Diet and exercise are universally recommended. They are some of the best interventions we can take part in to improve our physical health.
Doctors have known for a while that heart disease risk factors may be associated with cognitive function and dementia.
Based on this knowledge, researchers set out to find whether improving diet and exercise can improve cognition and reduce the odds of dementia.
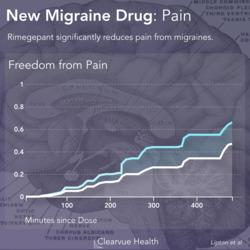
Many of us fear getting older. We fear losing some of our mental sharpness as we age. These data suggest that some degree of mental aging may be preventable.
Source: Lifestyle and neurocognition in older adults with cognitive impairments
The Study Design
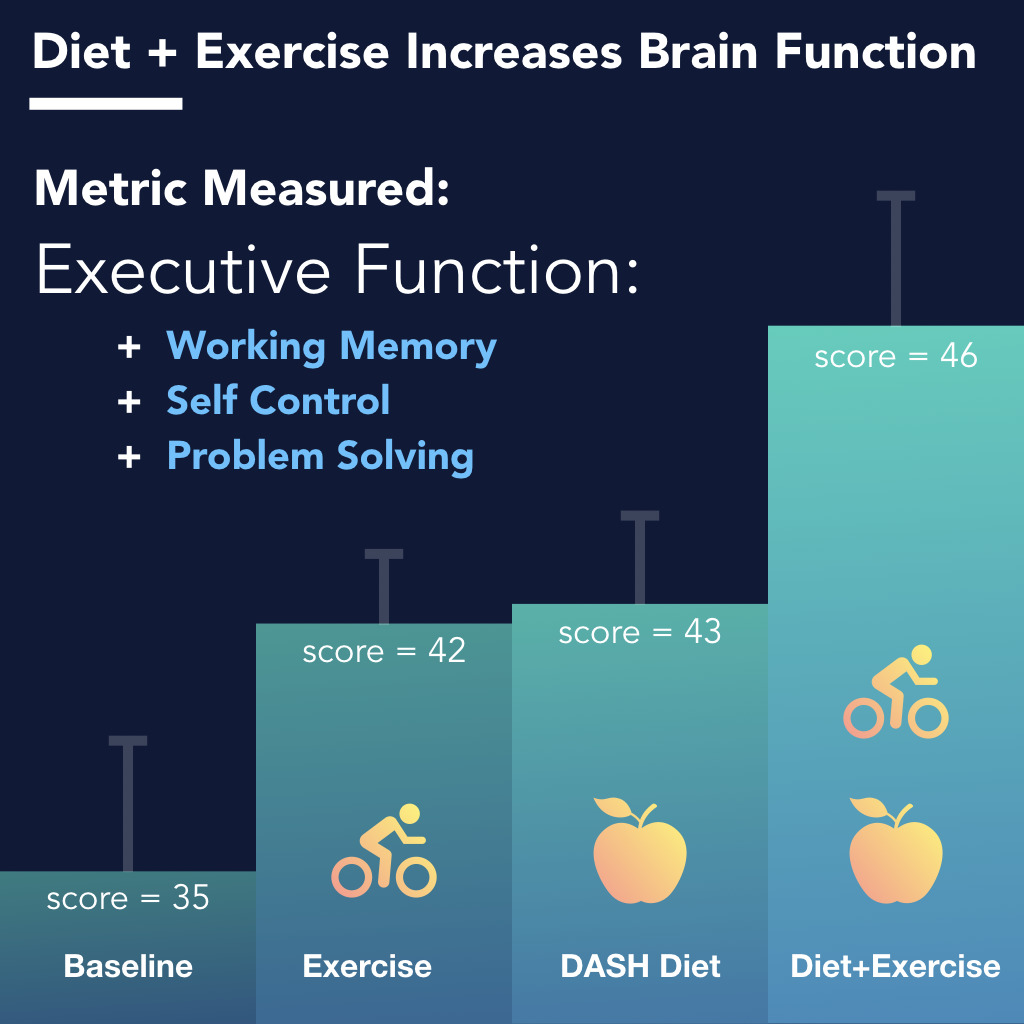
Researchers recruited 160 men and women, ages 55 and older, and split them into four groups.
One group received 6 months of a structured exercise program, group 2 was put on a special diet for 6 months, group 3 received both the special diet and exercise program, and group four received general health education.
This design allowed researchers to see whether exercise, diet, or both, could improve cognition. Unlike an observational study, where researchers can only determine correlations between group, this type of study can provide insights into causation.
The primary goal of the study was to see whether exercise and/or diet could improve executive function, or higher level thinking. Executive function forms much of the basis of what we consider to be intelligence. These functions include working memory, attention, focus, and problem-solving.
More Information: Executive Functions
Researchers also looked into whether diet and/or exercise could improve verbal ability and reduce dementia symptoms.
The Results

Researchers found that their hypothesis was correct. Six months of structured exercise improved cognition. The best improvement was found in patients who receive both the diet and the exercise interventions.
This shows that when it comes to cognitive function, diet and exercise are both great. There was no significance between diet and exercise. However the best intervention of all is improving both your diet and your exercise.
These results also show that education alone is not enough, which is what the fourth "control" group received. Just knowing what’s good for you and reading about your health is not the same as taking the leap into a committed structured diet and/or exercise program.
The Diet Used: The DASH Diet

The study used a well-known diet called the DASH diet. This eating plan is designed specifically to reduce high blood pressure. It has been shown to be better for cardiovascular health than the standard American diet. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute promotes this diet as a key strategy to improve your heart health
The study only used one diet for the intervention so it’s hard to say for sure whether any diets are better or worse.
What we do know is that this diet works. We have summarized the basics of the DASH diet above.
Source: DASH Eating Plan
Aerobic Exercise Program for Brain Health

Researchers used a relatively simple aerobic exercise program. This is an exercise program that most people should be able to do without a gym. However despite its simplicity, the program did lead to significant benefits.
Participants were asked to warm up for 10 minutes, and then proceeded to either walk for 35 minutes or or use a stationary bike for 35 minutes. They targeted a heart rate that was approximately 70-85% of a patient’s heart rate reserve, which is a significant but not too challenging pace. Heart rate reserve represents the difference between your resting heart rate and your maximum heart rate.