎
🩸
Blood Thinner Interaction:High vitamin K may interfere with anticoagulant medications.
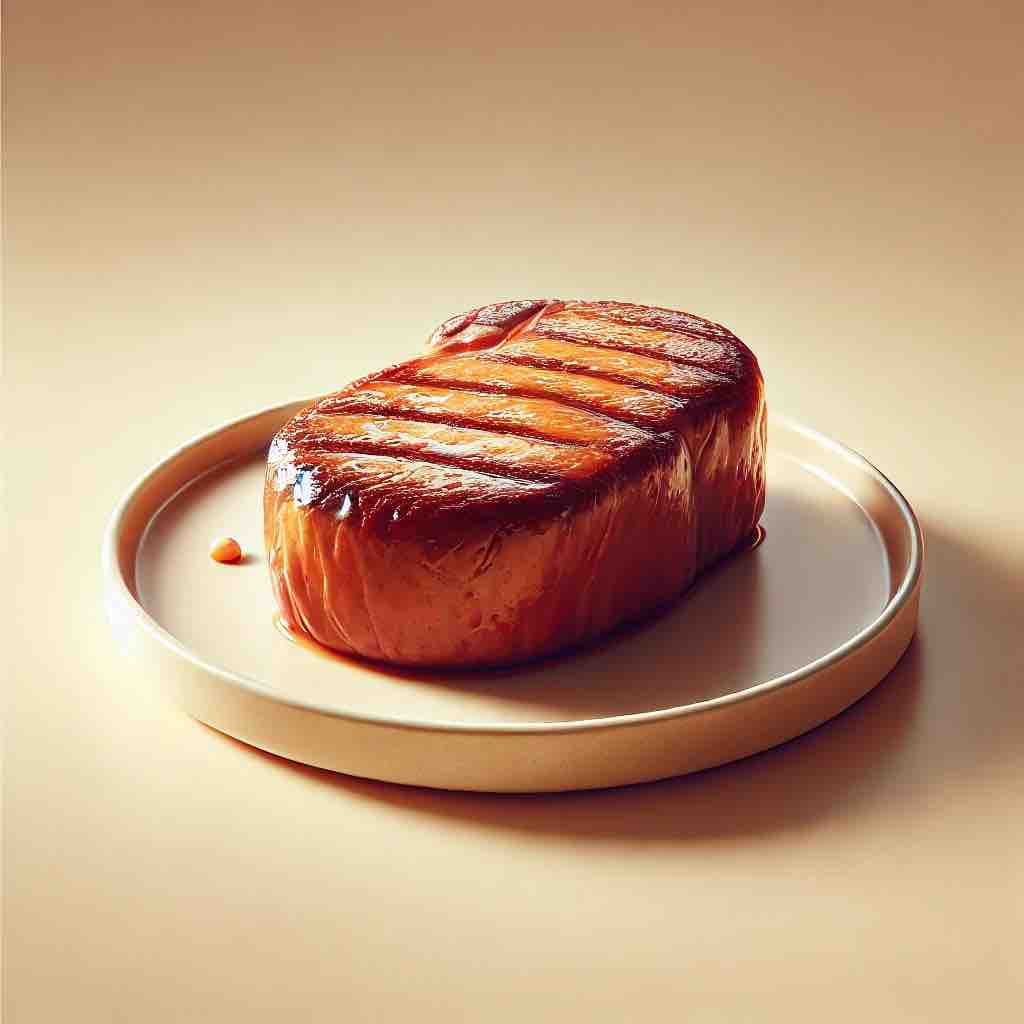

Protein
Kale provides slightly more protein (2.92 g) than broccoli (2.57 g) per 100 grams, which may contribute to muscle repair and general health.

Dietary Fiber
Kale has significantly more dietary fiber (4.1 g) compared to broccoli (2.4 g), which supports digestive health and satiety.

Calories
Both broccoli (31 kcal) and kale (35 kcal) are low-calorie vegetables, making them excellent choices for weight management.

Carbohydrates
Kale contains fewer carbohydrates (4.42 g) than broccoli (6.27 g), which may be preferable for low-carb diets.

Calcium
Kale provides a much higher amount of calcium (254 mg) compared to broccoli (46 mg), which supports bone health.