Adderall Study Database
Visual Abstract
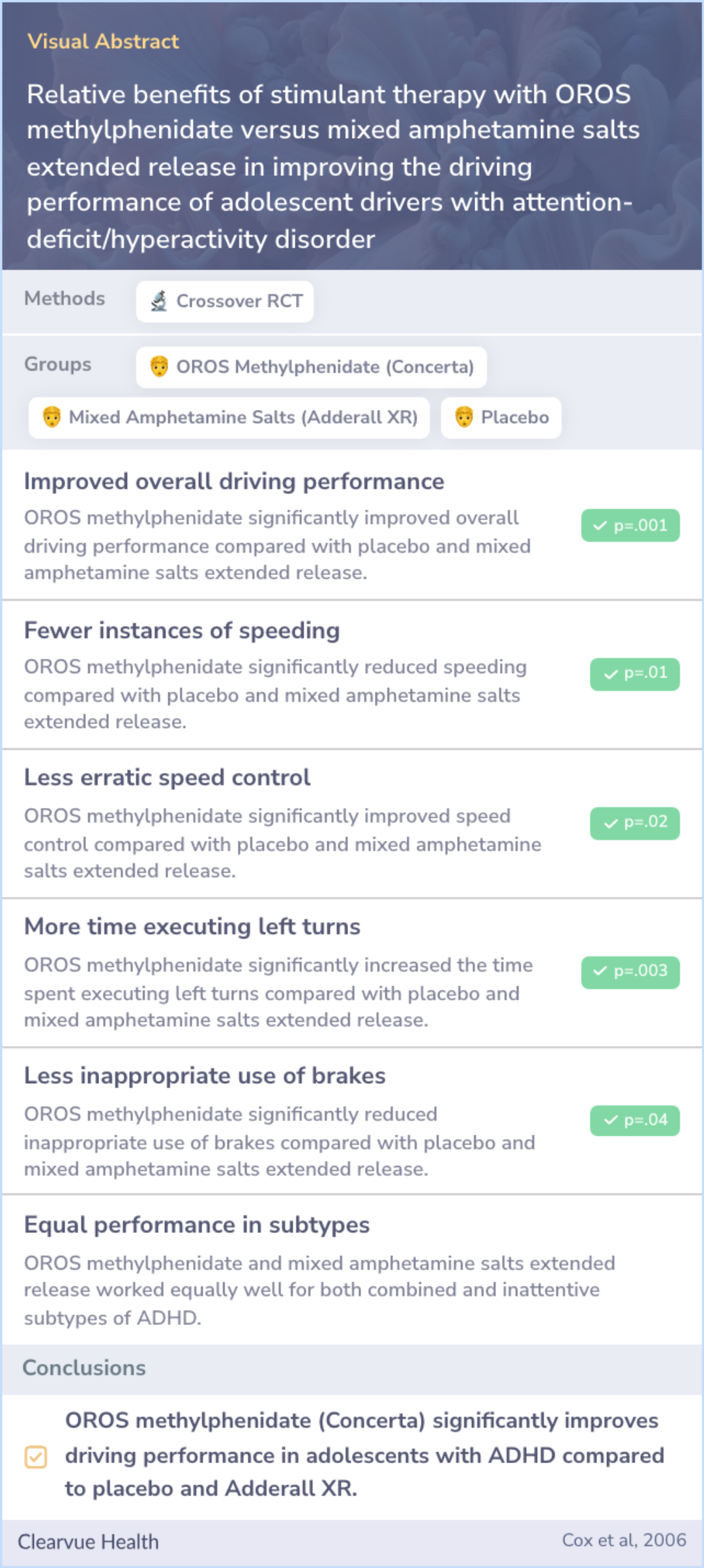
Relative benefits of stimulant therapy with OROS methylphenidate versus mixed amphetamine salts extended release in improving the driving performance of adolescent drivers with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
Concerta (OROS Methylphenidate) Outperforms Adderall in Improving Teen Driving in ADHD
September 9, 2024
author
Cox DJ, Merkel RL, Moore M, Thorndike F, Muller C, Kovatchev B
journal
Pediatrics
Date Published
2006 Sep
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study examined how OROS methylphenidate (Concerta) and mixed amphetamine salts extended release (Adderall XR) affect driving performance in adolescents with ADHD compared to a placebo.
💡
What They Found
The study found that OROS methylphenidate (Concerta) significantly improved driving performance in adolescents with ADHD compared to placebo and mixed amphetamine salts extended release (Adderall XR), which showed no statistical improvement over placebo.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that OROS methylphenidate (Concerta) may be more effective than mixed amphetamine salts extended release (Adderall XR) in enhancing driving performance in adolescents with ADHD, aligning with current evidence on the benefits of stimulant medications for managing ADHD symptoms.
Study Summary
Study Overview
Stimulants can enhance driving skills in teenagers with ADHD. OROS methylphenidate improves steering and speed control while reducing impulsive driving behavior. Adolescents taking this medication showed better performance than those on placebo or mixed amphetamine salts. Those with ADHD have higher risks of car accidents, and stimulant therapy may help them drive more safely. It's important to treat ADHD symptoms beyond school hours, especially as accidents often occur during evenings and weekends. Both male and female adolescents benefited from OROS MPH, suggesting it should be considered for treating adolescent drivers' symptoms.
These results support current guidelines on using stimulants for treating ADHD-related issues.
These results support current guidelines on using stimulants for treating ADHD-related issues.
Abstract: background
Automobile accidents are the leading cause of death among adolescents, and collisions are 2 to 4 times more likely to occur among adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Studies have demonstrated that stimulants improve driving per...more

Stimulants and Driving Performance
"This study validates the use of stimulants to improve driving performance in adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder."
Implications of Improved Driving Performance
"This study adds to the literature demonstrating that stimulant therapy improves driving performance in adolescents with ADHD, and the results suggest that OROS MPH should be the initial treatment of choice for adolescent drivers."
Driving Safety for Adolescents
"Given the elevated risk for driving mishaps among adolescents with ADHD and given that fatal collisions are more likely to occur in the evenings, on weekends, and during the summer months, the current findings suggest that the use of stimulant medication to manage the symptoms of ADHD should not be limited to school hours/days."
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers looked at teenage drivers with ADHD using a driving simulator. They gave participants either 72 mg of OROS methylphenidate (Concerta), 30 mg of mixed amphetamine salts extended release (Adderall XR), or a placebo. The study was randomized, meaning participants didn't know which pill they were taking each time.
They tested driving at different times: 5:00 pm, 8:00 pm, and 11:00 pm. Both the teenagers and the researchers rated the driving performance after each session.
They tested driving at different times: 5:00 pm, 8:00 pm, and 11:00 pm. Both the teenagers and the researchers rated the driving performance after each session.
Abstract: methods
Adolescent drivers with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder were compared on a driving simulator after taking 72 mg of OROS methylphenidate, 30 mg of mixed amphetamine salts extended release, or placebo in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-con...more

Study Summary
Results
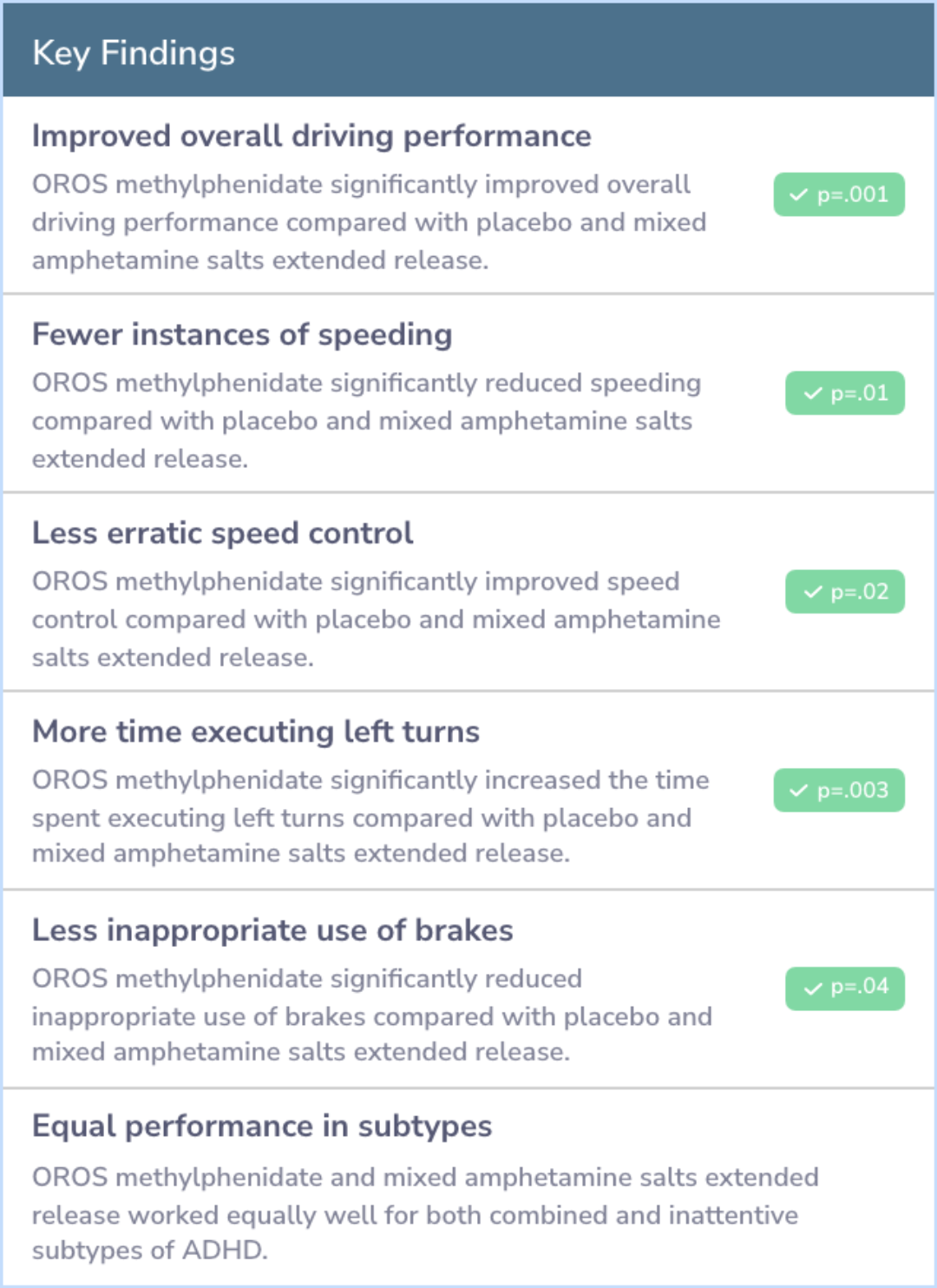
The study involved 35 teenagers with ADHD, including 19 boys and 16 girls, with an average age of 17.8 years. Results showed that those who took OROS methylphenidate (Concerta) generally drove better, with fewer accidents than those who took a placebo or Adderall XR.
Specific improvements with Concerta included spending less time off the road, speeding less, better speed control, longer time on left turns, and fewer braking errors. Both medications worked similarly well for boys and girls, and for teens with different types of ADHD, whether combined or inattentive.
Specific improvements with Concerta included spending less time off the road, speeding less, better speed control, longer time on left turns, and fewer braking errors. Both medications worked similarly well for boys and girls, and for teens with different types of ADHD, whether combined or inattentive.
Abstract: results
The study included 35 adolescent drivers with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (19 boys/16 girls). The mean age was 17.8 years. The overall Impaired Driving Score demonstrated that OROS methylphenidate led to better driving performance compar...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
The study confirms that stimulants can help improve driving abilities in teens with ADHD. Notably, OROS methylphenidate (Concerta) showed a marked improvement over both a placebo and mixed amphetamine salts extended release (Adderall XR) in enhancing driving skills.
This suggests Concerta may be the preferred choice for better road safety in adolescents dealing with ADHD.
This suggests Concerta may be the preferred choice for better road safety in adolescents dealing with ADHD.
Abstract: conclusions
This study validates the use of stimulants to improve driving performance in adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. In the study, OROS methylphenidate promoted significantly improved driving performance compared with placebo and m...more

Background Information
Patient Guide
🧠
Methylphenidate Action
Methylphenidate boosts norepinephrine and dopamine, enhancing neurotransmitter levels in the brain.
📦
Adderall Formulations
Adderall comes in both immediate and extended-release forms, supporting versatile ADHD treatments.
👨⚕️
Use in Adolescents
Both OROS methylphenidate and Adderall are FDA-approved for ADHD treatment in adolescents.
🔍
Monitoring Requirements
Both stimulants require rigorous monitoring for side effects, abuse, and drug interactions.
🚗
Driving Performance
Stimulants, like methylphenidate, improve driving performance in adolescents with ADHD.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Benefits of Stimulant Therapy in Adolescents with ADHD
The findings underscore the necessity for medication coverage to manage symptoms of ADHD while driving, as reflected in professional guidelines.
Stimulant medications, including the evaluated methylphenidate formulation, exhibit a significant effect size in treating ADHD, emphasizing their therapeutic potency.
Despite being highly recommended in adolescents, it is crucial to acknowledge the variability in patients' responses to these medications and the ongoing interest in pharmacogenetic approaches to enhance personalized treatment plans.
Moreover, methylphenidate's efficacy is supported not only in improving driving performance but also in overall ADHD symptom management.
Balancing medication benefits with potential cardiovascular risks remains a key consideration in ADHD treatment.
Stimulant medications, including the evaluated methylphenidate formulation, exhibit a significant effect size in treating ADHD, emphasizing their therapeutic potency.
Despite being highly recommended in adolescents, it is crucial to acknowledge the variability in patients' responses to these medications and the ongoing interest in pharmacogenetic approaches to enhance personalized treatment plans.
Moreover, methylphenidate's efficacy is supported not only in improving driving performance but also in overall ADHD symptom management.
Balancing medication benefits with potential cardiovascular risks remains a key consideration in ADHD treatment.
Evidence Summary
Cognitive and Self-Esteem Differences in ADHD Subtypes
Children with ADHD were studied based on their subtype: hyperactive, inattentive, or combined, using tests like the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children. The research identified differences in cognitive abilities, with working memory being a common challenge. Inattentive subtype showed the weakest cognitive skills, while hyperactive had the best.
Cognitive abilities linked positively with self-esteem. Hyperactive subtype children, having stronger cognitive skills, reported higher self-esteem. Cognitive interventions may be useful based on these insights.
Cognitive abilities linked positively with self-esteem. Hyperactive subtype children, having stronger cognitive skills, reported higher self-esteem. Cognitive interventions may be useful based on these insights.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Stimulants on Adolescent Driving Skills
The comparison showcases the effectiveness of different stimulant medications on adolescents with ADHD. Evaluated through a driving simulator, participants showed varying levels of improvement in driving skills. One medication notably led to fewer errors and safer driving practices than others, spotlighting its potential impact. This discussion aligns with broader findings on enhancing everyday tasks in adolescents.
Understanding medication effects aids in sharpening daily performance, especially in complex activities like driving. Highlighting these differences fosters an informed approach when considering treatment options, reflecting detailed research assessments.
Understanding medication effects aids in sharpening daily performance, especially in complex activities like driving. Highlighting these differences fosters an informed approach when considering treatment options, reflecting detailed research assessments.
Evidence Summary
Impulsivity Differences in ADHD Adolescents
Impulsive behavior in adolescents is tied to ADHD, involving two main types: quick responses without thought and difficulties in delaying rewards. An analysis of 28 tasks from 26 studies reveals that children and adolescents with ADHD are moderately more impulsive in decision-making than their peers. The study found similar impulsiveness patterns in ADHD kids when facing tasks like postponing gratification or discounting delays.
Furthermore, outcomes varied based on diagnostic methods and gender inclusion, revealing larger differences in studies with single informants and male-only groups.
Furthermore, outcomes varied based on diagnostic methods and gender inclusion, revealing larger differences in studies with single informants and male-only groups.
Evidence Summary
ADHD Subtypes: Unique Responses to Treatment
Different ADHD subtypes show varied responses to methylphenidate, highlighting a link between the type of ADHD and the effectiveness of this medication. The study further explores how executive functions seem to play a role in these variations. Children with distinct ADHD characteristics respond differently to treatment, shedding light on the complex relationship between these characteristics and treatment outcomes.