Generalized Anxiety Disorder Papers
Visual Abstract
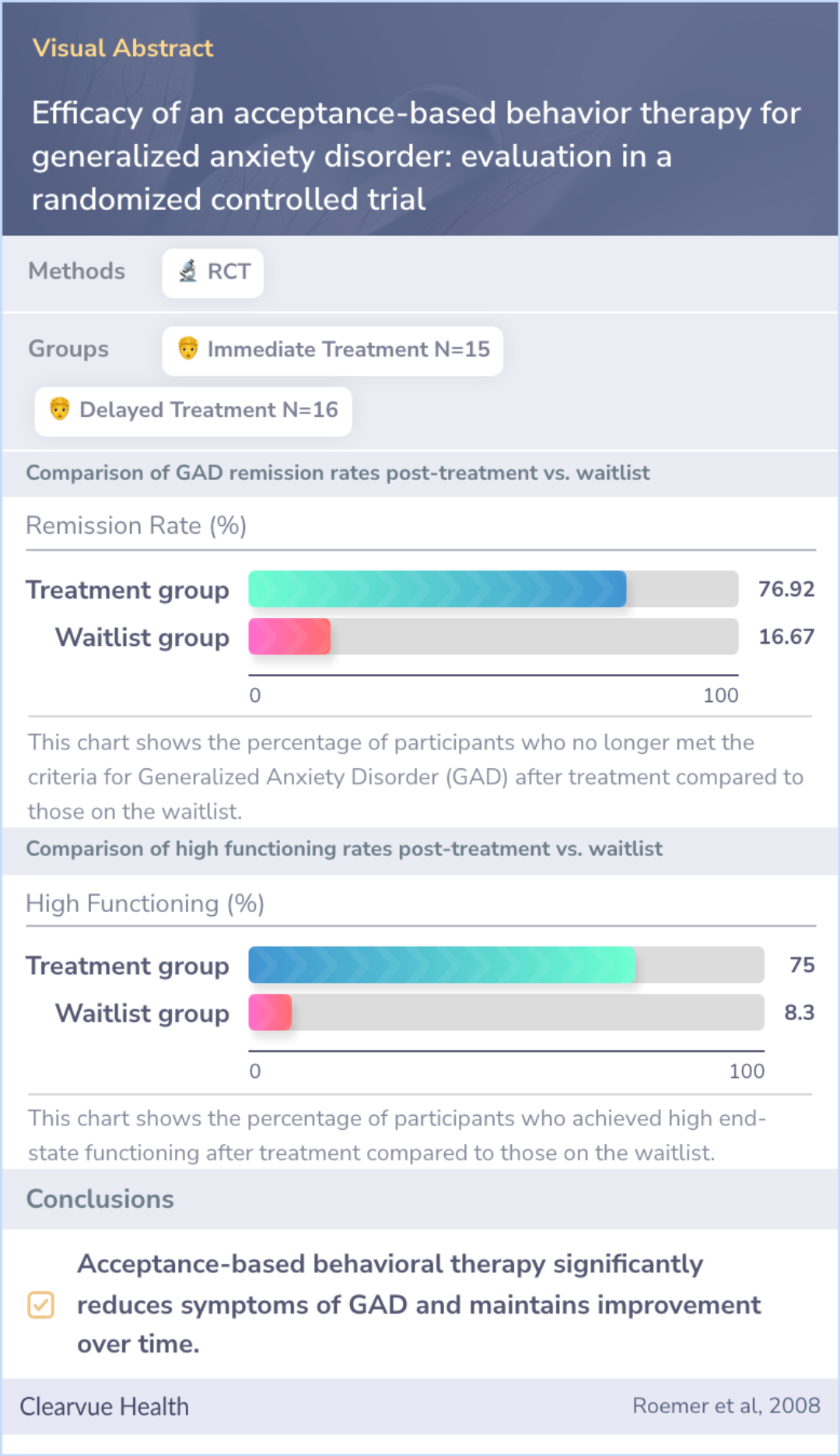
Efficacy of an acceptance-based behavior therapy for generalized anxiety disorder: evaluation in a randomized controlled trial
Acceptance-based therapy for GAD
November 25, 2024
author
Roemer L, Orsillo SM, Salters-Pedneault K
journal
J Consult Clin Psychol
Date Published
December 2008
Why link to a visual abstract?
What is a visual abstract?
Original
Study Summary
🔬
What They Studied
The study aimed to examine the effectiveness of acceptance-based behavioral therapy for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
💡
What They Found
The therapy led to significant reductions in GAD and depressive symptoms, with many participants no longer meeting criteria for GAD after treatment.
📚
What This Means
These findings align with existing evidence that behavioral therapies can reduce symptoms of GAD and improve overall patient outcomes.
Study Summary
Study Overview
This study aimed to improve treatments for Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), a condition that many struggle with despite existing therapies. The researchers focused on a new approach called acceptance-based behavior therapy (ABBT). This method targets how individuals react to their thoughts and emotions, promoting acceptance and mindful engagement in daily life. The findings show that addressing these internal experiences might enhance treatment outcomes for people with GAD.
Initial results support ABBT's potential, as it led to significant improvements in clients' experiences with anxiety, encouraging further research in this area.
Initial results support ABBT's potential, as it led to significant improvements in clients' experiences with anxiety, encouraging further research in this area.
Abstract: background
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a chronic anxiety disorder, associated with comorbidity and impairment in quality of life, for which improved psychosocial treatments are needed. GAD is also associated with reactivity to and avoidance of interna...more

Need for Better GAD Treatments
"Although efficacious individual cognitive behavioral therapies (CBT) have been developed for Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), a large proportion of individuals treated fail to meet criteria for high end state functioning, suggesting that further treatment development may be needed."
Focus on Acceptance
"Our efforts have focused on an individual acceptance-based behavior therapy (ABBT) that targets experiential avoidance, using strategies aimed at increasing awareness and intended action in important life domains."
Improving Treatment Efficacy
"Directly targeting these problematic relationships and responses to internal experiences may improve the efficacy of GAD treatments."
Study Summary
Methods
Participants in the study were randomly assigned to either start treatment immediately or after a waiting period. Fifteen individuals began treatment right away, while sixteen waited. The therapy they received focused on acceptance-based behavioral techniques. This included teaching them how to better accept their thoughts and feelings, and take purposeful actions in their lives.
Researchers measured the effects of the therapy by assessing symptoms of GAD both before and after the treatment period. Follow-up assessments were conducted three and nine months later. The assessments included both clinician evaluations and self-reported measures to gauge symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Researchers measured the effects of the therapy by assessing symptoms of GAD both before and after the treatment period. Follow-up assessments were conducted three and nine months later. The assessments included both clinician evaluations and self-reported measures to gauge symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Abstract: methods
Clients were randomly assigned to immediate (n=15) or delayed (n=16) treatment. Acceptance-based behavior therapy led to statistically significant reductions in clinician-rated and self-reported GAD symptoms that were maintained at 3- and 9- month fo...more
Study Summary
Results
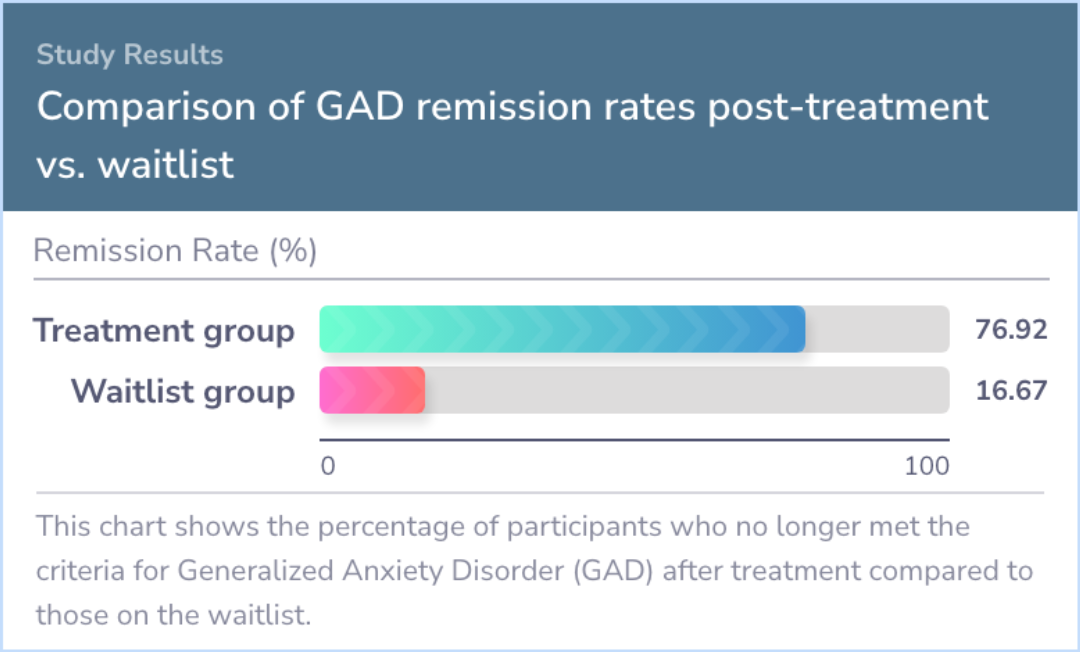
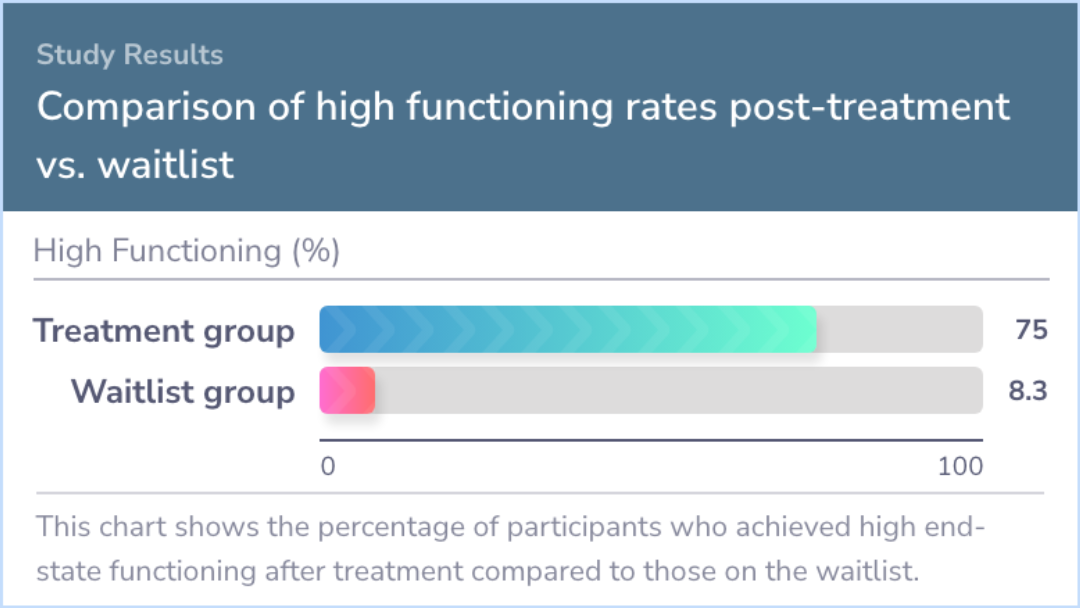
The results were promising, showing that 78% of the participants who received treatment no longer met the criteria for GAD after the therapy. Additionally, 77% of them achieved high levels of functioning. These improvements were not only sustained over time but also occasionally increased.
The study also showed that the therapy effectively reduced behaviors where individuals avoid their internal experiences. Moreover, there was an increase in mindfulness, indicating that participants became more aware and accepting of their thoughts and feelings.
The study also showed that the therapy effectively reduced behaviors where individuals avoid their internal experiences. Moreover, there was an increase in mindfulness, indicating that participants became more aware and accepting of their thoughts and feelings.
Abstract: results
Seventy-eight percent of treated participants no longer met criteria for GAD and 77% achieved high end-state functioning at post-treatment assessment; these proportions stayed constant or increased over time. As predicted, treatment was associated wi...more
Study Summary
Conclusions
The study concludes that acceptance-based behavioral therapy is an effective treatment for GAD. It leads to lasting improvements in both reducing symptoms and helping individuals function better in their lives. One key aspect highlighted by the findings is the reduction of experiential avoidance, which refers to avoiding emotional experiences.
Another important element is the increase in mindfulness practices, which help individuals become more aware and accepting of their emotions and thoughts. These findings underscore the potential of this therapy to make a meaningful difference for people struggling with GAD.
Another important element is the increase in mindfulness practices, which help individuals become more aware and accepting of their emotions and thoughts. These findings underscore the potential of this therapy to make a meaningful difference for people struggling with GAD.
Abstract: conclusions
The findings suggest that acceptance-based behavior therapy is an effective treatment for GAD that leads to sustained improvement. The importance of reducing experiential avoidance and enhancing mindfulness is highlighted.

Background Information
Patient Guide
😟
Characteristics of GAD
GAD involves persistent, unrealistic worry affecting daily life, leading to both mental and physical symptoms.
🔗
Common Comorbidities
GAD often occurs alongside other mental health disorders such as depression, complicating treatment.
💊
Current Treatments
Standard treatments for GAD include Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and medications like SSRIs, SNRIs, and benzodiazepines.
🔄
Challenges in Treatment
Patients often face compliance issues with medications due to side effects and GAD's chronic nature increases relapse risk.
🤝
Importance of Support
Education, communication, and participation in support groups are beneficial in managing GAD effectively.
Professional Guide
Expert Opinion: Acceptance-based therapy for GAD
The findings suggest that acceptance-based behavior therapy delivers effective long-term relief for GAD patients.
Current professional recommendations state that CBT improves both disorder-specific symptoms and overall functioning in GAD patients.
CBT sessions may need to be extended in cases of comorbidity.
Meanwhile, acceptance and mindfulness techniques enhance GAD treatment by reducing anxiety.
Computer-based CBT provides an accessible alternative, improving key anxiety symptoms.
Pharmacotherapy, particularly SSRIs and SNRIs, remains a common initial treatment choice, especially for patients with accompanying depressive symptoms.
Incorporating aerobic exercise and mindfulness practices may further alleviate GAD symptoms.
Ongoing therapy or booster sessions help in preventing relapse post-CBT.
Current professional recommendations state that CBT improves both disorder-specific symptoms and overall functioning in GAD patients.
CBT sessions may need to be extended in cases of comorbidity.
Meanwhile, acceptance and mindfulness techniques enhance GAD treatment by reducing anxiety.
Computer-based CBT provides an accessible alternative, improving key anxiety symptoms.
Pharmacotherapy, particularly SSRIs and SNRIs, remains a common initial treatment choice, especially for patients with accompanying depressive symptoms.
Incorporating aerobic exercise and mindfulness practices may further alleviate GAD symptoms.
Ongoing therapy or booster sessions help in preventing relapse post-CBT.
Evidence Summary
Managing Anxiety with CBT and Mindfulness Techniques
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Generalized Anxiety Disorder focuses on changing thought patterns that fuel anxiety. Through CBT, individuals can manage their anxiety by recognizing and shifting negative thinking. Incorporating mindfulness techniques alongside CBT further enhances its impact, enabling better control over symptoms.
Regular practice of both CBT and mindfulness is key to maintaining these improvements over time, making them more effective in the long run.
Regular practice of both CBT and mindfulness is key to maintaining these improvements over time, making them more effective in the long run.
Evidence Summary
Comparing Treatment Effectiveness for Anxiety Reduction
The comparison looks at how well different treatments work for generalized anxiety disorder. It highlights various studies that analyze the effectiveness of these methods, focusing on their ability to reduce anxiety symptoms.
By comparing data across multiple studies, it identifies which treatments are most effective in easing symptoms of anxiety and provides insight into which methods yield the most improvement.
By comparing data across multiple studies, it identifies which treatments are most effective in easing symptoms of anxiety and provides insight into which methods yield the most improvement.
Evidence Summary
CBT vs Applied Relaxation: Different Paths to Treating GAD
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps people change negative thought patterns that fuel anxiety, offering a practical way to address GAD by altering both thoughts and behaviors. Applied Relaxation, on the other hand, focuses on teaching muscle relaxation techniques to ease physical symptoms of anxiety.
Both therapies approach GAD differently: CBT targets mental habits, while Applied Relaxation focuses on calming the body’s physical response to anxiety.
Both therapies approach GAD differently: CBT targets mental habits, while Applied Relaxation focuses on calming the body’s physical response to anxiety.