Adderall
Evidence Based Answers
3 Studies on Adderall Dose Timing
These studies show the importance of timing Adderall doses to match daily routines, how gradual adjustments help balance effectiveness with side effects, and how different forms (IR and XR) provide varying durations of symptom control.
Published: October 24, 2024
Click to explore a section:
Studies on Adderall show timing impacts symptom control, and dose adjustments balance relief with side effects.
Background: Adderall's Onset and Duration
Adderall comes in two main forms: immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (XR). IR typically starts working within 20 to 60 minutes and lasts up to 6 hours. XR provides effects for up to 12 hours.
The IR form is taken 2 to 3 times a day, with 4 to 6 hours between doses, while XR is taken once in the morning.
Timing doses correctly can help reduce insomnia and control symptoms throughout the day.
The IR form is taken 2 to 3 times a day, with 4 to 6 hours between doses, while XR is taken once in the morning.
Timing doses correctly can help reduce insomnia and control symptoms throughout the day.
“
Source Quotes:
Amphetamine medications for ADHD are available in immediate- and extended-release formulations and have an onset of action of 20 to 60 minutes.
The immediate-release formulation of dextroamphetamine-amphetamine has a duration of up to 6 hours. Longer-acting formulations may last up to 10 to 12 hours.
Background: Tailoring Adderall Dosing to Daily Needs
Adderall doses are personalized based on the patient's daily routine and the amount of time they need symptom control. Short-acting forms are used for specific parts of the day like work or school.
Long-acting formulations help manage symptoms over the whole day for those who need consistent coverage.
Choosing the right dose depends on how the medication fits into daily activities and symptom control.
Long-acting formulations help manage symptoms over the whole day for those who need consistent coverage.
Choosing the right dose depends on how the medication fits into daily activities and symptom control.
“
Source Quotes:
Our choice of stimulant preparation is based on the patient's preference, time to onset and length of desired effect, concern about misuse or diversion, cost, and availability of the medication.
Some adults value the ability to target the short-acting drugs' coverage to the desired part(s) of the day (eg, time in class or at work).
Background: Gradual Adderall Dose Adjustment
Adderall dosing begins with a low dose that is gradually increased based on how it works and any side effects.
This process, called titration, can take one to three months and involves regular check-ins with a healthcare provider.
The goal is to find the right balance between symptom relief and side effects.
This process, called titration, can take one to three months and involves regular check-ins with a healthcare provider.
The goal is to find the right balance between symptom relief and side effects.
“
Source Quotes:
We typically begin treatment with a low dose of the chosen agent and increase weekly while monitoring for clinical response, duration of the effect during the day, and side effects.
The titration phase typically lasts from one to three months [7]. It requires close monitoring (usually weekly) by the clinician, some of which can be done by phone or telemedicine.
Background: Insights from Clinical Trials on Adderall Dosing
Clinical trials have shown how different doses of Adderall impact ADHD symptoms. This data helps doctors choose the right dose for symptom management.
Findings from these trials provide a guide for adjusting doses to maximize effectiveness while minimizing side effects.
Findings from these trials provide a guide for adjusting doses to maximize effectiveness while minimizing side effects.
“
Source Quotes:
In a trial, 255 adults with ADHD were randomly assigned to treatment with mixed amphetamine salts extended-release at dose of 20 mg, 40 mg, 60 mg, or placebo over four weeks. Improvement in symptoms based on the ADHD-Rating Scale were shown at each of the three doses respectively versus placebo.
We typically begin at 10 mg orally each morning. If there are no adverse effects after three or four days, we increase to 20 mg once per day in the morning. We increase by 10 mg at weekly (or longer) intervals until clinical response or a dose of 40 mg per day is reached.
Peer Reviewed Study
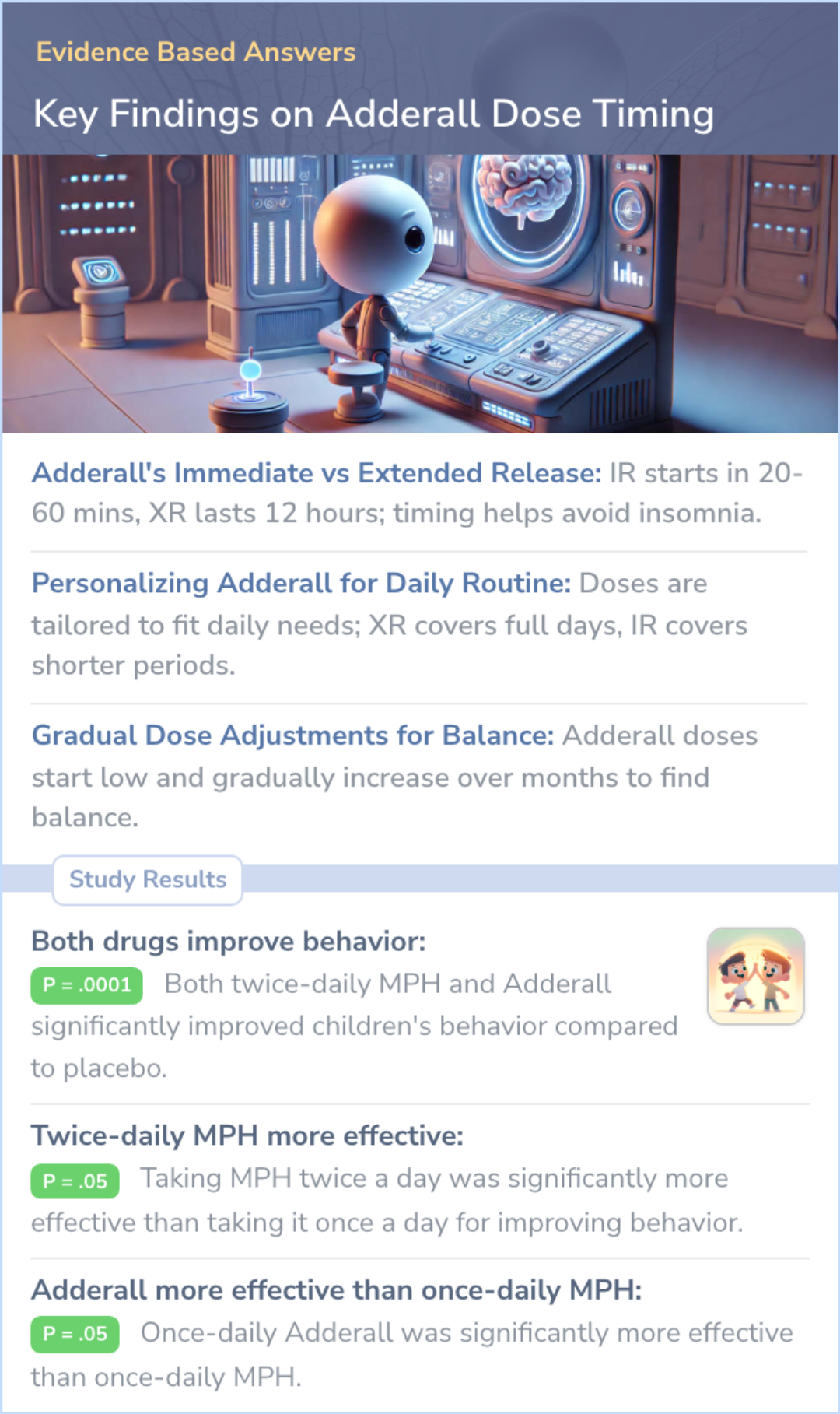
Study: Adderall's Effectiveness Throughout a School Day with Single Morning Dose
The study compared a single morning dose of Adderall to standard twice-daily methylphenidate (MPH) dosing. It found that one morning dose of Adderall produced equivalent behavioral effects to twice-daily MPH dosing, lasting throughout the school-day period.
This suggests that Adderall may serve as a long-acting stimulant option for children, reducing the need for midday dosing in a school setting.
This suggests that Adderall may serve as a long-acting stimulant option for children, reducing the need for midday dosing in a school setting.
author
Pelham WE, Gnagy EM, Chronis AM, Burrows-MacLean L, Fabiano GA, Onyango AN, Meichenbaum DL, Williams A, Aronoff HR, Steiner RL
journal
Pediatrics
Date Published
1999 Dec
Peer Reviewed Study
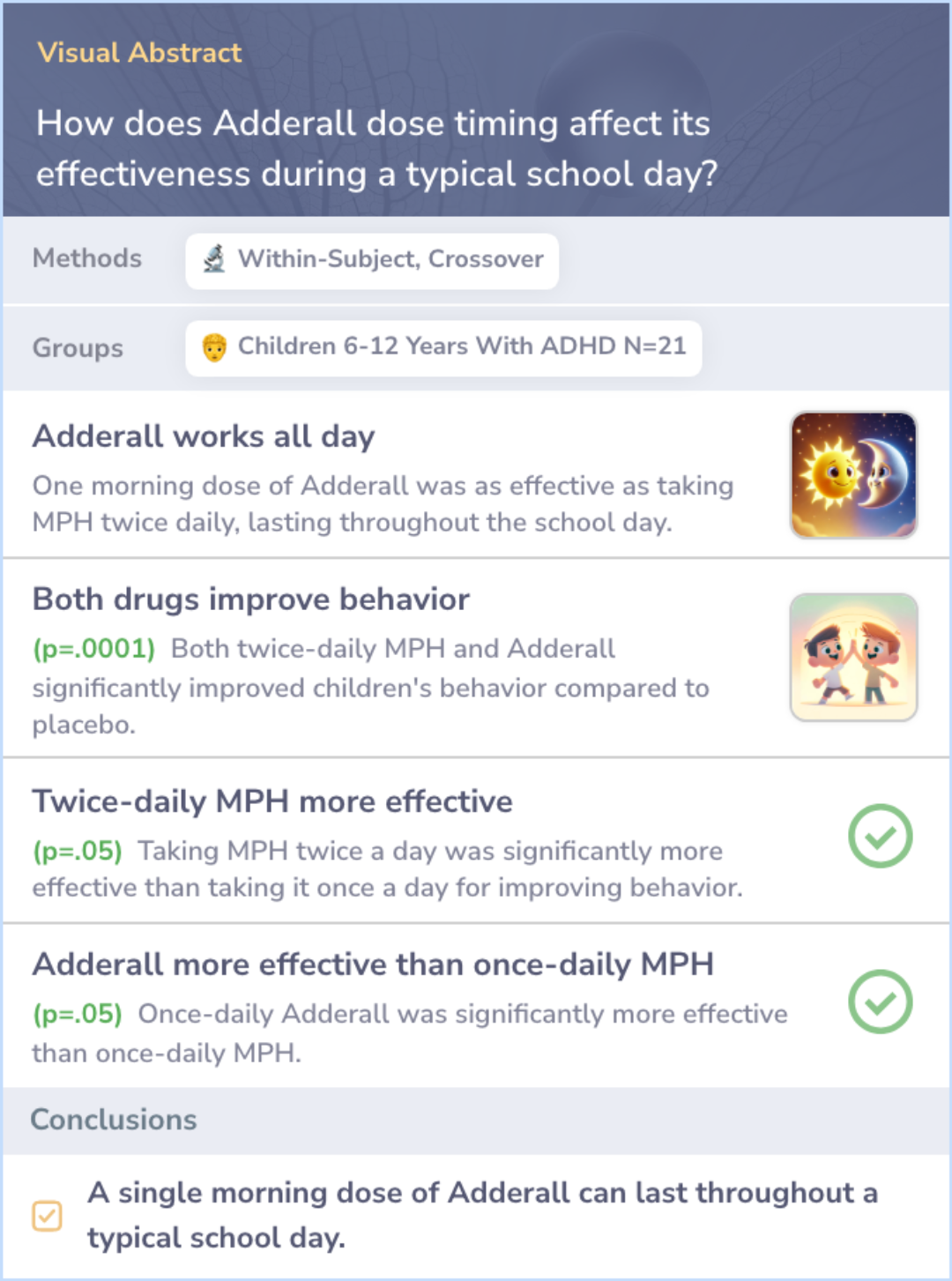
Study: Adderall XR: Consistent All-Day Behavioral Improvement with Morning Dose
This study examined the effects of a once-daily morning dose of Adderall XR (SLI381) on children with ADHD. The trial compared different doses of Adderall XR with a placebo over three weeks, focusing on behavior in the morning, afternoon, and late afternoon. Results showed that all doses of Adderall XR significantly improved behavior compared to placebo throughout the day. The extended-release formulation of Adderall XR demonstrated continued improvement, particularly in the afternoon and late afternoon.
This data highlights the effectiveness of Adderall XR in maintaining therapeutic effects across the entire day with just one morning dose.
This data highlights the effectiveness of Adderall XR in maintaining therapeutic effects across the entire day with just one morning dose.
author
Biederman J, Lopez FA, Boellner SW, Chandler MC
journal
Pediatrics
Date Published
2002 Aug
Peer Reviewed Study
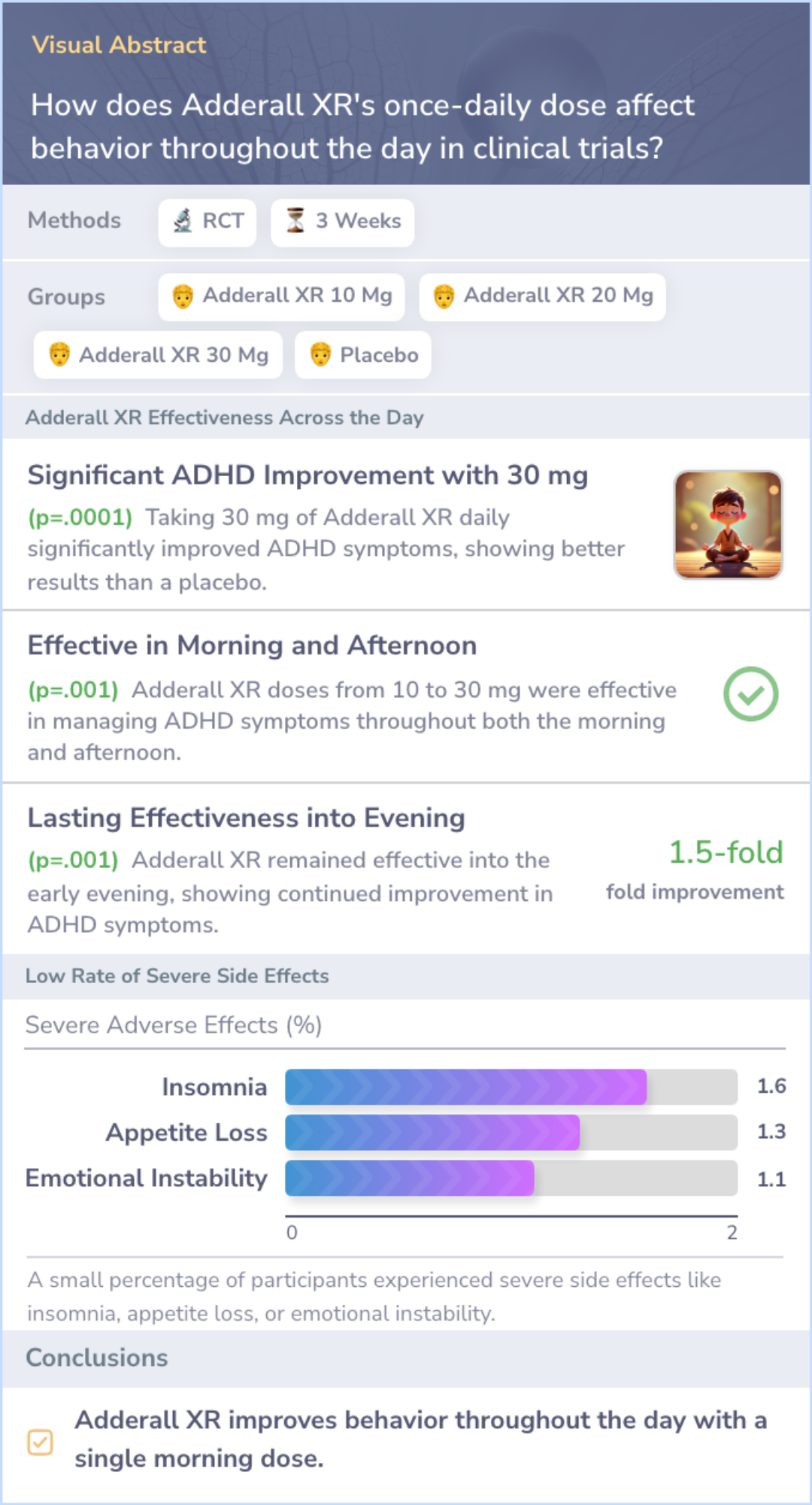
Study: Extended Duration of Adderall XR in Clinical Trials
This study tested three doses of SLI381 (Adderall XR) and compared them to a placebo and a standard Adderall dose in children with ADHD. The children took the medication once daily, and their behavior and test performance were measured every 1.5 hours over 12 hours.
The results showed that SLI381 20 mg and 30 mg had a lasting effect, improving behavior and test scores up to 12 hours after dosing. These findings highlight the extended duration of Adderall XR compared to standard Adderall.
The results showed that SLI381 20 mg and 30 mg had a lasting effect, improving behavior and test scores up to 12 hours after dosing. These findings highlight the extended duration of Adderall XR compared to standard Adderall.
author
McCracken JT, Biederman J, Greenhill LL, Swanson JM, McGough JJ, Spencer TJ, Posner K, Wigal S, Pataki C, Zhang Y, Tulloch S
journal
J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry
Date Published
2003 Jun
Peer Reviewed Study
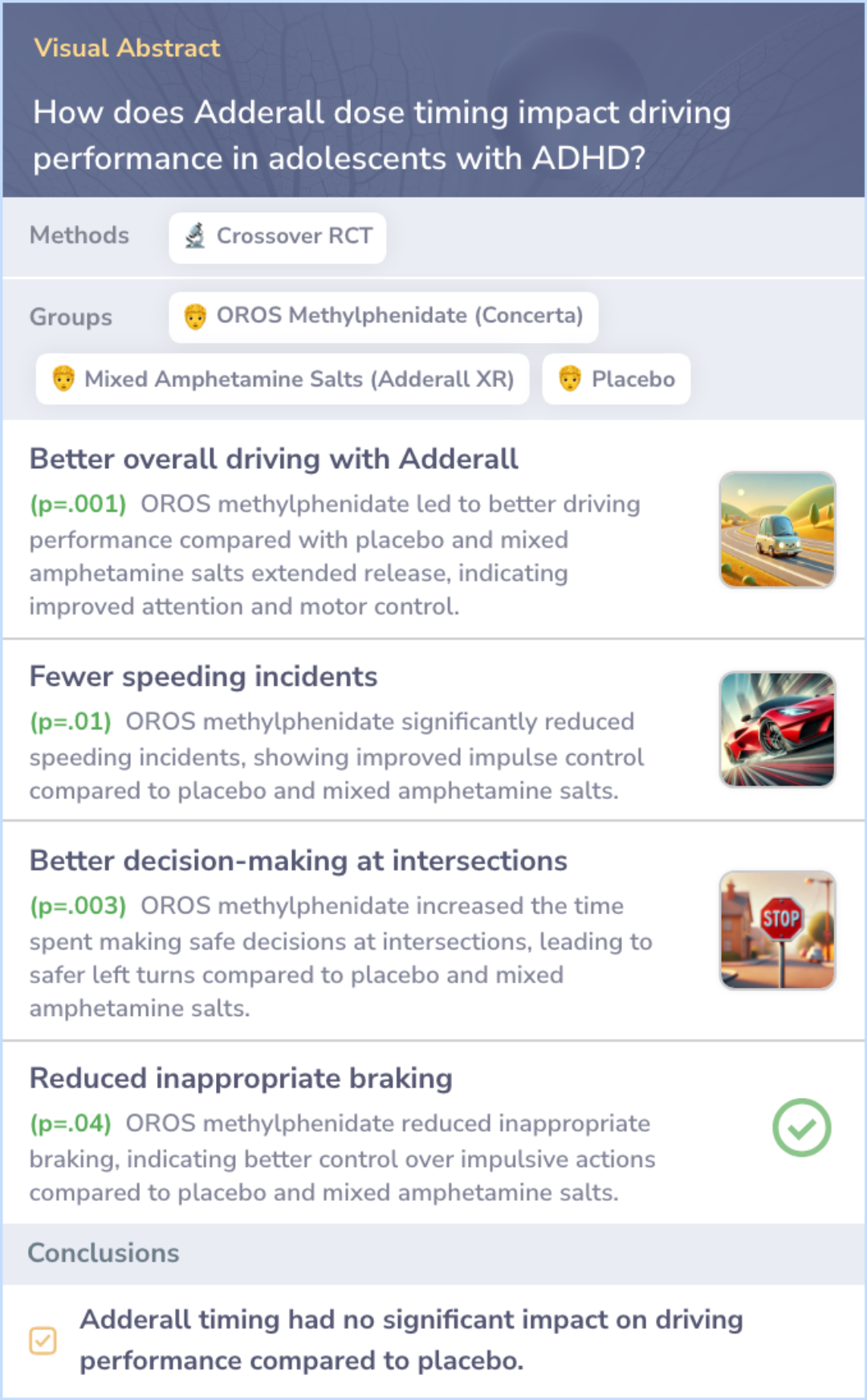
Study: Adderall Dose Timing and Driving Performance in Adolescents with ADHD
This study compared driving performance in adolescents with ADHD after taking 72 mg of OROS methylphenidate, 30 mg of mixed amphetamine salts extended release (Adderall), or a placebo at 5:00 pm, 8:00 pm, and 11:00 pm.
Results showed that OROS methylphenidate led to better driving performance than both the placebo and Adderall. Specifically, OROS methylphenidate resulted in safer driving behaviors, while Adderall did not show significant improvement over the placebo.
Results showed that OROS methylphenidate led to better driving performance than both the placebo and Adderall. Specifically, OROS methylphenidate resulted in safer driving behaviors, while Adderall did not show significant improvement over the placebo.
author
Cox DJ, Merkel RL, Moore M, Thorndike F, Muller C, Kovatchev B
journal
Pediatrics
Date Published
2006 Sep
Key Takeaways
Conclusions
