Trending ADHD Papers
Visual Abstract
ADHD at the workplace: ADHD symptoms, diagnostic status, and work-related functioning
ADHD and Work Functioning
December 5, 2024
author
Fuermaier ABM, Tucha L, Butzbach M, Weisbrod M, Aschenbrenner S, Tucha O
journal
J Neural Transm
Date Published
2021 Jul
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original

Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
Researchers examined how ADHD symptoms influence work problems and compared these to neuropsychological test results.
💡
What They Found
The study found that ADHD symptoms, particularly inattention, strongly relate to work issues, while neuropsychological test performance doesn't significantly predict work functioning.
📚
What This Means
These findings suggest that managing ADHD symptoms is crucial for improving work performance, highlighting the significance of attention rather than test outcomes, adding depth to our understanding which previous medication-focused studies didn’t explore.
Study Overview
Background & Objectives
ADHD symptoms can affect one's work life significantly. The study explores how ADHD symptoms, particularly inattention, are linked to work-related issues.
Using a sample from the community and a clinical group, researchers investigate the connection between ADHD traits, workplace challenges, and neuropsychological function, aiming to bring understanding to these impactful effects.
Using a sample from the community and a clinical group, researchers investigate the connection between ADHD traits, workplace challenges, and neuropsychological function, aiming to bring understanding to these impactful effects.

Abstract: background
The present study seeks to examine the nature of work-related problems and impairments of adults with ADHD, and explores the associatio...more
Study Summary
Methods
Researchers gathered data from over 1,200 individuals who did not have a diagnosis but showed ADHD symptoms, using questionnaires about their work problems. Alongside, they selected another group of 134 adults clinically diagnosed with ADHD from a hospital setting. This group also filled out the same surveys.
A smaller group of 51 adults with ADHD underwent additional mental tests to gauge focus and problem-solving skills, known as executive functions, to compare these results to work performance.
A smaller group of 51 adults with ADHD underwent additional mental tests to gauge focus and problem-solving skills, known as executive functions, to compare these results to work performance.

Abstract: methods
A community sample of 1231 individuals took part in this study and completed a set of questionnaires assessing ADHD symptoms and work-r...more
Study Results
Results
The analysis revealed that both those showing ADHD symptoms and diagnosed individuals face challenges in meeting personal job standards and realizing their potential, rather than receiving poor reviews or being fired. This suggests a self vs. external perception gap.
ADHD symptoms, particularly inattention, heavily linked to work-related issues, whereas mental task tests didn’t reliably predict how one performed on the job, indicating symptoms over test scores matter more.
ADHD symptoms, particularly inattention, heavily linked to work-related issues, whereas mental task tests didn’t reliably predict how one performed on the job, indicating symptoms over test scores matter more.

Abstract: results
Work-related problems were found both in individuals of the community sample with symptoms of ADHD and individuals diagnosed with ADHD....more
Study Summary
Conclusions
These findings highlight that ADHD symptoms can heavily impact how effectively individuals function at work. Therefore, addressing ADHD challenges is crucial during both healthcare evaluations and workplace screenings.
The study suggests that workplaces should implement strategies to identify and support employees having ADHD-related difficulties, ensuring they receive proper assistance when needed.
The study suggests that workplaces should implement strategies to identify and support employees having ADHD-related difficulties, ensuring they receive proper assistance when needed.
Abstract: conclusions
This study emphasizes the susceptibility of individuals' functioning at work to ADHD symptoms and impairments associated with ADHD. ADHD related difficulties at work should be considered in the clinical evaluation and targeted screening at the work p...more
Clinical Guidelines
Guidelines suggest that ADHD significantly impairs occupational functioning. Combination therapy with medication and CBT addresses executive dysfunction in adults with ADHD. Stimulant medication offers immediate effects and enhances work performance.
Long-acting stimulants reduce the risk of misuse. CBT further diminishes ADHD symptoms compared to standard treatments.
Long-acting stimulants reduce the risk of misuse. CBT further diminishes ADHD symptoms compared to standard treatments.
Literature Review
de Braek et al, 2011
Core Insight:The main paper identifies ADHD symptoms, particularly inattention, as major contributors to work-related problems, whereas the comparison paper highlights executive functioning issues.
What It Adds:
Executive Function Focus: The comparison paper emphasizes executive function over attention in ADHD.
Distinctive Symptoms: It challenges the distinction of concentration and hyperactivity.
Shared Themes:Both papers explore ADHD's impact on daily functioning, underlining its broad effects.

Literature Review
Schneider et al, 2015
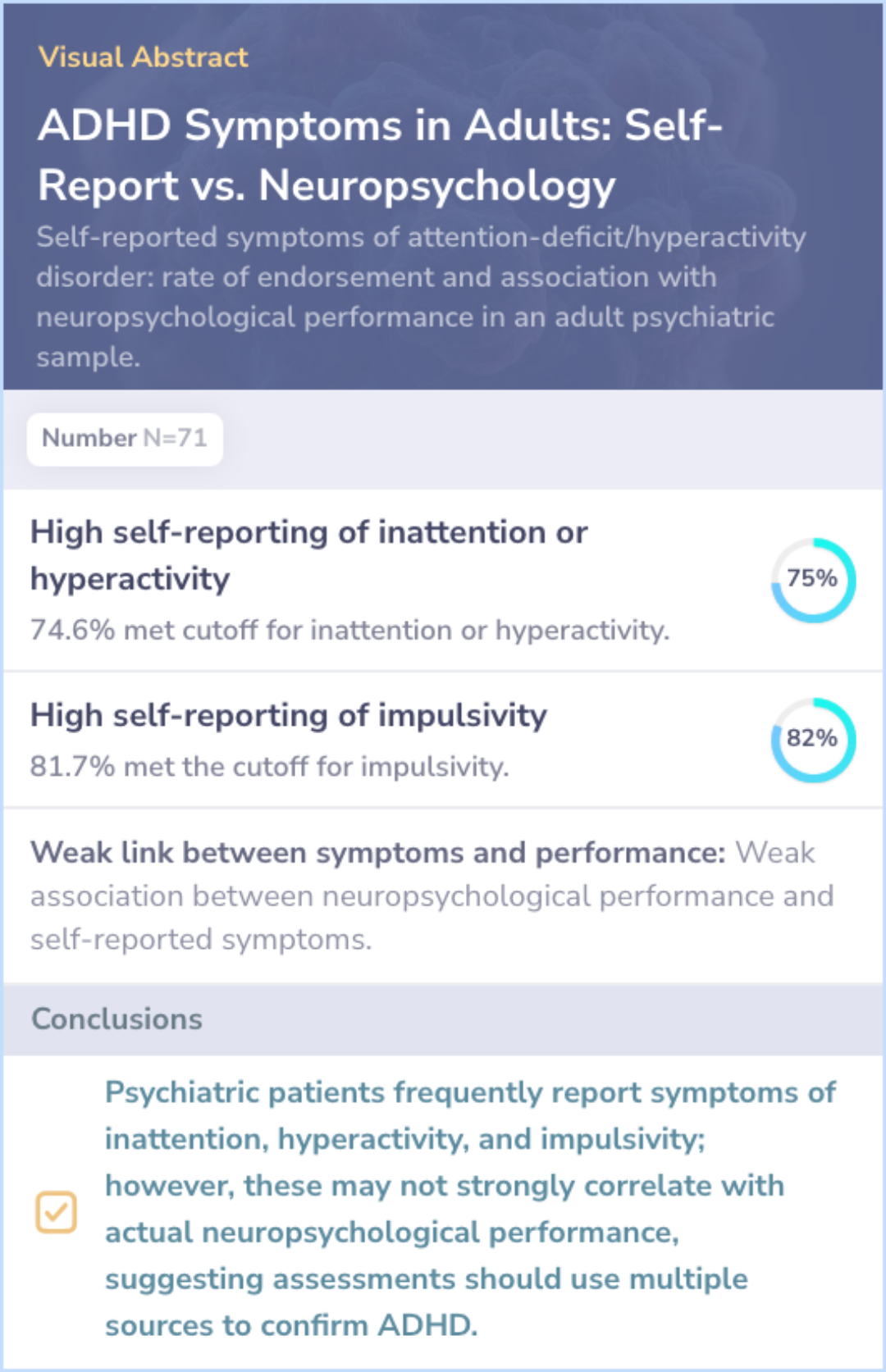
Core Insight:Both papers investigate ADHD symptoms and their impact, but in different populations. The main paper focuses on work-related problems in adults with ADHD, while this paper explores diagnostic challenges in a psychiatric sample.
What It Adds:
Diagnostic Challenges: Highlights nonspecific ADHD symptoms complicating diagnosis.
Self-report vs. Reality: Self-reported symptoms often don't match neuropsychological findings.
Shared Themes:Both papers find weak links between ADHD symptoms and neuropsychological tests, suggesting self-reports might not fully reflect actual impairments.
Literature Review
Barkley et al, 2012
Core Insight:This paper explores sluggish cognitive tempo (SCT) in adults separate from ADHD, affecting work and executive function, contrasting with the main paper's focus on ADHD-specific work-related issues.
What It Adds:
SCT vs. ADHD at Work: SCT leads to more work impairment than ADHD, unlike the main paper.
SCT's Unique Impact: SCT uniquely impacts executive functions beyond ADHD symptoms.
